Musculoskeletal part 1 Flashcards
since joints are situated obliquely within the body, MR imaging is acquired in the (plane)
oblique plane
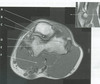
figure B 38 arrow A

frontal lobe
figure B 38 arrow B

temporal lobe
figure B 38 arrow C

temporal bone
figure B 38 arrow D

meniscus
figure B 38 arrow E

condyle of the mandible
figure B 38 arrow F

sylvian fissure
figure B 38 arrow G

eminence
figure B 38 arrow H

meniscus
figure B 38 arrow I

external auditory meatus
figure B 38 shows the images of the TMJ for the evaluation of range of motion, whereby images are acquired

closed and open mouth
TMJ imaging is acquired with oblique acquisition. The sagittal oblique images figure B 39 lower left are acquired with slices

perpendicular to the madibular condyle
TMJ imaging is acquired with an oblique acquisition, the coronbal oblique images V lower right are acquired with slices

parallel to the madibular condyle
figure B 39 arrow A

rectus muscle
figure B 39 arrow B

temporal bone
figure B 39 arrow C

meniscus
figure B 39 arrow D

condyle of the mandible
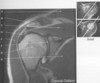
shoulder imaging is acquired in the oblique acuisistion. the coronal oblique images figure B 40 with slices

along the supraspinatus muscle (upper rt -top)
perpendicular to the glenoid fossa (upper rt-bottom)
figure B 40 arrow A

trapezius muscle
figure B 40 arrow B

acromion
figure B 40 arrow C

supraspinatus muscle
figure B 40 arrow D
rotator cuff
the structures that make up the rotator cuff
supraspinatus muscle/tendon
infraspinatus muscle/tendon
teres minor muscle/tendon
subscapularis muscle/tendon
figure B 40 arrow E

deltoid muscle