Biochemistry-Amino Acid Synthesis & Degradation Flashcards
A mother gives birth to a healthy baby. A few hours after birth the baby becomes lethargic. She brings the child into the hospital the next day and the baby is vomiting, has hypothermia, respiratory alkalosis, encephalopathy and cerebral edema. What congenital defect is causing this child’s condition?
The child has orotic acidemia. This happens when the enzyme that converts carbamoyl phosphate to citrate in the mitochondria is defective. Carbamoyl phosphate builds up and is transported into the cytosol where it reacts with aspartate and CPSII takes it to carboy-aspartate, then it goes on to form orotic acid which goes out into the urine.

What lab results are common to all of the disorders in the urea cycle?
High NH4+, low urea and high glutamine (because Glu is the main carrier of free ammonia in the blood)

A mother brings in her newborn boy complaining of lethargy, irritability and hyperventilation 36 hours after birth. Over the next 24 hours, the lethargy increased and progressed to coma requiring mechanical ventilation. Hemodialysis was started at 5 days and the child died after one week. Two of the mother’s four brothers died shortly after birth from encephalitis. Labs at 36 hours reveal high blood pH, low blood CO2 and low BUN. On day 5 high plasma ammonium, high glutamine, Arg/Citrulline undetectable and high orotic acid in the urine. What is the pathogenesis of this disease?
The child has ornithine transcarbamoylase deficiency. Loss of the enzyme causes build up of carbamoyl phosphate in the mitochondria and prevents formation of citrulline, arginine and urea. Upstream, carbamoyl phosphate leaves the mitochondria and is converted to orotic acid, hence the orotic acid in the urine. Also upstream, CPSI isn’t as active from excessive amounts of carbamoyl phosphate and NH4+ builds up. This pushes the equilibrium of glutamine synthetase from glutamate to glutamine and Gln builds up.

What lab values would you expect to see in a patient with carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS I) deficiency?
Ammonia increase, glutamine increased, carbamoyl phosphate decreased, orotic acid decreased, citrulline decreased, arginine down and urea down.

What molecules are commonly attached to drugs so that they can be excreted in the urine? How is this used to treat defects in the urea cycle?
Glycine and glutamine. When people have urea cycle malfunction, you can give benzoate and phylacetate. The body tags these with glycine and glutamine, which are nitrogen carries, and they are excreted, taking the excess nitrogen with it.
What are the three key enzymes in amino acid and nitrogen metabolism?
PLP (pyridoxal phosphate does everything), BH4 (tetrahydrobiopterin catalyzes ring hydroxylations) and FH4 (tetrahydrofolate transfers single carbons)
What enzyme is the quintessential cofactor?
The C=O forms a bond with the nitrogen of the amino acid and can go on to form many different things.

Why are essential amino acids essential?
We cannot synthesize the carbon skeleton.
What is a semi-essential amino acid?
Carbon skeleton can be synthesized from glucose but not in sufficient quantity
Glucogenic amino acids
Carbon skeleton can be converted to glucose: NONESSENTIALS: Ala, Asp, Asn, Cys, Glu, Gln, Gly, Pro, Ser and Tyr (both gluco and ketogenic). ESSENTIALS: Arg, His, Met, The, Val and Iso, Phe, Trp (last 3 are both gluco and ketogenic)
Ketogenic amino acids
Carbon skeleton can be converted to acetyl CoA. ESSENTIALS: tyrosine is both gluco and ketogenic. NONESSENTIALS: Leucine and Lysine. Iso, Phe and Trp are both gluco and ketogenic.
What else do you need essential amino acids for besides protein synthesis?
Neurotransmitters
What are the essential amino acids?
*

What are the nonessential amino acids?
*

How do we synthesize Ala?
Transamination of pyruvate

How do we synthesize Glu? Why is it important that we can do this?
TCA cycle alpha-ketoglutarate transamination to glutamate. You need to get to glutamate so you can get to Gln, Pro and Arg
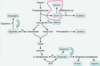
How do we synthesize Asp? Why is it important that we can do this?
TCA cycle OAA transamination to aspartate. You need to get to aspartate so you can get Asn.
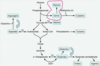
How do we synthesize Ser? Why is it important that we can do this?
Phosphoglycerate goes to Ser. This is important because you need to be able to do this so you can form Gly and Cys. This is also important because Ser -> Gly is important in developing the one carbon pool for THF (shown below).

How does synthesis of Arg take place?
You can’t just take Arg out of the urea cycle, otherwise you bleed the cycle. A new glutamate enters the cycle -> ornithine -> citrulline -> argininosuccinate -> arginine and that arginine is now taken out of the cycle

Why are the TCA intermediates called the amphibolic intermediates?
They can be used to break down amino acids to CO2 and H2O or can be used to synthesize other molecules from amino acids

What enzymes are responsible for phenylketonuria?
It can be a deficiency in dihydropteridine reductase that prevents you from generating tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). It can also be a deficiency in phenylalanine hydroxylase that prevents direct addition of OH to Phe to form Tyr.

How do we catabolize branched chain amino acids?
Isoleucine, leucine and valine 1st undergo transamination to their beta-keto derivative. Then they undergo oxidative decarboxylation by a keto acid dehydrogenase. These then go on to degradation pathways similar to beta-oxidation.

Why are alcoholics prone to have sweet smelling urine?
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD). The enzyme alpha ketoacid dehydrogenase used in branched chain amino acid catabolism need thiamine. Alcoholics can become thiamine deficient and build up of the alpha ketoacids causes the urine to smell like maple syrup.
Why does muscle release so much glutamine in a fasted state?
The branched chain amino acids are degraded 1st because they are energy rich. After the transamination reaction, the branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase has NH4+ as a byproduct. Glutamate reacts with it to form glutamine and is sent out of the muscle.















