Pharynx and Larynx Flashcards
(29 cards)
List and describe the 3 phases of Swallowing (Deglutition).
- Oral Phase: Synonymous with Mastication
- Oropharyngeal Phase: Elevation of the floor fo teh mouth and tongue in order to push the bolus into the oropharynx
- Pharyngo-Esophageal Phase: Oropharynx ELEVATES and constricts around the bolues, and propels it down the esophagus
*** Food should NOT enter the Laryngeal Aditus
Differentiate between the Larynx location in the Newborn and Adult humans?
Newborn: HIGHER up and located close to the nasal cavity (So they can suckle AND breathe at the same time!)
Adult: Moves INFERIOR to the throat (this changes the Intonation of the voice)
List the Boundaries of the Pharynx.
1. Choanae: Nasal Cavity and Nasopharynx
2. Pharyngeal Isthmus: Nasopharynx and Oropharynx
3. Faucial Isthmus: Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
Be able to locate the Odontoid Process, Body of C2, and the Anterior Arch of C1 on this picture!


Which bony landmark is at the level of:
- Transition of Laryngopharynx into the Esophagus
- Anterior Arch of the Crichoid Cartilage
6th Cervical Vertebra
The Stylopharnygeus muscle is innervated by which nerve?
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
List the elevator and constrictor muscles of the pharynx, and their innervation.
ELEVATORS of the pharynx:
- Stylopharyngeus - Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- Salpingopharyneus
- Palatopharyngeus
CONSTRICTORS of the pharynx:
- Superior, Middle, and Inferior Constrictors
- Innervated by Pharyngeal Branch of the VAGUS nerve
What does the Buccopharyngeal Fascia cover? Which structure runs within this fascia?
Covers the outer surface of teh BUCCINATOR muscle and muscles of the PHARYNX
PHARYNGEAL PLEXUS is embedded in the portion of the fascia covering the MIDDLE constrictor

Retropharyngeal Mass and Infection can spread to the base of the skull or the Mediastinum through the Retropharyngeal Space
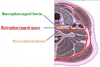
List the structures that are associated with the various pharyngeal constrictors. Where do you get various types of “outpouchings” and diverticula?
- Superior - Mandible near the 3rd molar
- Middle - Hyoid Bond
- Inferior - Laryngeal and Cricoid Cartilage
*** Between the Inferior Constrictor and Other muscles below it

Which artery does the Ascending Pharyngeal Artery come off of?
EXTERNAL Carotid Artery
Describe the Innervation of the Pharynx and Gag Reflex.
Pharyngeal Plexus recieves SENSORY (GVA) from the pharyngeal branch of the GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE (IX)
MOTOR (SVE) fibers from the pharyngeal branch of the VAGUS NERVE (X)
*** The GVA fibers will bring afferent information about the GAG Reflex
List the Three different branches off of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX).
- Pharyngeal Nerve to pharyngeal Plexus
- Sensory (GVA) to mucosa of POSTERIOR 1/3 of tongue and pharynx AND Sensory (SVA) to taste buds of POSTERIOR 1/3 of tongue
- MOTOR (SVE) to STYLOPHARYNGEUS Muscle
Which nerve/artery penetrates the Thyroihyoid Cartilage?
Internal Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve
Superior Laryngeal Artery
What is the purpose of the Valleculae Epiglottica?
- During intubation you have to pull the tongue forward in order to open up the airway!
- They are separated from each other by the MEDIAN glossoepiglottic fold and bounded laterally by the LATERAL glossoepiglottic folds.
***During intubation of a patient the blade is often placed in the valleculae epiglottica. As the end of the blade is moved forward so is the tongue and epiglottis. This movement opens the LARYNGEAL ADITUS. To examine the valleculae more distinctly, the examiner asks the patient to phonate. Large veins are frequently seen in the valleculae; these are normal.

The Cricothyroid Joint has a relationship with which nerve?
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
Which is the only muscle in the Larynx to ABDUCT the vocal folds?
Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscle

What is the function of the Vocalis Muscle?
Runs parallel with the vocal cord to DECREASE tension and LOWER the pitch of your voice
What is the function of the Cricothyroid Muscle?
INCREASES vocal tension by tilting the thyroid cartilage forward.
*** Opposes the VOCALIS muscle
Explain the Laryngeal Expiration Reflex (LER).
Stimulus: Material gets into the laryngeal vestibule and STIMULATES receptors in the MUCOSA
Afferent: Internal Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve will innervate the recetpors in the MUCOSA. Afferents enter the medulla with the VAGUS nerve
Efferent: Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (laryngeal muscles), Intercostal Nerve (intercostal muscles), and Abdominal Nerve (abdominal muscles)
Effect: Abrupt, Involuntary EXPIRATORY coughing
*** External Abdominal Obliques will contract by FORCING the Diaphragm UP!
Describe the Innervation and Vascular supply to the Larynx.

Describe the phenomena of “Pharyngeal Speech”.
Patients who have had a total laryngectomy (removal of the larynx) may learn to use esophageal speech, which is the vibration of the CRICOPHARYNGEUS muscle by regurgitation of swallowed air.
Describe the purpose and innervation/vascular supply of the piriform recesses. What happens when you get a “pooling” sign?
- The piriform recesses slightly dilate if the patient says “a-a-a” in a low voice. Secretions may gather here, but they should disappear on swallowing. If they do not, the patient has a “pooling” sign, which suggests obstruction or paralysis of the upper esophagus.
- The epithelium in this area is innervated by the INTERNAL BRANCH of the superior laryngeal nerve, and supplied by the SUPERIOR laryngeal artery.

List the different cartilages that will make up the Larynx.
- Thyroid Cartilage
- Cricoid Cartilage
- Arytenoid Cartilages
- Corniculate Cartilages
- Cuneiform Cartilages
- Epiglottic Cartilage






