LE Anterior Thigh Flashcards
Anterior Thigh Muscles
- Function – hip flexion & extensors of knee
- Includes -pectineus, iliopsoas, tensor fascia lata (TFL), sartorius, quadriceps femoris (rectus femoris [superifical] vastus lateralis, vastus medius, vastus intermedius[deepest])

Pectineus
FROM: superior ramus of pubis
TO: pectineal line of femur (posterior), inferior to lesser trochanter
AXN: adducts & flexes hip; assists with internal rotation of thigh based on where it inserts on femur
INNERVATION: femoral nerve (L2, L3) (like majority of ant ms group); sometimes branch from obturator n
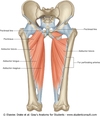
Psoas Major
FROM: lateral aspect of T12-L5 and discs in between, & transverse processes of all lumbar vertebrae
TO: lesser trochanter of the femur along with iliacus
ACTION: flexes hip & stabilizes the hip joint along with the psoas minor & iliacus
INNERVATION: L1, L2, L3 ventral rami
*Note: psoas major and iliacus “merge” to insert on the lesser trochanter. Commonly called the iliopsoas muscle*

Iliopsoas
- More medial and deep to sartorius
- Iliopsoas is main activator here (when doing double leg lift and see arching in back IF rectus abdominus is weak, iliopsoas is the only thing doing the work here so creates arch in back bc wants to flex the hip)
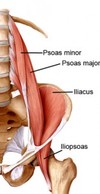
Psoas Minor
FROM: lateral aspect of T12-L1 and disc in between
TO: iliopectineal eminence
AXN: acts with psoas major & iliacus to flex the hip & stabilize the joint
INNERVATION: L1, L2 ventral rami

Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL)
FROM: ASIS and anterior part of iliac crest
TO: iliotibial tract/band (w/ fibers of glut max) to the lateral tibial condyle at Gerdy’s tubercle
AXN: abducts, medially rotates, and flexes hip
- helps support the femur on the tibia when standing, but has no direct action on the leg
- Some references state TFL can assist with knee flexion once the knee is flexed > 30degrees (secondary)
- Steadying the trunk on the thigh
INNERVATION: Superior gluteal n. (L4, L5)

Hip Abduction (TFL vs glute bias)
- In picture attached, are abd hip, IR, ext which biases the glute min and ant fibers glute med
- If flexed the hip and abducted, would bias the TFL

Sartorius
*Two joint muscle, longest muscle in the body
FROM: ASIS & superior part of the notch inferior to it
TO: superior part of medial surface of tibia (is superficial, covers the tendons of gracilis & semitendinosus; pes anserine. Recall: “SGT”)
AXN: flexes, abducts and ER the hip; flexes the knee joint; medial rotation of tibia on femur with knee flexion
•Considered “secondary” muscle to assist all other muscles with helping to cross legs
“tailor muscle”
INNERVATION: Femoral n. (L2, L3)

Femoral Triangle Borders
•Triangular depression inferior to the inguinal ligament
Borders:
- Superiorly - inguinal ligament (triangular base)
- Medially - adductor longus mm
- Laterally - Sartorius mm
- Muscular floor - iliopsoas & pectineus mm
- Roof - (Deep to superficial) fascia lata & cribiform fascia, subcutaneous tissue, skin

Saphenous Opening
– fibrofatty tissue localized membranous layer of subcutaneous tissue that spreads over the saphenous opening to CLOSE IT
- The portion of fascia covering the fossa ovalis/saphenous opening in the thigh is perforated by the great saphenous vein and by numerous blood and lymphatic vessels, hence it has been termed the cribrosa fascia (Hesselbach’s fascia or fascia cribrosa )
- the openings for these vessels having been likened to the holes in a sieve (A sieve is a kitchen utensil consisting of plastic mesh in a frame used for straining solids from liquids)
*in picture, saphenous opening is opening of fascia lata where saphenous vein exits, covered by the cribiform fascia that is thinner and looser than the fascia lata (deep fascia)
*Falciform margin=most lateral portion of the saphenous opening

Femoral Triangle Contents
- Acronym: NAVEL (from lateral to medial)
- Nerve/artery/vein/empty space(femoral canal)/lymph
- Femoral sheath(thick piece of tissue) – goes around femoral artery, vein and canal, NOT FEMORAL NERVE
•3 Compartments within sheath: (femoral canal)
•Lateral: femoral artery
•Intermediate: femoral vein
•Medial: femoral canal
•Purpose: sheath allows for femoral aa and vv to glide and expand deep to the to the inguinal lig with hip motion, so not compressed when move into deep knee or hip motions
- Femoral canal - most medial compartment of sheath
- Contains loose connective tissue, fat and lymph vessels
- Femoral ring- proximal and weak opening into canal
- *CLINICAL:** - Femoral aa palpation and/or pressure
- Trigger Point Dry Needling, dont want to prick artery or nerve
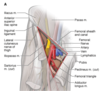
Femoral Hernia
- Femoral Ring is a weak part of the abdominal wall.
- commonly the site of a femoral hernia:a protrusion of abdominal viscera (often a loop of the small intestine).
- The intestine enters the femoral ring and then moves down into the femoral canal.
Symptoms/Signs: bulging mass within triangle, tender to palpation.
- Occurs predominantly in females given wider pelvis and most often occurs post-partum due to enlargement of the femoral ring over time from the pregnancy
- don’t usually need surgery unless theres strangulation

