Lecture 15- Peripheral arterial and venous disease Flashcards
(72 cards)
lower limb venous anatomy- the venous system is divided into
superificial and deep veins
movemetn of blood from superifical to deep veins via
perforating viens with valves

deep veins found
underneath deep fascia with major arteries
x
Superficial veins found
subcutaneous tissue
name the superidical veins of the leg
short and long sapehnous

names the deep veins of the leg
external iliac –> femoral
femoral –> deep femoral or popliteal
popliteal –> anterior tibial/ posterior tibial/ peroneal

what is known as the peripheral heart
calf muscle pump
calf muscle pump
Is the motive force enhancing return of venous blood from the lower extremity to the heart. It causes displacement of venous blood in both vertical and horizontal directions
which are the main muscles which contribute to the calf muscle pump
soleus and gastrocnemois contirbute to pushing the blood against gravity back towards the heart
outline actions of the calf muscle pump
- When the valves are open –>blood pushed through to deep veins via the pressure contracting muscle puts on the veins–> then valves close to prevent retrograde movement
- Perforating valves open again allowing filling from the superficial veins
- Venous pressure in the foot reduced during exercise

Peripheral venous disease
Venous diseases usually occur as people age
a common vein pathology
varicose veins
varicose veins
Tortured, twisted or dilated veins
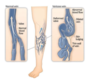
what happens to valves in varicose veins
infective and blood movement is slowed or reversed
which vein is commonly affected by varicose veins
saphenous
In healthy veins
- Normally venous blood from the legs flows upwards through superficial veins which eventually flow into deeper veins
- Blood flow is assisted by valves in veins which allow blood to move up towards the heart and prevent blood from flowing back down
- Ensures venous blood only flows in one direction
In varicose veins
- If veins become dilated due to the weakening of the walls of the vein, the leaflets of the valves are pulled apart
- This lets blood leak back through the valve by the downward pull of gravity (retrograde flow)
- Causes a build-up of blood, increased pressure on the valves upstream of the faulty valve, casing further retrograde flow through overwhelmed valves
- Cycle continues and causes blood to pool in the lower leg, forming varicose veins
causes of varicose veins
Pregnancy
Older age
Obesity
Occupation that involves a lot of standing
Symptoms of varicose veins
- Leg feels heavy
- Tense
- Itchy
- Veins can be seen and look bump
complications of varicose veins
- haemorrhage
- thrombophlebitis
- venous hypertension
Haemorrhage
- Wall of varicose veins are thin and bulge from the skin making them more susceptible to damage through trauma
- Emergency treatment for this is to raise the leg to a level higher than the heart
- Helps venous blood drain from leg and apply pressure to the blood
Thrombophlebitis
Inflammation of a vein caused by formation of a small clot
which do clots form as a result of varicose veins
Clot forms due to stasis of blood within varicose vein