LE Posterior Leg Flashcards
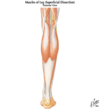
Posterior Compartment of Leg
- Largest of the 3 leg compartments
- Calf muscles are divided into superficial & deep groups by the transverse intermuscular septum
- Innervated by the tibial nerve (L4-S3)
- Blood supply - posterior tibial artery/vein
- Superficial Group - Gastrocnemius, Soleus, & Plantaris muscles
- Deep Group - Popliteus, FDL, FHL, & Tibialis Posterior muscles
**gastroc/soleus on top of these deep ms in pic**

Gastrocnemius
FROM: proximal (2 heads); biarticular
LATERAL HEAD: from the lateral aspect of the lateral condyle of femur
MEDIAL HEAD: from the popliteal surface of the femur, superior to the medial condyle
TO: the posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon(pretty wide)
AXN: PF ankle; flex the knee joint. Eversion/inversion almost in neutral ankle position (depends on start position how it functions)
*IS A 2 JOINT MS*
INNERVATION: Tibial Nerve (L4-S3)
Triceps Surae – gastroc and soleus combined; have a common calcaneal tendon (aka Achilles)
*superficial group
Soleus
FROM: post aspect head of fibula, sup 1/4 of post surface of fibula, and soleal line of tibia & medial border of tibia
*below the knee!!!*
TO: the post surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
INNERVATION: Tibial n. (S1, S2)
AXN: PF ankle (regardless of knee position), inversion, no influence on knee
**Proximal attachment is below knee; therefore, no knee action influence** so when want to stretch it, must isolate from gastroc by bending knee
*superficial group

Plantaris
- “Fools Nerve”
FROM: inferior end of lateral supracondylar line of femur & oblique popliteal ligament
TO: posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
AXN: weak assist in PF of ankle, & weak flexion of knee, very small influence
INNERVATION: Tibial N. (S1, S2)
*is 2 joint ms: knee and ankle jts*
-Often absent in 10-15%; is used commonly for grafting during reconstructive surgery (thats how insignificant it is)
*superficial group, superficial to soleus, deep to gastroc!*

Popliteus
- thin, triangular muscle forms the inferior part of floor of popliteal fossa
FROM: lateral surface of lateral condyle of femur and lateral meniscus
TO: posterior surface of tibia, superior to soleal line
AXN: weakly flexes the knee; with foot free off ground can help with IR tibia on femur (unlocks knee)
INNERVATION: Tibial N. (L4,5, S1)
*1 jt muscle*
*deep group*

Flexor Digitorum Longus (FDL)
FROM: medial part of the posterior surface of tibia, inferior to soleal line
TO: base of distal phalanges of lateral 4 toes
AXN: flexes lateral 4 digits (digits 2-5); PF ankle, inversion of foot; supports longitudinal arch of foot
INNERVATION: Tibial N. (S2, S3)
- Intrinsic foot muscles attach(extrinsic (crosses joints) vs intrinsic (starts and stops in same area):
- Quadratus plantae inserts on FDL
- Lumbricales arise from it

Flexor Hallicus Longus (FHL)
FROM: inferior 2/3 of post surface of fibula, & inf part of interosseous membrane
TO: plantar surface, base of distal phalanx of great toe
AXN: flexes great toe; PF ankle; inversion of foot; supports medial long arch
-Powerful “push-off” muscle during walking
INNERVATION: Tibial N. (S2, S3)
-tendon runs between 2 sesamoid bones in the tendons of the flexor hallicus brevis; sesamoid bones protect FHL tendon from repeated pressure of weight bearing at the 1st MT
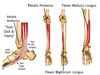
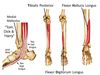
Tibialis Posterior
FROM: interosseous membrane, post surface of tibia inferior to soleal line, & post surface of fibula
TO: tuberosity of navicular, all cuneiform bones, sustentaculum tali, cuboid, & base of 2nd, 3rd, & 4th MT
*All of the tarsal bones except the talus
AXN: main invertor of foot, PF of ankle; resists the collapse of the arch main supporter
INNERVATION: Tibial Nerve (L4, L5)
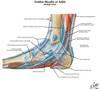
Posterior medial mallolus tendons
*Ant to Post at level of medial malleolus*
Tom - tibialis posterior
Dick – FDL
A Very Naughty – Posterior tibial a/v, tibial n
Harry - FHL
*anterior to malleolus on medial side is Ant tib and EHL (ant tib is more medial)*
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
FROM: the floor of the sinus tarsi of the calcaneous and the ext retinaculum
TO: Divides to the lateral 4 toes
AXN:: aids EDL in extending 4 medial toes at the MTP joints
INNERVATION: Deep peroneal n.
*on dorsum of foot*
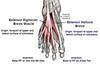
Extensor Hallicus Brevis
FROM (Same as EDB): the floor of the sinus tarsi of the calcaneous and the ext retinaculum
TO: dorsal aspect of base of prox phalanx of great toe/hallux
AXN: aids the EHL in extending great toe at the MTP(bc of insertion)
INNERVATION: Deep peroneal n.
*dorsum of foot*

