LE Hip Flashcards
Superficial fascia of lower limb
•Superficial Fascia (aka subcutaneous fascia)
- Lies deep to the skin
- Comprised of a loose connective tissue
- Contains fat, cutaneous nerves, superficial veins (greater saphenous v. from ant of spine to foot), & lymphatics
- Continuous with the fascia of the inferior, anterolateral abdominal wall & buttocks

Deep Fascia of lower limb
-Deep Fascia (“Fascia Lata”)
Definition: dense layer of connective tissue between the subcutaneous tissue and the muscles (just deep to superficial fascia)
- Non-elastic! Right over muscles
- Especially strong in LE
- Encircles limb like a stocking
- Prevents bulging of muscles during contraction making more efficient
- Continuous with the deep fascia of the leg (transitions into this crural fascia)
*This is the fascia that becomes really thick and lives on the outside of muscles
- you cant stretch this type of fascia, if theres an internal injury to any structure (vessel, ms, bone fracture) and theres swelling within…..swelling blows up and occupies space within this fixed space(tissue that doesn’t expand) will start compressing ns, vesselsàcuts off blood supply
- everything distal to that area of compression will start dying within minutes of not having blood supply
Surgical Fasciotomy
- Treats Compartment Syndrome, when swelling in that tight fascia lata (deep fascia) occurs
- common in high impact trauma
- urgent medical situation!!
*surgeons put needle in and measure pressure to see how bad this swelling is, if reaches certain point need to do fasciotomy and cut through skin, superficial, and deep fascia to relieve some pressure
*after fasciotomy, which should happen within hours of injury, there will be more swelling so this needs to be allowed to grow
Pelvic Bones and ligaments
Gluteus Maximus
- From: posterior ilium to the posterior gluteal line, dorsal surface of sacrum & coccyx, & sacrotuberous ligament (downward oblique direction of fibers)
- To: iliotibial tract that inserts on lateral tibia condyle; some fibers to gluteal tuberosity of femur (gerdyes tubercle, on tibia just inferior to lateral condyle)
- AXN: extends thigh; extension of trunk when LEs are fixed; assists in lateral rotation of thigh
- Innervation: Inferior gluteal nerve (L5,S1,S2) (comes out underneath piriformis ms)
*Most superficial to glute med and min

Pelvic Gluteal Lines
Posterior Line: Glute max is between posterior sacroiliac ligs and posterior line
Anterior line: Glute med between posterior line and anterior line
Inferior line: Glute min between anterior line and inferior line

Gluteus Medius
- From: external surface of ilium between anterior & posterior gluteal lines
- To: lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur
- AXN: ant fibers: IR, abd, post fibers: ER, abd
–Strength deficits leads to a pelvic drop gait on opposite side of hip from weak ms side (Trendelenburg Sign/Gait)
–-primary concentric and eccentric ms.
•Innervation: Superior gluteal n. (L4,5, S1) (comes out above piriformis ms)
*Filling of glute sandwich, from superficial to deep (max–>medius–>min)

Trendelenburg Gait
- If deficits or issues with glute med, the contralateral side of pelvis will drop
- See contralateral shift (opposite pelvis drops) when the indicated side is limited
*in that pic, his right glute med is involved, the standing leg hip on left leg is dropping too far (see it come out a lot on right side) which means glute med on right side isnt strong enough to stabilize as much as should
(*pelvis on unsupported side DROPS)—AKA weakness of hip abd (when hike up hip of non standing leg, hip of standing leg is abd, when drop hip of non standing leg, hip of standing leg is add)

Gluteus Minimus
- From: external surface of ilium between anterior & inferior gluteal lines
- To: anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur
- AXN: abducts & medially rotates thigh; abduction of pelvis, stabilizes pelvis
- Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve (L4, 5, S1)

Piriformis
- From: anterior surface of sacrum and sacrotuberous ligament (exits greater sciatic foramen)
- To: superior border of greater trochanter of femur
- AXN:
–lateral rotation (ER) of the extended/neutral thigh
–abducts the flexed thigh
–steadies the femoral head in acetabulum
- Innervation: N. to piriformis (S1, S2)
- Piriformis used as a key landmark:
–superior gluteal n.a.v. exits above piriformis, between that and glute min
–inferior gluteal n.a.v. exits below piriformis
–sciatic n. relationship – can vary

