M1 L2: Objective Assessment Principles- “Movements” Flashcards
(36 cards)
What does M (1) stand for MOVEMENT?
Motion
- Initiates and moves voluntarily with good frequency
What are the 2 types of Motion?
- [-] Reduced motion
- [+] Excess motion (hyperactivity)
What are the 4 features of “Reduced Motion” in M (Motion)?
- Fear/anxiety
- Due to balance, hurt themselves, fall over
- Behaviour/motivation
- Not motivated to move
- Environment/culture
- Child has to be very well behaved (don’t move around)
- Physical impairment

What is a feature of “Excess Motion” (hyperactivity) in M(Motion)?
ADHD

What does O stand for in MOVEMENT?
Orientation
- Orients to task and environment, transitions well
What are the 2 types of Orientation?
- Delayed/inadequate orientation
- Excessive/hypervigilant
What are the 4 features of “Delayed/inadequate orientation” in Orientation?
- Between body segments
- Poor alignment (slumping)
- To task
- Head down for task
- To gravity
- Falling over –> poor alignment –> hit head on ground
- To environment
- Wil not respond to visual and auditory feedback
- Eg. load sound –> orient head to sound
- Eg. fireworks –> look up at the fireworks
- Wil not respond to visual and auditory feedback

What is a feature of “Excessive/hypervigilance” in ORIENTATION?
More orientation strategies than necessary

What is does V stand for in MOVEMENT?
Variety
- Shows movement variety, adaptability and ability to improve
What are the 2 types of “Variety” in MOVEMENT?
- Poor repertoire, habitual/obligatory movements
- Excess, random, uncontrolled movement
What are the 4 features of “Poor repertoire, habitual/obligatory movements” in VARIETY?
- Persistent infant patterns
- Basic reflexes
- Pathological patterns
- Eg. brain injury (flexor spasticity y eg. thumin palms)
- Inactive/sedentary
- Eg.medically unwell/ illness –> cardiac illness
- Pain/musculoskeletal problems
- Haemophilia or juvenile arthritis

What are 2 features of “Excess, random, uncontrolled movement” in VARIETY
- Poor coordination/control
- Impulsivity
ADHD (can be sometimes unsafe)

What does E(1) stand for in MOVEMENT?
EASE
Movements are easy/free/fluid and without restriction
What are 2 types of “Ease” in MOVEMENT?
- Not easy/free/fluid
- Too easy/free/fluid
What are 3 features of “Not easy/free/fluid” in EASE?
- Pain (Eg. burns (skin contracture and pain))
- Stiffness
- Fear (Fear avoidant behaviour)
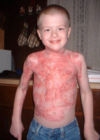
What are 2 features of “Too easy/free/fluid” in EASE?
- Poor coordination/control
- Impulsivity
Eg. Down syndrome –> hypotonia (highly flexible) –> hard to get postural orientation

What does M(2) stand for in MOVEMENT?
MODULATION
- Effort (force) and amplitude (range) are well controlled
What are the 2 types of “Modulation” in MOVEMENT?
- Not enough
- Too much
Whar are 3 features of “Not enough” in MODULATION?
- Force
- Amplitude
- Direction
Not enough muscle strength to get up with only legs –> uses arms to get up

What is a feature of “Too much” in MODULATION?
Proprioceptive control (eg. pressing hard on pen that they rip paper or break the lead or too much force when kicking ball –> fall over)

What does E(2) stand for in MOVEMENTS?
EFFECTIVE
- Movement is purposeful, accurate and achieves intended effect
What are the 2 types of “Effective” in MOVEMENTS?
- Poor effect due to inadequate/few attempts
- Poor outcome despite excessive/multiple attempts
What is a feature of “Poor effect due to inadequate/few attempts” in EFFECTIVE?

What is a feature of “Poor outcome despite excessive/multiple attempts” in EFFECTIVE?









