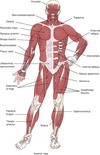
Muscular System Flashcards
Compare the three types of muscle tissue
- Skeletal muscle is voluntary, whereas smooth and cardiac muscle is involuntary
- Skeletal and cardiac muscle are striated
- Cardiac muscles have intercalated disks and branchlike networks
- Skeletal muscles have long cells with multiple nuclei
What are the three functions of skeletal muscle?
1) Movement of the skeleton
2) Maintenance of posture
3) Generation of heat
The ______ is the deepest layer of this connective tissue and surrounds the individual fibers within fascicles.
The ______ is a connective tissue layer around each fascicle.
The ______ is a connective tissue sheath that encases the entire muscle and forms the innermost layer of the deep fascia.
endomysium(endo- “within”)
perimysium (peri- “around)
epimysium (epi- “above”)

List compounds stored in muscle cells that are used to generate energy:
_____ stores oxygen
_____ is the storage form of glucose
Myoglobin
Glycogen
Explain what happens in muscle cells contracting anaerobically.
- Breakdown of _____, a compound similar to ATP in that it has a high-energy bond that breaks down to release energy. This energy is used to make ATP for muscle contraction. It generates ATP very rapidly, but its supply is limited.
- ________ This process breaks glucose down incompletely without using oxygen. A few ATPs are generated in these reactions, as is a byproduct called ____, which is later oxidized for energy when oxygen is available.
creatine (KRE-ah-tin) phosphate
Anaerobic glycolysis
lactate
This type of exercise results in hypertrophy, where the muscle cells grow in size, which allows the myofibrils to form more cross bridges. It also increases muscle stores of creatine and glycogen, and therefore more rapid ATP.
Resistance training
a steady partial contraction of the muscle that keeps the body in position
muscle tone
Individual muscle fibers (cells) are arranged in bundles, or _____, held together by dense connective tissue
fascicles

a band of dense regular connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone
tendon
Muscle Cells
The muscle fiber’s cytoplasm is called the ____, and its plasma membrane is the ____.
Extensions of this membrane tunnel deep in the interior of the muscle fiber as a network of ____, which are important in muscle cell stimulation.
sarcoplasm; sarcolemma
T-tubules

Muscle Cells
Muscle fibers contain large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, known as the _____ _____, where calcium is stored.
The vast majority of the muscle fiber’s volume is taken up by bundles of protein filaments called _____, which work to contract the muscle.
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
myofibrils

stem cells that can produce new myoblasts
satellite cells
the transmission of electrical and chemical signals between cells or even within a single cell
communication
Chemical Communication
Chemical signals alter cell activity by binding to specific proteins called _____. The signal that binds the receptor is known as the ____.
A ____ fits into a ____ like a key in a lock.
receptors
ligand
nerve cells that carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to stimulate movement
motor neurons
nerve cells that carry signals from the peripheral to central nervous system
sensory neurons
a single neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates constitute a _____
motor unit

In a resting cell, the intracellular fluid contains a small excess of negative ions, and the extracellular fluid contains a small excess of positive ions. As a result of these unpaired charges, the plasma membrane of a living cell carries a difference in electric charge (voltage) on either side that is known as a ____ _____
membrane potential
Because the membrane potential can change, muscle cells and neurons show the property of _____
These changes create electric signals, because they spread along the membrane, much like an electric current spreads along a wire. This spreading wave of electric current is called the _____ _____ because it calls the cell into action.
excitability
action potential
A nerve fiber contacts a muscle cell at a kind of synapse called the _____ _____
At the synapse, there is a tiny space known as the _____ _____, across which acetylcholine travels to attach to a receptor in the muscle cell’s receiving membrane, known as the ____ ____ _____.
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
synaptic cleft
motor end plate

A contracting subunit of skeletal muscle is called a ______
It consists of a band of protein filaments, _____ and ____ , which give muscles their striated appearance.
sarcomere
myosin
actin

This image shows the _____ _____ mechanism of muscle contraction

sliding filament
In addition to actin, myosin, and ATP, ____ is needed for muscle contraction. It enables cross-bridges to form between actin and myosin so the sliding filament action can begin.
When muscles are at rest, two additional proteins called ____ and ____ block the sites on actin filaments where cross-bridges can form
calcium
troponin (tro-PO-nin)
tropomyosin (tro-po-MI-o-sin)

Muscle Contraction:
- ____ is released from a neuron ending into the synaptic cleft at the NMJ.
- Acetylcholine then binds to receptors in the muscle’s motor end plate and stimulates an action potential.
- The action potential travels down the sarcolemma and T-tubules and activates ____ channels in the SR.
- The SR releases calcium into the cytoplasm.
- Calcium shifts troponin and tropomyosin so that binding sites on actin are exposed.
- Myosin heads bind to actin, forming cross-bridges.
- Using the chemical energy contained in ____, myosin heads pull actin filaments together within the sarcomeres, and the cell shortens.
- New ATP is used to detach myosin heads and move them back to position for another “power stroke.”
- The muscle relaxes when stimulation ends, and the calcium is pumped back into the SR.
acetylcholine
calcium
ATP