Sciatic Nerve Positioning
Below priformis, split by piriformis, above piriformis
- Bulk of population (80-85%)-n. exits below piriformis ms
- 20%- n. splits the piriformis (belly of piriformis split by sciatic n.)
OR sciatic n. will split and some will exit above and below
•Passive hip IR can compress sciatic n
–Why?pirifiormis is ER, so if IR its opposite which means is lengthening so can compress

Piriformis Syndrome
- Irritation of the sciatic nerve caused by “compression” or irritation of the nerve within the buttock area by the piriformis muscle-piriformis is ER, so if moved into passive IR then ms is lengthened which compresses n. OR if moves into active ER n. can also be compressed with lenghtening
- Etiology/Some possibilities include:
- Hypertrophy, inflammation or spasm (rare) of piriformis ms
- Direct trauma resulting in hematoma and scarring
- Gender: females:males 6:1
- Pseudoaneurysm of inferior gluteal a
- Anatomical Abnormalities
- Split piriformis (maybe)
Symptoms:
- Pain posterior buttock and may but not always radiates into the posterior thigh
- Increased by contraction of the piriformis muscle, prolonged sitting, or direct pressure applied to the muscle, OR in internal rotation of thigh when ms is lengthened
Piriformis Syndrome Physical Exam
•Pain with….
–Pain with active external rotation of hip – why?concentric contraction shortens muscle fibers
–Pain with passive internal rotation of hip – why?opposite direction extends fibers and creates tension (lenghtens)
- Imaging is not useful except to rule out other causes of sciatic compression (ie tumor, aneurysm, etc.)
- Differential diagnosis:
–Nerve root compression (lumbar)
–Lumbar Spine Referred Pain
LE Dermatomes

Referred Pain
Referred pain is from specific structure going into other structures (localized problem)
*Pic: lumbar facet referred pain

Radicular Pain
Radicular pain=more nerves, nerve root up in spine becomes problematic (dermatomal, muscle deficit)

Obturator Internus
- From: pelvic surface of the obturator membrane & surrounding pelvis bones
- To: medial surface of greater trochanter of the femur, blending with the gemelli ms. insertion at trochanteric fossa
- AXN:
- lateral rotation (ER) of the extended thigh
- -*abducts the flexed thigh
- -*steadies the femoral head, depends on hip position
•Innervation: N. to obturator internus & superior gemellus (L5, S1)
*sandwiched between superior and inferior glemelli

Nerves of Hip and Buttock
Right to left: Sciatic n, inferior gluteal nerve, posterior femoral cutaneous nn, nn to the obturatus internus and superior gemellus, pudendal nn

Superior Gemelli
From: ischial spine
To: the medial surface of greater trochanter with superior gemelli & obturator internus at the trochanteric fossa
AXN: together with inf gemelli
–lateral rotation of the extended thigh
–abducts the flexed thigh
–steadies the femur
INNERVATION: –Sup gemelli-N. to obturator internus & superior gemellus (L5,S1)

Inferior Gemelli
From: the ischial tuberosity
To: the medial surface of the greater trochanter with inferior gemelli & obturator internus at the trochanteric fossa
AXN:with superior gemelli
–lateral rotation of the extended thigh
–abducts the flexed thigh
–steadies the femur
Innervation:–Inf gemelli -N. to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus (L5, S1)

Quadratus Femoris
- From: lateral border of the ischial tuberosity
- To: quadrate tubercle on intertrochanteric crest of femur and just inferior to it
- AXN: lateral rotation (ER) of thigh
- steadies the femoral head
•Innervation: N. to quadratus femoris & Inferior Gemellus (L5, S1)

Obturator Externus
- From: margins of obturator foramen & obturator membrane
- To: trochanteric fossa of the femur
- AXN: lateral rotation (ER) of the thigh
- steadies the head of the femur
- secondary adduction bc of location
•Innervation: Obturator N. (post division)- L3, L4

Deep Lateral Rotators of Thigh (ER)
- piriformis
- superior gemelli
- obturator internus
- inf gemelli
- quadratus femoris
- obturator externus