Pedal Pulse
- Just distal to med/lat malleoli
- Between 1st and 2nd metatarsal
*anterior tibial artery (ends as dorsalis pedis artery)
-travels with the deep peroneal n. which becomes cutaneous and provides sensation to webspace between great toe and 2nd toe

Plantar fascia
- Deep fascia of the plantar foot
- Has a thick central part (plantar aponeurosis) and weaker medial/lateral part (entire foot, everywhere arrows are going)
- Role of plantar fascia:
- Holds foot together
- Protects plantar surface from injury
- Supports longitudinal arches of foot
- Plantar Aponeurosis- fascia gets thick in the center
FROM: calcaneous
TO: divides into five bands and becomes continuous with tendon sheath of each toe

Plantar Layer #1
ABD Sammich

•Abductor Hallucis - med plantar n.
- Flexor Digitorum Brevis - med plantar n.
- Abductor Digiti Minimi - lateral plantar n.
Plantar Layer #2
Quadratus Plantae -Lateral plantar n.
AXN: Assists in flexing lateral 4 digits
(4) Lumbricals – axn same as hand (flex MTP, ext IPs)
- 1st lumbrical* – medial plantar n.
- lateral 3* - lateral plantar n.
*Attach to the FDL and FHL*

Medial vs Lateral Plantar n.
Medial Plantar NN
- Larger and more anterior of two terminal branches of the tibial nerve
**Digits 1,2,3, half of 4th is medial plantar nerve**
Lateral Plantar NN
- Smaller and more posterior of the two terminal branches of the tibial nerve
*Border between med/lat plantar nn is along the 4th metatarsal*

Quadtraus PLantae and lumbrical attachments
Quadratus Plantae and Lumbricals insert onto FHL tendon and FDL tendons

Layer # 3
Flexor Hallucis Brevis - med plantar n. (2 heads)
Adductor Hallucis - lat plantar n. (2 heads)
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis - lat plantar n.

Plantar Layer # 4-Dorsal interossei
Four dorsal Interossei - lat plantar n.

Plantar Layer #4-Plantar Interossei
Three Plantar Interossei - lat plantar n.

Nero Deficits Review of leg
Common Peroneal Nerve (L4-S2) at the level of the knee:
- Denervation of: Deep Peroneal N
- Muscles: Tibialis Ant., EHL, EDL, Peroneus Tertius, Ext Dig Brevis & Ext Hallicus Brevis
- Sensory Loss between the 1st & 2nd toes, ankle jt. & tarsal jts.
- Denervation of Superficial Peroneal N
- Muscles: Peroneus Longus, Peroneus Brevis
- Sensory Loss: Lateral & anterior side of lower leg & Dorsum of foot except between 1st 2 toes and lateral side of foot
Loss v. Weakness:
Loss of ankle DF
Loss of ankle eversion
Weakness of ankle inversion
Weakness of ankle PF
Loss of toe extension
Loss of sensation dorsum of foot and lateral aspect of shank
Cutaneous supply of leg
- Saphenous Nerve - arises from femoral N.
- Superficial Peroneal Nerve – arises from common peroneal
- Deep Peroneal nerve – arises from common peroneal
- Lateral Sural Nerve - arises from Common Peroneal N.
- Medial Sural Nerve - arises from Tibial N.
- Sural Nerve - Lat & Med Sural nerves combine to form this (sometimes)
- Calcaneal Branches of the Tibial and Sural N - arise from Tibial & Sural Nerves
- Med/Lat Plantar Nerves - arise from Tibial N.


