Pediatric Hematology and Oncology Flashcards
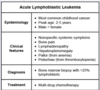
Acute leukemia is defined as a neoplastic proliferation of blasts > […]% on bone marrow biopsy.
Acute leukemia is defined as a neoplastic proliferation of blasts > 25% on bone marrow biopsy
e.g. ALL is diagnosed by presence of > 25% lymphoblasts in the bone marrow

Aplastic anemia may be caused by Fanconi anemia, which occurs due to a […] defect, resulting in bone marrow failure (pancytopenia).
Aplastic anemia may be caused by Fanconi anemia, which occurs due to a DNA repair defect, resulting in bone marrow failure (pancytopenia).
defect in nonhomologous end joining (double stranded break repair)

Aplastic anemia may be caused by […] anemia, which occurs due to a DNA repair defect, resulting in bone marrow failure (pancytopenia).
Aplastic anemia may be caused by Fanconi anemia, which occurs due to a DNA repair defect, resulting in bone marrow failure (pancytopenia).
defect in nonhomologous end joining (double stranded break repair)

Aplastic crisis is often seen in patients with sickle cell disease and is characterized by […] reticulocyte count.
Aplastic crisis is often seen in patients with sickle cell disease and is characterized by decreased reticulocyte count.
important distinguishing feature from splenic sequestration

Aplastic crisis is often seen in patients with sickle cell disease and is characterized by […] platelet count.
Aplastic crisis is often seen in patients with sickle cell disease and is characterized by normal platelet count.
important distinguishing feature from splenic sequestration and aplastic anemia

At baseline, patients with sickle cell disease have […] levels of HbF.
At baseline, patients with sickle cell disease have increased levels of HbF.
due to prolonged lifespan of HbF-containing RBCs

Avascular necrosis of the femoral head results in pain on hip […] and […]. (movements).
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head results in pain on hip abduction and internal rotation. (movements)
there is no erythema, swelling, or point tenderness, which helps differentiate avascular necrosis from other etiologies

Children with sickle cell disease should take daily oral […] prophylaxis until 5 years of age.
Children with sickle cell disease should take daily oral penicillin prophylaxis until 5 years of age.

Cytoplasmic aggregates of periodic acid Schiff (PAS) positive material are characteristic of […]-blasts.
Cytoplasmic aggregates of periodic acid Schiff (PAS) positive material are characteristic of lympho-blasts.
versus myeloblasts, which often have peroxidase positive granules and/or Auer rods
Cytoplasmic aggregates of peroxidase positive granules and/or Auer rods are characteristic of […]-blasts.
Cytoplasmic aggregates of peroxidase positive granules and/or Auer rods are characteristic of myelo-blasts.
versus lymphoblasts, which often have aggregates of periodic acid Schiff (PAS) positive material
Diamond-Blackfan anemia is associated with congenital anomalies, such as short stature, webbed neck, cleft lip, shield chest, and […] thumbs.
Diamond-Blackfan anemia is associated with congenital anomalies, such as short stature, webbed neck, cleft lip, shield chest, and triphalangeal thumbs.
suspect in children with the aforementioned anomalies and a macrocytic pure red cell aplasia

Heinz bodies form due to precipitation of denatured […] within RBCs.
Heinz bodies form due to precipitation of denatured hemoglobin within RBCs
Hb sulfhydryl groups donate an electron to hydrogen peroxide, forming hemoglobin crosslinks

How do the following laboratory values change in anemia of chronic disease?
Serum iron: […]
TIBC: […]
% Saturation: […]
Ferritin: […]
How do the following laboratory values change in anemia of chronic disease?
Serum iron: decreased
TIBC: decreased
% Saturation: decreased
Ferritin: increased
high ferritin and low TIBC help distinguish ACD from iron deficiency anemia

How do the following laboratory values change in iron deficiency anemia?
Serum iron: […]
TIBC: […]
% Saturation: […]
Ferritin: […]
Serum iron: decreased
TIBC: increased
% Saturation: decreased
Ferritin: decreased
low ferritin and high TIBC help distinguish iron deficiency from anemia of chronic disease

How do the following laboratory values change in sideroblastic anemia?
Serum iron: […]
TIBC: […]
% Saturation: […]
Ferritin: […]
Serum iron: increased
TIBC: decreased
% Saturation: increased
Ferritin: increased
“iron overload”

In patients with sickle cell disease, chronic damage and autoinfarction typically causes functional asplenia by age […].
In patients with sickle cell disease, chronic damage and autoinfarction typically causes functional asplenia by age 5.
Iron deficiency anemia can be differentiated from thalassemia by an elevated […].
Iron deficiency anemia can be differentiated from thalassemia by an elevated red cell distribution width (RDW).
typically > 20% in iron deficiency

Iron deficiency anemia in children is often caused by excess consumption of […].
Iron deficiency anemia in children is often caused by excess consumption of cow’s milk (> 24 ounces/day).

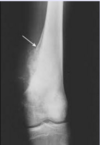
Osteosarcoma arises in the […] of long bones, often around the knee.
Osteosarcoma arises in the metaphysis of long bones, often around the knee
i.e. distal femur or proximal tibia

Polycythemia in term neonates is defined as a hematocrit > […]%.
Polycythemia in term neonates is defined as a hematocrit > 65%.
risk factors include delayed cord clamping, maternal hypertension, and maternal diabetes mellitus

Pure red cell aplasia is associated with […], lymphocytic leukemias, and parvovirus B19 infection.
Pure red cell aplasia is associated with thymoma, lymphocytic leukemias, and parvovirus B19 infection.
severe anemia with normal granulopoiesis and thrombopoiesis
Risk factors for neonatal polycythemia include delayed cord clamping, maternal […], and maternal […].
Risk factors for neonatal polycythemia include delayed cord clamping, maternal hypertension, and maternal diabetes mellitus.

Splenectomy is associated with a long-term risk for sepsis with […] bacteria.
Splenectomy is associated with a long-term risk for sepsis with encapsulated bacteria.
risk is present for up to 30 years, and perhaps longer
Splenic sequestration is characterized by normocytic anemia with […] reticulocyte count.
Splenic sequestration is characterized by normocytic anemia with increased reticulocyte count.
important distinguishing feature from aplastic crisis