Lecture 8- Aetiology of congenital heart disease Flashcards
pathophysiology basics
- Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated bloods to lungs
- Pulmonary circulation has low resistance
- Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood at systemic blood pressure to aorta
- Each ventricle is morphologically adapted for its task
- Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated bloods to lungs
- pO2 is 67%
- Venous pressure in atrium 4mmHg
- Pressure 25/4 mmHg in the ventricle
- Blood moves from the atria to ventricle due to ventricle diastole and atria systole (contraction)
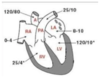
- Pulmonary circulation has low resistance
- pressure is 25/10mmg in pulmonary trunk
- Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood at systemic blood pressure to aorta
- pO2 is 99-100%
- left atria- slightly higher pressure than in right atria- 8-10mmHg
- Left ventricle – 120/10 mmHg
- 120 is the pressure needed to pump around the whole body
- aorta pressure- 120/80mmHg
- Each ventricle is morphologically adapted for its task
Left ventricle has much more muscle
pressure in right atria
0-4 mmHg
pressure in right ventricle
pressure in pulmonary artery
25/10
pressure in left atrium
8-10 mmHg
pressure in left ventricle
120/10 mmHg
pressure in aorta
120/80
there is ……. between either sides of the heart
no mixing
How is blood pumped back to the heart?
- Residual pressure
- Muscle movement
- Valves
Aetiology of congenital HD
- Genetic
- Downs, Turners, Marfan’s
- Polygenic
- Environmental
- Teratogenicity from drugs, alcohol etc
- Maternal infections
- Rubella, toxoplasmosis
Shunts
- Atrial
- Ventricular
- Atrioventricular
- Aorto-pulmonary (ductal)
- Present in foetal life- should close after birth
- Bypass channel from the lungs
- Resistant in the lungs would be too high and damage lungs
Ductus venosus
- by-pass the liver (highly metabolic)
Foramen ovale-
by-pass the right ventricle and lungs
Ductus arteriosus
- by-pass the lungs
classification of congenital heart disease
acyanotic, cyanotic, respiratory cyanosis
Acyanotic (not blue blood)- red
- Left to right shunt (ASD, VSD, PDA)
- Obstructive lesions: aortic stenosis (hypoplasia)
- Pulmonary stenosis (valve, outflow branch)
- Coarctation of the aorta (narrowing) and mitral stenosis
Cyanotic
*
- blue
- Circulating systemic oxygen levels are lower (complex, right to left shunts)
- Tetralogy of fallow (VSD/pulm stenosis)
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage
- Univentricular heart
Respiratory cyanosis
- Asphyxiation
- Pneumonia
Central vs peripheral cynosis
Central cyanosis occurs when the partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) in the systemic circulation is low.
–> Babies have a blue discolouration to their face, mouth and tongue.
Peripheral cyanosis is blue discolouration of the peripheries due to reduced perfusion, e.g. in cold weather, arteries to the fingers and toes constrict














