Physiology and Pathophysiology of Pain Flashcards
What is pain?
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience which we primarily associate with tissue damage or describe in terms of such damage or both
Is not a stimulus
Final product of complex-information processing network
What are the steps in the pain pathway?
Step 1. Periphery
- Detection
- Transmission to spinal cord (first order neurons)
Step 2. Spinal cord
- Processing
- Transmission to brain (Thalamus) (second order neurons)
Step 3. Brain
• Perception, learning, response
Step 4. Modulation
• Descending tracts

What does the thalamus do?
Recieves all sensory information then sends it to all different parts of the brain
What is nociception?
The detection of tissue damage by specialized transducers connected to A-delta and C fibers
What are nociceptors and what do they respond to?
Free nerve endings of A delta and C-fibres
Respond to thermal, chemical, mechanical noxious stimuli
Where is the cell body of primary afferents/1st order neurons located and where do they synapse?
Cell body in Dorsal root ganglion
First order neurons
Synapse at spinal cord

Describe the features of the different types of fibres

Are C fibres myleinated and therefroe do they conduct fast or slow?
non-myelinated
conduct slowly
What do axons entering the spinal dorsal horn continue as?
tracts
What is the spinothalamic tract?
Major ascending tract for nociception
Arises in Rexed Lamina 2 & 5
Forms the lateral spinothalamic tract
Ends in:
Ventroposterior thalamic nuclei
Medial thalamus

Thalamus is the second ___________
Thalamus is the second relay station
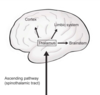
Where does the thalamus have connections with?
cortex
limbic system
brain stem

Where is the main area in the thalamus that spinothalamic tracts go?
Ventroposterior thalamic nuclei
Medial thalamus
Pain perception occurs in ________________
Pain perception occurs in somatosensory cortex
Why does the thalamus send information about pain to the limbic system?
to help form memories, learning and emotion
Descending pathways come form the brain to ______
dorsal horn
What do the descending pathways do to the pain signal
usually decrease it
What is allodynia?
Allodynia refers to central pain sensitization (increased response of neurons) following normally non-painful, often repetitive, stimulation. Allodynia can lead to the triggering of a pain response from stimuli which do not normally provoke pain
What is A?
Defnition of Allodynia

Decreased threshold for response

What is B?
Definition of Hyperalgesia

Exaggerated response to normal and supranormal stimuli

What is C?
Definition of Spontaneous Pain

Spontaneous activity in nerve fibres

What is Central sensitization?
Central sensitization is a condition of the nervous system that is associated with the development and maintenance of chronic pain
It is the response of second order neurons in the CNS to normal input both noxious & non-noxious
What are the 3 main components of Central sensitization?
wind-up
classical
long-term potentiation
What is wind up central sensitisation?
Involves only activated synapses
Homosynaptic activity dependent progressive increase in response of the neurons
Manifests over the course of stimuli & terminates with stimuli
Wind-up is literally winding up the response to the input. So the wind-up happens only in neurons taking part in the synapses with primary afferent input. It is activity dependent; progressively increases the response of the neurons





