Pediatric Endocrine, Diabetes, Metabolism Flashcards
Diabetic ketoacidosis is often precipitated by acute […] due to systemic release of catecholamines and cortisol.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is often precipitated by acute infection due to systemic release of catecholamines and cortisol.
these hormones are counter-regulatory to insulin and produce hyperglycemia and ketonemia with osmotic diuresis
Diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency is supported by elevated […] levels.
Diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency is supported by elevated 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels.

Fetal hyperglycemia […] the first trimester is associated with macrosomia, birth injury, and hypoglycemia. (during or after)
Fetal hyperglycemia after the first trimester is associated with macrosomia, birth injury, and hypoglycemia. (during or after)
hyperglycemia in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters trigger the release of insulin, which causes increased glycogen and fat storage (organomegaly) and increased growth factor production (macrosomia)

Fetal hyperglycemia […] the first trimester is associated with malformations. (during or after)
Fetal hyperglycemia during the first trimester is associated with malformations. (during or after)

How do total body stores of K+ change in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis?
Decreased
secondary to osmotic diuresis; serum K+ levels are typically normal or increased
How does serum K+ change in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis?
normal/increased
due to acidemia (H+/K+ exchange) and lack of insulin driving K+ into cells; total body K+ decreases
In gonadotropin-dependent (central) precocious puberty, LH levels are […] at baseline.
In gonadotropin-dependent (central) precocious puberty, LH levels are high at baseline.
due to early activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which results in pulsatile GnRH release with elevated FSH/LH levels

In gonadotropin-[…] precocious puberty, LH levels are high at baseline.
n gonadotropin-dependent (central) precocious puberty, LH levels are high at baseline.
due to early activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which results in pulsatile GnRH release with elevated FSH/LH levels

In gonadotropin-independent (peripheral) precocious puberty, LH levels are […] at baseline and […] increase with a GnRH agonist.
In gonadotropin-independent (peripheral) precocious puberty, LH levels are low at baseline and do NOT increase with a GnRH agonist.
caused by gonadal or adrenal release of excess sex hormones, resulting in low LH due to negative feedback

In gonadotropin-[…] precocious puberty, LH levels are low at baseline and do NOT increase with a GnRH agonist.
In gonadotropin-independent (peripheral) precocious puberty, LH levels are low at baseline and do NOT increase with a GnRH agonist.
caused by gonadal or adrenal release of excess sex hormones, resulting in low LH due to negative feedback

Medium chain acyl-CoA deydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency is characterized by […]-ketotic, […]-glycemia.
Medium chain acyl-CoA deydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency is characterized by hypo-ketotic, hypo-glycemia .

Patients with central precocious puberty require […] prior to starting GnRH agonist therapy.
Patients with central precocious puberty require MRI of the brain prior to starting GnRH agonist therapy.
needed to rule out CNS lesions (e.g. hormone secreting tumors or tumors affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis via mass effect)
Patients with von Gierke disease often have thin extremities, short stature, and a “[…]-like” face.
Patients with von Gierke disease often have thin extremities, short stature, and a “doll-like” face.
Patients with von Gierke disease typically have a protuberant abdomen, secondary to […].
Patients with von Gierke disease typically have a protuberant abdomen, secondary to hepatomegaly.
hepatomegaly occurs due to increased levels of glycogen trapped in the liver
Precocious puberty is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics in girls < 8 and boys <years of age.
Precocious puberty is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics in girls < 8 and boys < 9 years of age .

Refeeding syndrome is associated with […] serum levels of phosphorus, Mg2+, and K+ .
Refeeding syndrome is associated with decreased serum levels of phosphorus, Mg2+, and K+ .
due to intracellular uptake secondary to a surge in insulin activity

The initial evaluation of patients with precocious puberty is to determine the patient’s […], which helps differentiate true precocious puberty from other causes of early development.
The initial evaluation of patients with precocious puberty is to determine the patient’s bone age, which helps differentiate true precocious puberty from other causes of early development.
e.g. premature adrenarche

The pathogenesis of refeeding syndrome involves a rapid surge in […] activity as the body resumes anabolism.
The pathogenesis of refeeding syndrome involves a rapid surge in insulin activity as the body resumes anabolism.
insulin promotes cellular uptake of phosphorus, K+, and Mg2+, which can cause arrhythmias and cardiopulmonary failure due to low serum levels

von Gierke disease is associated with […] serum lactate, triglycerides, and uric acid.
von Gierke disease is associated with increased serum lactate, triglycerides, and uric acid.
i.e. lactic acidosis with hyperlipidemia and hyperuricemia
von Gierke disease is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme […].
von Gierke disease is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase.
von Gierke disease is characterized by severe fasting […]-glycemia.
von Gierke disease is characterized by severe fasting hypo-glycemia.
deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase prevents the breakdown of glycogen
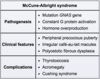
What cause of precocious puberty is associated with unilateral café-au-lait spots and polyostotic fibrous dysplasia?

McCune-Albright syndrome
girls typically have premature vaginal bleeding and breast development; syndrome develops due to mutation affecting G-protein signaling
What is the likely diagnosis in a newborn female that presents with salt wasting and clitoromegaly?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency)

What is the likely diagnosis in a newborn that presents with an enlarged tongue and jaundice with high TSH and low free T4?
Congenital hypothyroidism
routinely screened for in newborns; additional symptoms include lethary and umbilical hernia, though most patients are asymptomatic








