Lesson 3.4 - SARS-CoV-2 & COVID-19 Flashcards
(21 cards)
Where did COVID-19 originate?
Possibly a live animal/seafood market in Wuhan, China [Dec 2019]
Sars-CoV-2 stands for…
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(Original SARS in 2002)
What are initial symptoms of COVID-19?
Fever, cough, hard breathing; may progress to pneumonia (and high mortality among elderly)
What kind of virus is COVID-19?
- (+) sense ssRNA virus = mRNA (class IV)
- translates RNA dependent RNA polymerase
- (-) ssRNA is the template
- Enveloped, spherical (~120nm diameter)
- Linear (27-32kb), 29 orfs; longest known corona (crown) genome
- 5-G-cap & poly-A tail; associated w/ nucleocapsid
- Proofreading enzyme
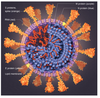
What kinds of viruses are MERS, SARS, and Sars-CoV-2?
- Beta-coronaviruses; bat origin
- MERS and SARS did not fully humanize, unlike Sars-COV-2 (no prior exposure/immunity)

2002 SARS Outbreak Stats
700-800 deaths worldwide; killed host which limited spread
2012 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Stats
>800 deaths; period outbreaks
Sars-CoV-2 is insidious due to…
-
the asymptomatic carrier phenomenon
- Transmits virus before symptoms appear
- Delays immune system; accessory genes / orfs have been implicated
- R0 = 2.5 to 3.1
SARS-CoV-2 has __ predominant proteins
-
4
-
Surface
- Spike (S)
- Membrane (M)
- Envelope (E)
- Interior
- Nucleocapsid (N)
-
Surface

S has ___ domains
-
2
-
S1 domain has receptor binding domain (RBD)
- After fusion, S protein releases S1 region & changes structure
- S2 required for viral fusion
-
S1 domain has receptor binding domain (RBD)
Spike glycoprotein binds to _____ _______ _______.
-
lung ACE2 receptors
- Involved in angiotensin II regulation (blood pressure control)
- Protease cuts spike, causing shape change = allows for fusion
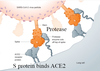
_____ ______ permits the Sars-CoV-2 to enter the cell.
-
Spike decapitation
- Facilitates conformational change
- Allows protein to insert into membrane & pull virion closer
- Nucleocapsid enters cell

What happens after viral RNA enters the cell [Sars-CoV-2]?
- Translation of abt. 12 genes in lung cells
- ER and Golgi form vesicles (where virion assmebly occurs)
- Vesicles w/ new virions fuse w/ cell membrane
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase synthesize (-) RNA
- ER and Golgi form vesicles (where virion assmebly occurs)
- N protein stablize RNA
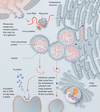
A single cell can produce ____ of virions and lead to cell ___.
-
100s, death
- Tc and NK cells eliminate viral infected cells with perforin (pore-forming cytolytic protein)

What proofreading enzyme(s) does Sars-CoV-2 have?
- Exoribonuclease
- 3’ to 5’ exonuclease
- Reverse and remove errors

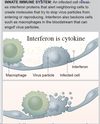
How long does the innate response take? What happens? [Sars-CoV-2]
- 0-3 days
- Neutrophils, macrophages, complement pathway
- Interferon (cytokine) attracts macrophages & NK cells
How long is the adaptive response? What happens? [Sars-CoV-2]
- 6-11 days
- APC activates TH, which activates B cell, which differentiates into memory & effector cells

What is the basis for Pfizer-BioNTech & Moderna vaccines?
Full length mRNA for the S protein
What prevents the pre-fusion to post-fusion structural change of Sars-CoV-2?
Subsitution mutations (K986 - Lysine & V987 - Valine) to proline
Define monoclonal antibodies (Mab)
- Produced in commercial antibodies
- B cells from mouse spleen fused with myeloma cells (cancerous plasma cells)
- Hybridoma cells cultured and produce Mab
- Mab bind to Sars-CoV-2 spike protein
- Block virus attachment/entry
- Administered via IV infusion

COVID-19 mortality rate [World, US, NV as of April 8, 2021]
- World: 2.2%
- US: 1.8%
- NV: 1.7%


