Management of Asthma- Adults Flashcards
What cells are responsible for the effects of asthma?
Th2 Cytokines - (IL-5, LT)
Eosinophils
Mast cells
What is the difference between occupational asthma and work-exacerbated asthma?
Occupational has no prior history of asthma
What is non-pharma management of chronic asthma?
Asthma Action Plan
Weight loss if ˄BMI
Vaccines – flu & pneum
Allergen avoidance
(inc. occup. Asthma)
Physiotherapy
Smoking Cessation
Bronchial Thermoplasty
What are the drugs used to treat acute asthma attack and chronic asthma?

What are the drugs to avoid during the treatment of asthma?
β-blockers
NSAIDS / Aspirin
Sedatives/strong opiates (unless in critical care)
What are the non-pharma methods of treatment of acute asthma attack?
ITU/HDU
Ventilation
ECCO2R
Chest drain if
pneumothorax
What are the benefits of inhalers?
- Small dose of drugs
- Delivery directly to the target organ (airways and lung)
- Onset of effect is faster
- Minimal systemic exposure
- Systemic adverse effects are less severe and less frequent
What are the problems associated with metered dose inhalers?
- Needs co-ordination
- Elderly, young children, unwell can’t use effectively
What are the benefits of spacers?
- Low oro-pharyngeal deposition of aerosol
- Reduced speed of the aerosol
- decreases bad taste associated with oral deposition
- reduced the risk of oral candidiasis and dysphonia with steroids
- Reduced “cold-Freon effect” in some
What are the benefits associated with dry powder inhalers?
- Less coordination required
- Similar issues with deposition
Requires high inspiratory flow
What does SABA stand for?
Short acting beta 2 agonists
Where do you find salbutamol?
MDI
DPI
Where do you find terbutaline?
DPI
What are the adverse side effects of beta 2 stimulants?

What are regular preventers?
Low dose Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS) - Preventers
- Beclomethasone
- Budesonide
- Fluticasone
- Ciclesonide
- Mometasone
When do you start ICS?
- Using inhaled β2 agonist (“Reliever”) x3/week or more
- Waking one night a week or more due to asthma
- Requiring oral steroid for an exacerbation in the past 2 years
- Symptomatic x3/week or more
What are the advantages of inhaled ICS?

What are the side effects of Long term oral cortical steroid use?
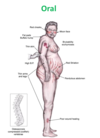
What are the long term side effects of inhaled long term steroids?
Dysphonia - difficulty in speaking due to a physical disorder of the mouth, tongue, throat, or vocal cords.
•Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
When do you move up the steps from SABA to ICS?
If it is being used three times a week
WHat is the first stage of management after Asthma diagnosed
Regular preventer
Add inhaled low-dose ICS
What is the 2nd stage of treating asthma
Initial add-on therapy
Add inhaled LABA to low dose ICS
Additional add on therapy
What should you do if there is no response to LABA?
Stop using it and consider an increased dose of ICS
Additional add on therapy
What should you do if there is a benefit from LABA but control is still inadequate?
Continue LABA and increase ICS to medium dose
Or Continue LABA and ICS and consider LRTA, SR theophylline, LAMA







