Pathology-Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Flashcards
A mother brings in her 1 year old baby boy complaining of hyperactivity, purposeless movements, rhythmic rocking and athetosis. He has had two seizures in the past week. History reveals projectile vomiting and pyloric stenosis at birth. Physical exam reveals a musty odor. What genetic alteration is causing this child’s symptoms?
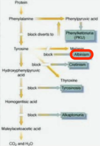
This child has phenylketonuria. It is an AR disorder of chromosome 12 that results in lack of phenylalanine hydroxylase. This results in a build up of phenylalanine in the blood (hence the odor) and in the urine. Note that it is often misdiagnosed as pyloric stenosis at birth.
A mother comes to see you who continues to have miscarriages. She had one child who survived a couple of weeks, but was mentally retarded, had microcephaly and a congenital heart anomaly. Why would you ask about the mother’s diet?
Pregnant women with PKU who are not on a low-phenylalanine diet have a high risk for spontaneous abortion and birth defects. She should restrict her Phe serum levels to 10 mg/dL.
A mother brings in her 1 year old baby boy complaining of hyperactivity, purposeless movements, rhythmic rocking and athetosis. He has had two seizures in the past week. History reveals projectile vomiting and pyloric stenosis at birth. Physical exam reveals a musty odor. How do you treat this child?
You put him on a special diet to maintain serum Phe levels between 3-15 mg/dL. This is especially important in the first 6 years of life.
A mother brings in her child with complaining of mental retardation and failure to thrive. Physical exam reveals hepatomegaly, jaundice and ascites. Labs reveal conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, elevated AFP, hypoglycemia, hypophosphatemia, aminoaciduria, tubular acidosis and elevated BUN. What is causing the symptoms seen in this child?
This is tyrosinemia. This is an AR lack of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH). The body cannot break down Tyr and it builds up in the blood. This results in mental retardation and major liver (cirrhosis and carcinoma) and kidney (Fanconi syndrome) abnormalities.
A child presents with hepatocellular carcinoma. What inborn error of amino acid metabolism are you thinking of?

Tyrosinemia. Usually kids with liver cancer present with hepatocellular blastoma.
Fanconi syndrome
Associated with tyrosinemia: renal tubular acidosis, hypophosphatemia and aminoaciduria
A mother brings in her child with complaining of mental retardation and failure to thrive. Physical exam reveals hepatomegaly, jaundice and ascites. Labs reveal conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, elevated AFP, hypoglycemia, hypophosphatemia, aminoaciduria, tubular acidosis and elevated BUN. How do you treat this patient?
1st line of defense is a low protein diet. The only effective treatment of type I tyrosinemia is liver transplant. Otherwise hepatocellular carcinoma develops in 50% of kids by age 2.
Primary gout
Overproduction (diet) or reduced excretion of uric acid w/normal production (90% of cases)
Secondary gout
Overproduction of uric acid w/increased urinary excretion (HGPRT deficiency) or reduced excretion of uric acid w/normal production (renal failure)
A mother brings in her 2 year old boy complaining of facial grimacing, involuntary writing, repetitive movements of the arms and legs and continuous biting of his lips and fingers. He complains of intense joint pain and kidney stones. Labs reveal hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria. What is your diagnosis?
He has Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. It is an X-linked HPRT gene mutation that causes deficient HGPRT enzymes and build up of uric acid in the blood.

A mother brings in her 2 year old boy complaining of facial grimacing, involuntary writing, repetitive movements of the arms and legs and continuous biting of his lips and fingers. He complains of intense joint pain and kidney stones. Labs reveal hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria. Why might this patient also be anemic?
Pernicious anemia from B12 deficiency results from lack of HGPRT in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
A mother brings in her daughter complaining of nystagmus, strabismus, photophobia. Physical exam reveals apigmented irises. What is causing this girl’s symptoms?

This patient has albinism. This is an AR congenital disorder causing an absence of tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is a Cu-containing enzyme involved in production of melanin and generation of skin pigment/iris color. Albinism is also associated with optic nerve hypoplasia, which is why most symptoms of albinism are optic.
Albino
Complete absence of melanin
Albinoid
Diminished amount of melanin
A 20 year old man presents with fatigue, difficulty breathing and jaundice. Imaging reveals liver cirrhosis and emphysema. What is your diagnosis?
This patient has alpha-1-antitrypsin (A1AT) deficiency. This is an AR deficiency in A1AT, a protease inhibitor that inhibits neutrophil elastase release. PiZZ results in severe alveolar damage by uninhibited elastase and liver disease. PiMZ is usually a carrier.

What is the most common cause of liver disease in children and emphysema in adults?
A1AT Deficiency.
A mother brings in her baby who was jaundiced for 7 days as a newborn, then it went away and came back a year later. Liver biopsy from when she was a newborn and 1 year old are shown below. What is your diagnosis? What is the child at risk for?

The 1st image looks like neonatal hepatitis; however, immunohistochemical staining reveals aggregation of A1AT in the cells. The second image shows aggregation of A1AT seen without immunohistochemical staining. Finally, the child is at risk for liver cirrhosis as shown below.

A 36 year old man presents with symptoms of liver disease. Liver biopsy reveals, ballooning degeneration, cholestasis, acidophilic bodies and lymphocyte infiltration. He has no history of alcohol abuse. Physical exam reveals Keiser-Fleschner rings. What is your diagnosis?

This patient has Wilson disease. This presents similar to alcoholic hepatitis.

A child is born that fails to pass meconium. Later on in life he develops nasal polyps, bronchiectasis, clubbing of the fingers, chronic pancreatitis, rectal prolapse, infertility and liver disease. Lung biopsy is shown below. What is causing his condition?
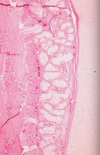
This patient has cystic fibrosis. This is an AR single gene defect. The most common mutation is Phe deletion at 508 (delta F508). This results in decreased Cl- secretion, decreased fluid secretion, hyper concentrated mucous and obstructive tubulopathy in the pancreas, intestines, lung, liver and testes.
Why do kids with cystic fibrosis have salty skin?
Defect in Cl- secretion results in less Na+ reabsorption by the sweat glands as sweat is secreted.
What contributes to most poor outcomes in people with cystic fibrosis?
Recurrent pneumonia (esp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in kids) causes COPD.
What kind of liver disease to people with cystic fibrosis typically present with?
Hepatobiliary fibrosis from fluid secretion blockade of bile ducts.
How do you test for cystic fibrosis?
Sweat chloride test or genetic testing
How do you treat cystic fibrosis?
Percuss the lungs, loosen up mucous secretions and prevent infection for as long as you can. Ultimately they will need a lung transplant.


