Biochemistry-Purine:Pyrimidine Synthesis Flashcards
What processes require rapid DNA and RNA synthesis?
Embryogenesis, hematopoiesis, rapidly regenerating tissues (enterocytes), tumor growth.
How do you number pyrimidines?
*
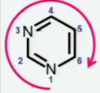
How do you number purines?
*

What is this molecule?

Nitrogenous base + Sugar + Phosphate = Nucleotide
What is this molecule?

This is the purine nucleoside: adenosine.
What is this molecule?

This is the purine nucleotide: inosinic acid (IMP). Note that the nitrogenous base is actually called hypoxanthine.
What is this molecule?

This is the purine nucleotide: guanylic acid (GMP)
What is this molecule?

This is the purine: uric acid. Note that this is the product of purine breakdown and we do not have a way to further break it down.
What molecule is this?

This is the pyrimidine nucleoside: Cytidine
What molecule is this?

This is the pyrimidine nucleotide: uridylic acid (UMP)
What molecule is this?

This is the pyrimidine nucleotide: orotidylic acid (OMP)
What are the purine bases, their nucleosides and their nucleotides?
*

What are the pyrimidine bases, their nucleosides and their nucleotides?
*

What are 2 ways we get ribonucleotides?
1) De novo synthesis 2) Salvage
What has a higher concentration in the body: ribonucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides?
Ribonucleotides
What enzymes are responsible for the steps a, b and c shown below?
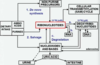
*

What happens to the nucleotides and bases that are not salvaged?
They are converted to uric acid and secreted in the urine (2/3) and feces (broken down by bacteria).
A patient presents with a chills, a fever and a painful swollen big toe. He has had a history of this in the past, but attacks are becoming more frequent. What will be the ultimate result of his condition if he does not receive treatment?
There are 4 phases of gout: 1) Asymptomatic hyperuricemia 2) Acute attacks of gouty arthritis 3) Intercritical periods 4) Chronic tophaceous gout (permanent deformities of the joint) happens without treatment.
What is the saturation point of uric acid in the serum?
7mg/dL
What do you use to treat the acute phase of gout?
NSAIDs for the acute phase. Colchisine is a microtubule inhibitor that prevents migration of PMNs to site of inflammation, prevents phagocytosis and prevents release of inflammatory mediators
A mother brings in her 3-9 month old child who can’t hold his head up or sit unsupported. He cannot crawl and is diagnosed with cerebral palsy. As he gets old her begins to demonstrate serious self-injurious behavior. What is most likely causing the disease in this kid?
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome. This is an inherited X-linked AR deficiency of the purine salvage enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). Deficiency in HGPRT results in over production of uric acid resulting in debilitating neurological symptoms.
What ingredients go into making the purine ring?
*

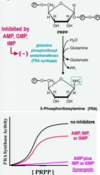
What pathway supplies the scaffold on which the nucleotides are build?
Hexose monophosphate shunt generates ribose-5-phosphate
What regulates the activation step in nucleotide synthesis?
PRPP synthetase and ATP activate ribose-5-phosphate to PRPP. PRPP synthetase is inhibited by ADP, GDP and other nucleotides.