Embryology 2 Flashcards
(37 cards)
What happens during week 3?
- Formation of germ layers – GASTRULATION
- Formation of neural tube – NEURULATION
- Development of somites
- Early development of cardiovascular system
How is the primitive streak formed?
Formed in midline of epiblast by dipping in of cells (invagination)

What is formed after the primitve streak is formed?
Axis of embryo is formed
Where do epiblast layers migrate to?
Space between epiblast and the hypoblast layers
Cells displace the hypoblast

From the original epiblast, what three layers are formed?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
Trilaminar disk

What is gastrulation?
Formation of three germ layers
What layer does the primitive streak form from?
Ectoderm
What is the name given to the solid tube of cells formed from the ectoderm called?
The notochord

What is does the notochord do?
Induces ectodermal cells on midline to form neural tube

What is the precursor for the neural tube?
The neural plate
What is neurulation?

What is the effect of the neural tube on the mesoderm?
Causes the mesoderm to thicken
What happens after the mesoderm thickens?
It splits into three parts
What is the name of the three parts of the mesoderm?
- Paraxial mesoderm
- Intermediate plate mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm

What happens to the lateral plate of the mesoderm?
Lateral plate mesoderm splits to form a somatic and splanchnic mesoderm
Space formed in between: intraembryonic coelom
What does the paraxial mesoderm form?
Somites
What does the intermediate plate mesoderm form?
Urogenital system (kidneys + repro)
What does the lateral plate form
Body cavity and coverings. Peritoneum, pleura, and body cavities
Segmentation of paraxial mesoderm forms?
Somites
What does each paraxial mesoderm divide into?
- Dermatome
- Myotome
- Sclerotome

What is the function of each of these divisions of the somites?

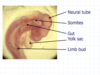
What happens during 4th – 8th weeks – Embryonic period / Organogenetic period?
- Folding into a tube (lateral folds) which started in 3rd week completes
- Neural tube – forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain and spinal cord development
- Heart starts to beat on Day 24
- Gut formation from endoderm
- Urogenital system formation from intermediate mesoderm
- Body cavities from lateral plate mesoderm
- 43 pairs of somites form in the paraxial mesoderm and differentiate further
- Limb buds form
- Neck development – pharyngeal arches

Which lateral plate is on the inside when the lateral folding of the embryo has been completed?
The splanchnic

What do the somatic mesoderm and the splanchnic mesoderm form?
Pleura:
Somatic = Parietal
Splanchnic = Visceral