Pediatric Male/Female Reproductive System Flashcards
(45 cards)
All sexually active women age [] should be screened for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
e.g. nucleic acid amplification testing
All sexually active women age >24 should be screened for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhae.
e.g. nucleic acid amplification testing

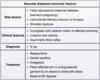
Congenital hydrocele occurs due to incomplete obliteration of the […] in infants.
Congenital hydrocele occurs due to incomplete obliteration of the processus vaginalis in infants.
Do adolescents seeking pregnancy prevention options (e.g. OCPs, emergency contraception) need parental consent?
No
Fetal macrosomia is associated with increased risk for shoulder […].
Fetal macrosomia is associated with increased risk for shoulder dystocia.
potential complications of shoulder dystocia include clavicle fracture, brachial nerve palsies, and perinatal asphyxia

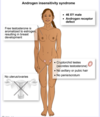
In […] syndrome a person is genotypically XY but has female external genitalia with male internal genitalia.

In androgen insensitivity syndrome a person is genotypically XY but has female external genitalia with male internal genitalia.
i.e. the presence of the lower vagina, clitoris, and labia with cryptorchid testes

In androgen insensitivity syndrome a person is genotypically XY but has […] external genitalia with […] internal genitalia.
In androgen insensitivity syndrome a person is genotypically XY but has female external genitalia with male internal genitalia.
i.e. the presence of the lower vagina, clitoris, and labia with cryptorchid testes
In 5α-reductase deficiency, a person is genotypically XY but has ambiguous […] genitalia with normal male […] genitalia.
In 5α-reductase deficiency, a person is genotypically XY but has ambiguous external genitalia with normal male internal genitalia.
due to lack of dihydrotestosterone, which is necessary for external genitalia development – at puberty, elevated levels of testosterone cause external genitalia growth
In […] deficiency, a person is genotypically XY but has ambiguous external genitalia with normal male internal genitalia.
In 5α-reductase deficiency, a person is genotypically XY but has ambiguous external genitalia with normal male internal genitalia.
due to lack of dihydrotestosterone, which is necessary for external genitalia development – at puberty, elevated levels of testosterone cause external genitalia growth
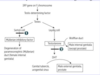
Kallmann syndrome presents as infertility in males and amenorrhea in females; […] may be present in both sexes.
Kallmann syndrome presents as infertility in males and amenorrhea in females; anosmia may be present in both sexes.
due to failure of GnRH migration (thus decreased FSH, LH, and testosterone) and olfactory bulb formation
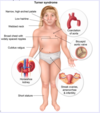
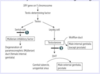
Klinefelter syndrome is characterized by a […],[…] karyotype.
Klinefelter syndrome is characterized by a 47,XXY karyotype.

Maternal hyperglycemia is associated with macrosomia, secondary to fetal […].
Maternal hyperglycemia is associated with macrosomia, secondary to fetal hyperinsulinemia.

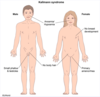
Patients with Turner syndrome typically have […] levels of estrogen.
Patients with Turner syndrome typically have low levels of estrogen.
due to ovarian dysgenesis; results in high levels of FSH/LH due to lack of negative feedback

Primary amenorrhea is defined as the absence of menarche by age […].
Primary amenorrhea is defined as the absence of menarche by age 15.

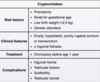
Size and tenderness of a fibroadenoma of the breast typically increases prior to […].
Size and tenderness of a fibroadenoma of the breast typically increases prior to menstruation.

Small for gestational age (SGA) infants have a birth weight that is below the […] percentile for gestational age.
Small for gestational age (SGA) infants have a birth weight that is below the 10th percentile for gestational age.
What hematologic complication may be seen in a newborn with low birth weight and intrauterine growth restriction?
Polycythemia
due to increased erythropoietin secretion in response to fetal hypoxia; other complications include hypoglycemia, hypothermia, and hypocalcemia

What is the first-line treatment for primary dysmenorrhea?
NSAIDs and/or OCPs
treatment preference depends if the patient is sexually active (OCPs) or sexually inactive (NSAIDs)

What is the likely diagnosis in a macrosomic newborn with crepitus over the clavicle and asymmetric Moro reflex?
Clavicular fracture (secondary to shoulder dystocia)
diagnosis is confirmed with X-ray

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with pelvic cramping during the first few days of menses with a normal physical examination?
Primary dysmenorrhea
due to uterine contractions triggered by prostaglandin release from sloughing endometrium

What is the likely diagnosis in a young girl that presents with breast development and a white, odorless vaginal discharge with an ovarian mass on ultrasound?
Granulosa cell tumor
white, odorless vaginal discharge is indicative of estrogen stimulation

What is the likely diagnosis in an adolescent female that presents with amenorrhea with a non-palpable uterus and normal-size ovaries on ultrasound?
Mullerian agenesis (Mayer-Rokitanksy-Kuster-Hauser syndrome)
primary amenorrhea due to lack of uterine development; still have normal ovaries with normal axillary and pubic hair

What is the likely diagnosis in an adolescent patient with a unilateral, mobile, well-circumscribed mass in the outer quadrant of the breast that becomes tender prior to menstruation?
Fibroadenoma
fibroadenoma is the most common cause of breast mass in an adolescent

What is the likely underlying etiology of painless, irregular, heavy menses in an adolescent girl that started menstruation one year ago?
Immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
results in anovulatory cycles, which causes abnormal uterine bleeding

What is the most common cause of vaginal bleeding in the neonatal period?
Maternal withdrawal of estrogen
typically manifests as a white vaginal discharge mixed with blood within the first 2 weeks of life