Quadriceps Femoris
- Major bulk of anterior thigh
- One of the largest & most powerful muscles
- The extensor of the leg
- Four heads of which one is a two joint muscle
- 3 superficial and 1 deep (vastus intermedius deep to rectus femoris)

Rectus Femoris
FROM: the AIIS and ilium superior to the acetabulum
-Two joint muscle
TO: the base of the patella via the quadriceps tendon & by the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity
AXN: all extend the leg at the knee jt
*Rectus Femoris also flexes the hip
INNERvATION:
- Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4)
- Patellar Tendon Reflex - integrity check of L2-4

Vastus Lateralis
FROM: from the greater trochanter and lateral lip of linea aspera of femur
TO: the base of the patella via the quadriceps tendon & by the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity
AXN: all extend the leg at the knee jt
INNERvATION:
- Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4)
- Patellar Tendon Reflex - integrity check of L2-4
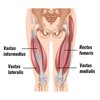
Vastus Medialis
FROM: from the intertrochanteric line & medial lip of linea aspera of femur
TO: the base of the patella via the quadriceps tendon & by the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity
AXN: all extend the leg at the knee jt
INNERvATION:
- Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4)
- Patellar Tendon Reflex - integrity check of L2-4
STUDIES: Conclusion: “There was, however, insufficient good quality evidence to state whether the VM is composed of two separate components, the proximal VML(vastus medialis) and the distal VMO(vastus medialis obliquus).”

Vastus Intermedius
FROM: from the anterior and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur
TO: the base of the patella via the quadriceps tendon & by the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity
AXN: all extend the leg at the knee jt
*DEEP TO RECTUS FEMORIS
INNERvATION:
- Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4)
- Patellar Tendon Reflex - integrity check of L2-4

Medial and Lateral Patellar Retinaculi
-Tendinous expansions of the vastus medialis and lateralis which attach to the margins of the patella

DTR
-patellar, achilles, hamstring
-How would you identify the LE DTR vertebral levels?
Medial Thigh Muscles
- Consists of adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, & gracilis
- Innervated heavily by Obturator Nerve and ventral rami (L2-4); however, add magnus receives dual innervation

Adductor Canal
- aka: subsartorial canal
- Middle 1/3 of medial thigh
- Contains the femoral A & V, saphenous n. (sensory) & usually N. to vastus medialis
- Bounded laterally by vastus medialis; medially by adductor longus and add magnus; superficially covered by sartorius
- Adductor hiatus – distal end of canal
*The saphenous nerve is a sensory branch of the femoral nerve, and supplies sensation to the anteromedial, medial and posteromedial surface of the leg.
-The nerve passes through the adductor canal, and gives off an infrapatellar branch.

Saphenous Nerve
sensory innervation to the:
- Anteromedial
- Medial, and
- Posteriomedial
surface of the leg
- branch off of the femoral nerve
- Passes through adductor canal and then supplies leg, gives off the infrapatellar branch

Adductor Longus
•From: the body of the pubis, inferior to pubic crest
•To: the middle third of linea aspera of femur
•AXN: adduction of hip; assists with hip/thigh flexion
•Innervation: Anterior branch obturator nerve; L2, L3, L4

Adductor Brevis
FROM: body & inferior ramus of pubis
TO: the pectineal line & proximal part of linea aspera of femur
*deep to adductor longus
*anterior obturator nerve runs on top of this between longus and brevis
AXN: Adduction of hip/thigh; assists with hip/thigh flexion
INNERVATION: Anterior branch obturator nerve; L2, L3, L4

Adductor Magnus- Adductor Portion
•Adductor portion
FROM: inferior ramus of pubis; ramus of ischium (more horiz/oblique fibers)
TO: gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera, medial supracondylar line
AXN: adducts hip/thigh, flexes hip/thigh
*Posterior branch of obturator n. runs on top, between adductor brevis and adductor magnus*
INNERVATION:
- Adductor portion: posterior branch obturator nerve (L2,3,4)
- Hamstring Portion: Tibial portion Sciatic Nerve L4

Adductor Magnus- Hamstring Portion
FROM: ischial tuberosity (more vertical fibers)
TO: adductor tubercle of femur
AXN: adducts hip/thigh, extends hip/thigh
*Posterior branch of obturator n. runs on top, between adductor brevis and adductor magnus*
INNERVATION:
•Hamstring Portion: Tibial portion Sciatic Nerve L4

Gracilis
FROM: the body & inferior ramus of pubis
•TO: the superior part of medial surface of tibia; (SGT, pes anserinus)
AXN: adducts hip/thigh; flexes knee; assists with medial rotation of leg
INNERVATION: Anterior branch obturator N. (L2,3)



