Abdomen and Pelvis part 1 Flashcards
(74 cards)
figure B 23 was acquired in the (plane)

coronal
figure B 23 is an example of (weighting)
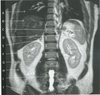
T2
figure B 23 arrow A

right lung
figure B 23 was acquired with

long TR and Long TE
no suppression
figure B 23 arrow B

liver
figure B 23 arrow C

spleen
figure B 23 arrow D

crux of the diaphragm
figure B 23 arrow E
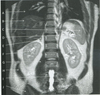
right adrenal gland
figure B 23 arrow F

kidney
figure B 23 arrow G

psoas muscle
figure B 23 arrow H

oblique abdominal juscle
figure B 23 the high signal arising within the abdomen, idicated by arrow I represents

CSF in the spinal canal
figure B 23 arrow J

gluteal muscle
the FDA approved oral contrast agent used in MRI makes bowel appear
dark on T1/dark on T2
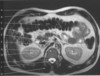
figure B 24 was acquired in the (plane)

axial
figure B 24 is a gradient echo image acquired with

fat suppression
figure B 24 arrow A

abdominal muscles
figure B 24 arrow B

stomach
figure B 24 arrow C

liver
figure B 24 arrow D

bowel
figure B 24 arrow E

portal vein
figure B 24 arrow F

aorta
figure B 24 arrow G

vertebral body
figure B 24 arrow H

spinal cord