Lecture 13- Heart block Flashcards
(19 cards)
Atrioventricular Heart block
Delay/failure of conduction of impulses from atria to ventricles via AV node and bundle of His.
Causes of heart block:
- Degeneration of electrical conducting system with age (sclerosis and fibrosis)
- Acute MI
- Medications
- Valvular heart disease
types of heart block
first degree AV block
Second degree AV block
Third degree AV block
first degree AV block
Caused by delayed conduction through the AV node resulting in a consistently prolonged interval
features of first degree AV block on ECG
- Slowed without skipped beat (PRI >2s)
- All normal P waves followed by QRS complexes, but PR interval is longer than normal
- Can develop into second or third degree

second degree heart block can be divided into
Mobitz type I
Mobitz type II
Mobitz type I also known as
Wenkenbach
features of second degree Mobitz type I on ECG
PR interval becomes progressively longer until one of the QRS complexes is dropped- PR interval then returns to normal and repeats the cycle
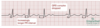
feautrs of second degree mobitz type II on ECG
PR interval is normal and constant, but occasionally the P wave is not conducted so a QRS complex is dropped.

is mobitz type I or II more dangerous
II
This type of second degree heart block is dangerous as it has a higher chance of progression to third degree heart block (complete)
No prior PR changes
Ventricular rhythm is irregular
Third degree AV block
is when there is no impulse transmission between the atria and ventricles and therefore they work independently – no relationships between the P wave and QRS.
in third degree AV block the ……. pacemaker takes over (escape rhythm)
Ventricular
ventricular pacemaker rate
40bpm
atrial rate approx
100bmp
no evidence that any of the atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles
escape rhythms occur when
the conduction system is blocked and so the ventricles have to manage themselves and become their own pacemaker.
how does third degree AV block appear on ECG
QRS complex becomes wider because the impulse isn’t travelling via the His-Purkinje system.

why is third degree heart block so dangerous
ventricular pacemaker is too slow and the blood pressure cannot be maintained so a proper pacemaker is urgently required for patients with third degree heart block.
bundle heart block
Delayed conduction within the bundle branches
Can be:
Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
Left bundle branch block (LBBB)
how does bundle branch block appear on ECG
Wide QRS complex (>3 small squares) because ventricular depolarisation takes long



