Module 00: Introduction, Measurement, and Estimation Flashcards
Lesson 0.1 - Measurement, Uncertainty, Significant Figures Lesson 0.2 - Units, Standards, SI, and Converting Units (46 cards)
Lesson 0,1
What is the purpose of Physics?
The search for order in our observations of the natural world
Lesson 0,1
How do theories and observations relate to each other?
Observations - one side of the scientific process
Theories: explain and order the observations
Observations inspire the theory but it is based on the results of observations and experimentation
Lesson 0,1
How verifiable are theories, laws, and principles?
- No measurement is perfect, so exact confirmation is impossible
- Not possible to test all circumstances
Result: replace one theory with a new one if it yields better results
Lesson 0,1
What is a model and what is its purpose? `
Definition: kind of analogy or mental image of phenomena in terms of something already familiar
Purpose: Approximate mental or visual picture
Lesson 0,1
Difference between a theory and a model:
The theory is broader, more detailed than a model, and can be quantitatively tested.
Lesson 0,1
Define a Law:
Certain a concise but general statement about how nature behaves.
Descriptive: they do not say how nature should behave, but rather are meant to describe how nature cases possible
In general, a scientific law is the description of an observed phenomenon. It doesn’t explain why the phenomenon exists or what causes it. The explanation for a phenomenon is called a scientific theory.
How not Why
Lesson 0,1
How do you determine the percent uncertainty?
Ratio of the uncertainty to the measured values multiplied by 100.
for example: For 8.8 +- 0.1
= 0.1/8.8 * 100% = 1%
Lesson 0,1
What is the scientific figure of the following number: 32.21
4 sig figs
Lesson 0,1
What is the scientific figure of the following number: 0.062
2 (the zeros are placeholders)
Lesson 0,1
What is the scientific figure of the following number: 80
1 (the zero is a placeholder unless there is a decimal)
Lesson 0,1
What is the rule when multiplying or dividing scientific figures?
The Final result should have no more digits than the numerical value of the value with the fewest significant figures.
Lesson 0,1
What is the percent accuracy vs. the significant figures?
Use the significant figure rule but consider the % uncertainty too, and add an extra digit if it gives a more realistic estimate of uncertainty
Lesson 0.2
Why are standards (or units) important?
Makes sure there is a uniform method of measuring something
Lesson 0.2
What is the conversion factor from inches to meters?
1 inch = 2.54 centimeters
Lesson 0.2
What is the standard unit of mass?
kilograms (kg)
Lesson 0.2
What is the atomic mass in kg?
1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27kg
Lesson 0.2
What is SI (Systeme International or International System)?
- Standard length: meter
- Standard time: second
- Standard mass: kilograms
MKS system (meter-second-kilogram)
Lesson 0.2
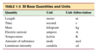
What are base and derivative quantities?
- Base quantity: defined in terms of a standard
- Derived quantities: all other quantities defined in terms of these seven base quantities
Lesson 0.2
What is an operational definition?
To define any quantity, whether base or derived, use a special rule or procedure.
Lesson 0.2
What is the conversion factor for feet to inches?
1 foot = 12 inches
Lesson 0.2
What are the three dimentions?
(1) mass, (2) length, and (3) time
Lesson 0.2
What are the steps of dimensional analysis?
Step 01: Identify what you know and what you need
Step 02: Set up conversion factors
Step 03: Cancel units and check
Step 04: Multiply the number
Practice Questions
- (I) How many significant figures do each of the following numbers have: (a) 214, (b) 81.60, (c) 7.03, (d) 0.03, (e) 0.0086, (f) 3236, and (g) 8700?
- 3 Significant Figures: 214
- 4 Significant Figures: 81.60
- 3 Significant Figures: 7.03
- 1 Significant Figure: 0.03
- 2 Significant Figures: 0.0086
- 4 Significant Figures: 3236
- 2 Significant Figures: 8700
Practice Questions
- (I) Write the following numbers in powers of 10 notation: (a) 1.156, (b) 21.8, (c) 0.0068, (d) 328.65, (e) 0.219, and (f) 444.
- 1.156 x 100
- 2.18 x 101
- 6.8 x 10-3
- 3.2865 x 102
- 2.19 x 10-1
- 4.44 x 102






