Musculoskeletal part 2 Flashcards
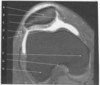
figure B 46 arrow A

metacarpal
figure B 46 arrow B

trapezium
figure B 46 arrow C

trapazoid
figure B 46 arrow D

capatate
figure B 46 arrow E

hammate
figure B 46 arrow F

triquitrium
figure B 46 arrow G

scaphoid
figure B 46 arrow H

lunate
figure B 46 arrow I

triangular fibrocartilage complex
figure B 46 arrow J

distal ulna
figure B 46 arrow K

distal radius
figure B 47 arrow A

extensor tendons
figure B 47 arrow B

hammate
figure B 47 arrow C

capatate
figure B 47 arrow D

carpal tunnel
figure B 47 arrow E

trapazoid
figure B 47 arrow F

trapezium
the evaluate the ip joints patient should be positined whereby the
feet are internally rotated
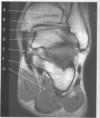
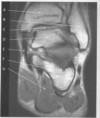
figure B 48 arrow A

psoas muscle
figure B 48 arrow B

iliacus muscle
figure B 48 arrow C

intervertebral disk
figure B 48 arrow D

ilium
figure B 48 arrow E

acetabulum
figure B 48 arrow F

femoral head