Physiology: Cardiac Myocytes Flashcards
1
Q
What effect does Digoxin have on the heart, and how?
A
- Positive inotropic effect
- Inhibits the Sodium-potassium pump, which indirectly inhibits the sodium Calcium-Sodium exchanger.

2
Q
- What does hyperkalemia do the resting membrane potential of cardiac myocytes, what effect does this have on action potentials?
A
- Hyperkalemia reduces the Nernst K+ equilibrium potential and, therefore, the resting membrane potential.
- This, in turn, diminishes the action potential, because the low resting potential prevents many Na+ channels from resetting from the inactivated state to the closed- but-activatable state.

3
Q
Label 1-3

A

4
Q
- What effects do the following agents have on the contractility of the heart, and through what mechanisms?
- Propranolol
- Verapamil
- Caffeine (+ milrinone)
A
- Propanolol
- Negative inotropic agent
- A non-selective beta blocker that does not allow NE to bind to the Gs subunit of Adenyl cyclase.
- This stops the conversion of ATP to cAMP.
- Verapamil
- Negative inotropic agent
- Blocks the influx of Ca2+ through the L-type Calcium channels, thus decreasing calcium within the cells and decreasing contraction force.
- Negative inotropic agent
- Caffeine (+ milrinone)
- Positive inotropic agent
- Inhibits the conversion of cAMP to AMP by phosphodiesterase III.

5
Q
- Describe how the state of the voltage-gated sodium channels changes along this action potential
- (Open vs closed, active vs inactive)

A

6
Q
This is the cardiac action potential of a ventricle.
- What causes the initial upstroke, seen at point 0?
- What causes the sharp stop in depolarization, seen at point 1?
- What causes the plateau phase, seen at point 2?
- What causes the steady repolarization, seen at 3?

A

7
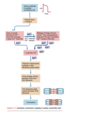
Q
- What kind of channel?
- What kind of channel?
- What complex?

A
8
Q
Concerning myocardial cells,
- Give the order from least to greatest for intracellular ion concentration for
- K +
- Na +
- Ca 2+
- Cl -
- Give the order from least to greatest extracellular ion concentration for
- K +
- Na +
- Ca 2+
- Cl -
- Give the order from least to greatest for Nernst equilibrium potential for
- K +
- Na +
- Ca 2+
- Cl -
A
- Give the order from least to greatest for intracellular ion concentration
- Ca 2+ , Na + , Cl - , K +
- Give the order from least to greatest for extracellular ion concentration
- K +, Ca 2+, Cl -, Na +
- Give the order from least to greatest for ion Nernst equilibrium potential
- K + , Cl -, Na +, Ca 2+

9
Q
Where would the following refractory periods go in this graph?
- Effective refractory period (ERP)
- Absolute refractory period (ARP)
- Relative refractory period (RRP)
- Supranormal refractory period (SRP)

A
- The effective refractory period (ERP) includes the absolute refractory period (ARP) and the first half of the relative refractory period (RRP).
- The RRP begins when the ARP ends and includes the last portion of the ERP.
- The supranormal period (SNP) begins when the RRP ends.

10
Q
What do cardiac glycosides do to the contraction of the heart?
A
- They have a positive inotropic effect
- Positively inotropic agents increase the strength of muscular contraction.

11
Q
How does adrenaline as well as pufferfish toxin affect the action potentials of Purkinje fibers?
A



