LE Posterior Thigh Flashcards
Posterior Compartment of Thigh
- separated into anterior, medial and posterior compartments by the intermuscular septa
- POSTERIOR Thigh mm:
Function: extension at hip and flexion at knee
Includes: hamstrings

Hamstring Muscles
- Semitendinosis
- Semimembranosis
- Biceps Femoris
Semitendinosis
From: the ischial tuberosity
To: the medial surface of superior tibia (pes ancerinus)
*medial side of thigh, more superficial to semimembranosis
AXN:
◦Extends the hip
◦Flexes knee
◦Medially rotates leg
◦Extends trunk if closed kinematic chain
Innervation: Tibial portion of sciatic N. (L5, S1, S2

Semimembranosis

From: the ischial tuberosity
To: the posterior part of medial tibial condyle & a reflected attachment to the oblique popliteal ligament (Semimembranosus and oblique popliteal ligament = remember “SMOP”)
*More medial side of thigh, deeper to semitendinosus
AXN:
◦Extends the hip
◦Flexes knee
◦Medially rotates leg
◦Extends trunk if closed kinematic chain
Innervation: Tibial portion of sciatic N. (L5, S1, S2)
* Semimembranous embeds with the joint capsule/MCL of the medial knee and the medial meniscus attaches to theses structures. THEREFORE, is the posterior medial aspect of the medial meniscus is repaired during surgery, active knee flexion strengthening should be deferred 2/2 stress to the structure. (look at front pic)

Biceps Femoris
From:long head - the ischial tuberosity
short head - the linea aspera & lateral supracondylar line of the femur (post)
To: Long and short heads insert distally to lateral head of fibula
AXN:
◦Flexes knee
◦Laterally rotate leg
◦Extends Hip (long head only)
Innervation: Long head - Tibial portion of sciatic N. (L5, S1, S2)
Short head- Common (fibular) peroneal portion of sciatic N. (L5, S1, S2)

SGT acronym
-Semitendinosus–>gracilis–>sartorius tendons (lateral to medial order)
Attach onto Pes anserine (duck foot)

Popliteal Fossa
- diamond shaped depression in post aspect knee
- superiorly bounded by the hamstrings
- inferiorly bounded by the 2 heads of the gastrocnemius & plantaris muscles
- posteriorly by skin & fascia
- anteriorly by popliteal surface of femur, oblique popliteal ligament, popliteal fascia over popliteus

Plantaris
From: inferior end of lateral supracondylar line of femur & oblique popliteal ligament
To: posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
*tendon of plantaris, often mistaken for “fools nerve” or tibial nerve

Popliteal Fossa Contents
- Lesser Saphenous Vein (superficial)
- Popliteal Arteries & Veins (deeper)
- Tibial & Common Peroneal Nerves (Med/Lat Sural Nerves; Sural Nerve)
- Posterior femoral cutaneous n. – inn. skin overlying fossa, exits in gluteal region underneath piriformis
- Popliteal Lymph Nodes and lymphatic vessels

Popliteal artery and vein
When femoral artery passes through the adductor hiatus changes to the popliteal artery

Blood Supply LE
*print out from txtbk
- Femoral Artery - supplies anterior & anteromedial surface of thigh
- Profunda Femoral Artery (Deep Femoral a) - arises from femoral a. near inguinal ligament; gives rise to perforating branches through add magnus m.(4) to supply posterior, lateral, & anterior aspect of thigh
- Medial Femoral Circumflex Artery - usually arises from profunda femoral a.; supplies head & neck of femur; ascending(back to glute)/transverse(back to femur)/descending (to knee) branches
- Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery - usually arises from profunda femoral a; ascending to gluteal region; transverse around femur; descending to knee

Cruciate Anastamosis of Hip
*Includes:
- Transverse & ascending branch of lateral femoral circumflex A.
- *Medial Femoral circumflex A.(one surgeons are most concerned with)
- Inferior Gluteal A. (see posteriorly)
- First Perforating Artery from Profunda Femoral A. (see posteriorly)
*Medical circumflex goes between iliopsoas and pectineus, see it splits, circles around and supplies femoral head/neck from post aspect
*Lateral circumflex aa splits into 1) Ascending (hip/glute), 2) transverse(femur) and 3) descending(Knee) branches of the circumflex femoral artery

