LE anterior leg Flashcards
Tibia
- Supports full body weight = super strong, 90% of body weight
- Articulates with femoral condyles, talus & fibula
- Medial and lateral tibial condyles
- Tibial plateau-superior surface of tibia
- Lateral tibial condyle-facet for articulation with fibula
- Surfaces :medial, lateral (interosseous membrane), and posterior
*print and memorize landmarks
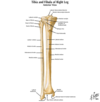
Tibia Anterior view
- Anterior border (crest) - tibial tuberosity-distal attachment for patellar ligament
- Interosseous border - lateral side
- Gerdy’s Tubercle - insertion IT band on proximal lateral side of tibia
- Tibial tuberosity - distal attachment for patella ligament (bone to bone)
- Distal end - facets for talus and fibula
- Medial malleolus - facet on its lateral border for articulation with talus
- Distal articulating surface: AKA “plafond”
- Normal tibial torsion at distal end-externally rotated (toe-out position in standing; normally 20◦ - 40◦)
Tibia is rotated in ER direction, 20-40 degs of rotation
-twisting motion of towel anteriorly just like femoral anteversion

Tibia posterior view
- Soleal line - posterior aspect
- “Third malleolus” - posterior margin of articular surface of the distal tibia

Fibula
- Only transmits small percentage of body weight
- Function is for attachment of muscle
- Fractures with directs forces
- Provides lateral stability of ankle joint (assists in stabilizing talus), makes up lateral melleolus
- Head - proximal end
- Articulates with proximal/lateral portion of tibia
- Apex - pointed end of head
- Lateral malleolus - more prominent; directed more posteriorly and ends 1 cm more distal than the medial malleolus
- articulates with lateral aspect of talus to make up some of ankle joint
- Malleolus = singular
- Malleoli = plural

Bimalleolar fracture
- Bi malleolar fracture (thru malleolus itself)
- Need ORIF when fracture, also just use general screws

Trimalleolar fracture
- involves the lateral malleolus, medial malleolus, and the distal posterior aspect of the tibia (posterior malleolus).
- usually caused by inversion sprain
- Often includes:
- Dislocation with ligamentous injury
- Disruption to the tib-fib syndesmosis; separation
- Treatment: surgical ORIF
-May use hardware across the distal tibfib jt. But may limit the moblity of the distal tib fib jt.

Proximal Tibiofibular jt
- Plane shaped, synovial joint between the slightly convex facet on the head of fibula and slightly concave facet on the lateral condyle of the tibia
- Surrounded by a joint capsule
- Supported by anterior and posterior ligaments to the head of the fibula
- Movements – small amounts
- Superior and inferior sliding of the fibula & fibular rotation during DF/PF of ankle joint, respectively
- ER of fibula during DF
- IR of fibula during PF

Distal Tibiofibular jt
- Syndesmosis (fibrous joint, interosseous membrane) between the concave facet of the tibia and the convex facet of fibula
- Tibia and fibula separated by fibroadipose tissue
- No joint capsule
- Primary support: interosseous ligament (extension of interosseous membrane where gets really thick at the bottom of interosseous membrane)
- Key joint that makes up the talocrual joint (ankle jt)
-If have disloaction then have instability in ankle jt

Additional support in tib fib joint
Additional support in the area:
Ligaments - restrict motion at the distal tib-fib joints & assists in maintaining a stable ankle mortise
- Anterior tib-fib ligament
- Posterior tib-fib ligament
- Medial collateral (aka deltoid) ligament: if ruptured will have lots of instability
Interosseous membrane - supports both superior and inferior tib-fib articulations

Mortise joint
- comprised of distal tib fib articulation
- Mortise is the rectangular hole (distal tib-fib)
- Talus is what inserts into it