Retinacular Arteries
- arising from medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries are the main supply to the hip joint
- Retinacular arteries from the medial circumflex femoral aa are most abundant bringing more blood to the head and neck of the femur. Ascending artery off the lateral circumflex aa also gives rise to retinacular aa.
- The artery to the head of the femur from the obturator artery travels through the ligament of the head
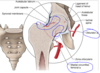
Blood supply interrupted with fracture of neck
- these areas are subject to infarction and avascular necrosis;
- three such regions are head of femur, body of talus, & scaphoid;
- they have the common feature that a very large portion of their total surface is covered with articular cartilage through which vessels do not penetrate;
- blood supply for these bones enters through very restricted spaces, & there is limited collateral circulation;
- when principal route of the circulation to these bones is interrupted by trauma or disease, the collateral circulation is inadequate

Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head
- Avascular necrosis (aka: aseptic necrosis, osteonecrosis) is a condition that results from poor blood supply to an area of bone causing bone death.
- Inherent poor blood supply may lead to ischemia and necrosis of bone tissue causing weakening of the bone with eventual collapse.
- Avascular necrosis can be caused by trauma and damage to the blood vessels that supply bone its oxygen.
Other risk factors for avascular necrosis:
◦ systemic steroids, sickle cell anemia, alcohol abuse, RT (radiation therapy)
- Femur at high risk b/c it is an end organ and lined with articular cartilage where arteries can not penetrate
- Arterial supply restricted to small space
- Requires a hemiarthroplasty or THR if in adult
◦But can vary depending on the severity of the degradation of the femoral head
*bone will disintegrate and collapse

Legg-Claves Perthes Disease
•Child Avascular Necrosis
•
- Unknown origin or congenital
- 1/1200 children: Boys> girls
- Age: 4-7*
- Treatment: historically casting/bracing/fixator was used but evidence suggests outcomes no different as compared to no treatment, often surgical repair.
- Pain in hip or knee (ALWAYS ON BOARD EXAM)
- Flat hip joint, leads to pain and discomfort

Slipped Capital Femoral Ephysis (SCFE)
- Epiphysis (growth plate) of the femoral head may slip away from the femoral neck due to a weakened epiphyseal plate
- Causes: acute trauma or repetitive microtrauma with shear stress; gradual slippage with associated hip pain that may refer to the knee; antalgic gait
- SCFE usually occurs in: EMERGENCY
◦children between 10- 16 years old*
◦Overweight
◦Boys > girls
◦African Americans > Caucasian
- Classified 2 types: stable and unstable (unstable-unable to weight bear, stable-can walk with crutches, 90%)
- An emergency situation
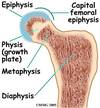
SCFE Treatment
-Common treatment: “in-situ fixation.”
◦the bone is held in place with a single central screw
◦keeps the femur from slipping and closes the growth plate
◦Good results with few complications
◦Prophylactic bilateral surgical intervention - sometimes
Conservative treatment (NWB) ~ poorer outcomes
*slippage disrupts growth bc disrupts growth plate
*orthopeds will usually choose surgery, if not will go to PT for conservative measures

SCFE vs Perthes

Great Saphenous Vein
- Ascends anterior to the medial malleolus
- Passes posterior to the medial condyle of the femur
- Passes through saphenous opening/fossa ovalis
- Empties into femoral vein
*blood flow is upward towards hip

Blood supply in popliteal fossa
Popliteal Artery - continuation of femoral artery; ends at the superior border of the popliteus mm
Branches of Popliteal A. – Profuse knee jt, Genicular Arteries (x5): superomedial, superolateral, middle, inferomedial, inferolateral
Genicular Arteries supply articular capsule & ligaments of knee
Genicular Anastomosis:
- includes all genicular arteries (x5) &
- descending genicular branch of femoral a. (anteriorly)
- descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex a.
- recurrent branch of ant tibial a.
Popliteal Artery - divides into ant and post tibial arteries

Genicular Anastomosis
- genicular arteries (x5)
- Middle genicular aa not shown - descending genicular branch of femoral a. (anteriorly)
- descending br. of lat fem circumflex a.
- recurrent branch of anterior tibial a.

Bursae
Bursa: located in areas that are subject to friction;
- membranous sacs lined with synovial membrane
- decreases friction between 2 pieces of tissue, very seldomly are there isolated bursa problems
*rarely is the bursa a primary cause of a problem
- Ischial - separates the glut max from ischial tuberosity (post)
- Iliopsoas - separates joint from muscle (ant)
- Trochanteric - separate glut max from greater trochanter, bursae covers to reduce friction on surrounding structures like IT band
- Gluteofemoral - separates the iliotibial band from superior portion of vastus lateralis