Distal Tibi-Fib fracture
- Second most common fracture in body
- Usually result of a sprained ankle… avulsion fracture or from a shear force on the talus along the surface of the tibia and fibula
- Comminuted fracture: (bones held within skin)
- Compound fracture: (bones break through skin)
- Avulsion fracture: occurs when a stretched ligament or tendon applies a tensile force on the bone causing it to fail.
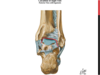
Talus
- Distal articulating surface of ankle joint
- Ankle = Talocrural jt
- Body - 3 articular surfaces: large lat facet, smaller medial facet, trochlear facet (superior)
- wider anteriorly than posteriorly
- Trochlear surface - large convexity with a central groove at an angle
- Talus articulates with fibula, calcaneus, and navicular bone
**Has no muscular attachments
- Talus - rests medially on sustentaculum tali ( part of calcaneus)-bony shelf that supports talus
Talocrural joint (ankle)
- Hinge joint; synovial; 1 DOF; 2 directions of motion including PF/DF
- Articulation between:
- the convex talus and the concave distal tibia, and
- the convex talus and concave distal fibula
- Proximal articular surface (tib-fib) resembles an adjustable “mortise” joint
- Closed pack position(maximum congruency of the articular surfaces and joint stability is derived from the alignment of bones aka most stability) = full DF
**Despite its role in weight bearing, the ankle joint rarely develops OA spontaneously… however if there is a trauma that alters alignment, jt degenerative changes almost always follow
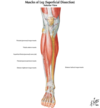
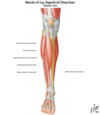
Anterior Compartment of the leg
- Located anterior to the interosseous membrane
- Collectively called the dorsiflexors or extensor compartment(tibialis ant, ext digitorum longus, peroneous tertis, extensor hallucis muscle)
Four muscles
- Tibialis Anterior
- Extensor Digitorum Longus (EDL)
- Extensor Hallicus Longus (EHL)
- Peroneus Tertius (Fibularis)
Innervation - Deep Peroneal (fibular) Nerve
Tibialis Anterior
FROM: lat condyle of tibia & sup half of lat surface of tibia & interosseous membrane
TO: medial & inferior surface of medial cuneiform & base of 1st MT
AXN: dorsiflexor of ankle and weak invertor of foot
INNERVATION: deep peroneal n. (L4,5)

Extensor Hallicis Longus (EHL)
FROM: middle part of anterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane
TO: dorsal aspect of base of distal phalanx of great toe
AXN: extends great toe, DF ankle, invertor of foot
Innervation: deep peroneal n (L4,L5,S1) – but can be variable
*deep to EDL and tibialis anterior*

Extensor Digitorum Longus (EDL)
FROM: lateral condyle of tibia and superior 3/4 of medial surface of fibula and interosseous membrane
TO: middle and distal phalanges of lateral 4 toes
AXN: dorsiflexes ankle, extends lateral 4 digits, weak eversion of foot
INNERVATION: deep peroneal n. (L4,5, S1)

Peroneus Tertius
FROM: inferior 1/3 of anterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane
TO: dorsum of base of 5th MT
AXN: DF ankle, assists in eversion of foot
INNERVATION: deep peroneal n. (L4-5, S1)
**Lateral –> medial= peroneus longus, peroneus brevis, peroneus tertius, EDL, EHL, tib ant**
Extensor Retinaculum
Superior extensor retinaculum
- Strong band of deep fascia, connecting the fibula to the tibia, proximal to the malleoli
- Binds down the muscles in the anterior compartment, prevents them from bowstringing during DF
Inferior extensor retinaculum
- Y shaped band of deep fascia, attaches laterally to the anterosuperior surface of the calcaneus
- Forms a strong loop around the tendons of the peroneus tertius and EDL
Compartment Syndrome
- pathology of leg
- septa dividing leg into 3 fascial compartments are very strong and then all 3 surrounded by crural fascia; trauma to the leg results in edema, hemorrhage or inflammation will cause compression of structures in that compartment; hence, a fasciotomy may be performed to reduce pressure
Deep Peroneal Nerve entrapment
- excessive use of muscles supplied by deep peroneal n.(tib ant, EDL, EHL, perneus tertius) resulting in muscle injury and edema in anterior compartment; pain dorsum between first 2 toes web space
Anterior Tibialis Tendinopathy
- Aka shin splints
- edema & pain in distal 2/3 of tibia resulting from repetitive microtrauma of tib anterior ms. and small tears in the periosteum of tibia
Superficial nerves of ant compartment
**If a patient c/o 1st web numbness, think compartment syndrome
- Deep fib nn is often influenced first

Lateral Compartment of leg
- Bounded by the lateral surface of the fibula, the ant & post intermuscular septa, & crural fascia
- Muscles include: peroneus (fibularis) longus and peroneus (fibularis) brevis
- Nerves include: superficial peroneal nerve (pops out between peroneus longus and brevis)

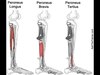
Peroneus Longus
FROM: the head & superior 2/3 of lateral surface of fibula
TO: the base of the 1st MT and medial cuneiform
- Enters a groove in the cuboid bone; crosses the foot obliquely (underneath)
- More superficial than brevis; shares a fascial compartment with brevis
AXN: eversion of foot; PF of ankle; depresses the base of the 1st MT bc of insertion
INNERAVTION: superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, & S2)

Peroneus Brevis
FROM: inf 2/3 of the lat surface of fibula
TO: dorsal surface of tuberosity on lat side of base of 5th MT
AXN: eversion of foot; weak PF of ankle
INNERVATION: Superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, & S2)