Femur
- Longest, heaviest bone in body
- Head - projects superomedially & slightly anterior
*note the fovea at center
- Neck - attaches the head to the femoral shaft/body at the intertrochanteric line (from anterior view)
- Shaft/body – distal end have condyles
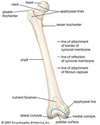
Interotrochanteric line and crest
- Anterior line between the greater and less trochanter
- Base of the neck of the femur
- Transition from neck to shaft
- Common fracture site (not the crest which is post)

Angle of Inclination of Femur
- Angle between long axis of femoral neck/head & long axis of mid shaft femur
- Normal Angle: Average 126◦
–Ranges 115◦ -140◦
–Lots of variance in people
- Coxa vara - angle of inclination is diminished (<126◦)-can be congenital, acquired, developed
- Coxa valga - angle of inclination is increased (>126◦) (L-LARGER)-femur looks almost straight
- Angle of inclination varies with age, sex, & development
- Infant/toddler – the angle is greater until ambulation (Wbing) and then angle decreases to adult normal
- May be changed by pathology that weakens the neck

Anterior Femur
- Greater trochanter - extends laterally
- Lesser trochanter - extends posteromedially
- intertrochanteric line – joins the trochanters anteriorly
- trochanteric fossa posteriorly
- Body - bowed slightly anteriorly
- femoral condyles (medial/lateral)
- patellar surface (on femoral condyles)
- lateral & medial epicondyles

Posterior Femur
- Intertrochanteric crest - joins the trochanters posteriorly
- Quadrate tubercle - rounded elevation on the intertrochanteric crest
- Gluteal tuberosity (gluteus maximus)
- Linea aspera - lat/medial lip
- Spiral line (vastus medialis) (see next slide)
- Pectineal line (pectineus) (next slide)
- Supracondylar lines (lat and medial)
- Intercondylar fossa/notch
- Adductor tubercle
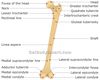
Angle of Anteversion
•Angle of anteversion (angle of femoral torsion): the plane of the femoral neck and head lies anterior to the plane of the femoral condyles
- Normal: In adults, average degree of anteversion is 15◦
- In infancy, average anteversion is 31◦, always larger til start walking and can weight bare
- Degree of anteversion may be altered in pathological conditions
- Excessive Femoral Anteversion: most frequent cause of childhood “in-toeing”(ages 3-10)
- Affected lower extremity is internally rotated.
- More common in females.
- Most noticeable between the ages of 4-6 years.
- Gait looks clumsy and “in-toeing” will often appear worse with running and at the end of the day when fatigued.
- Femoral anteversion will decrease naturally in 99% of cases.
- Studies have repeatedly shown that special shoes, twister cables, and braces make no difference in outcome.
- This is a structural (or bone) issue
- Need to wear braces to encourage boney change during growth/development
- If severe and without change, surgery indicated
- In mature skeleton, may need orthopaedic surgery, if symptomatic

“W” sitting position
- Encourages anteroversion development of the femur leading to toe-in gait- so don’t want kids doing this!!
- W position twists that femur
- if keep using it will never grow out of it

Hip Joint
- Articulation between the spheroidal shaped head of femur and acetabular socket; strong & stable
- Ball & socket - according to shape
- Tri-axial - according to degrees of freedom
- Acetabular labrum - fibrocartilaginous ring, which deepens the acetebular cup (*cup (bone) is U-shaped, empty or incomplete in inferior aspect)
- Transverse acetabular ligament - across acetabular notch
- More than 1/2 of the femoral head fits within acetabulum
- Fovea - pit in the head of femur
–Ligamentum teres attaches here
–Contains a small artery to the head of the femur
•Joint capsule – extensive
–From margins of acetabulum to the intertrochanteric line

Hip ligaments

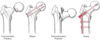
Femur Fractures
- Subcapital neck fracture
- transcervical neck fracture
- Intratrochanteric fracture (most common)
- subtrochanteric fracture
- fracture of greater trochanter
- fracture of lesser trochanter
*imp to know where fracture is bc will dictate to surgeon what need to do exactly (pin vs ORIF-if lower, creates more instability)

PIN vs ORIF femur fracture repair
THA or THR
Typical “Precautions” depending on surgical approach:
Posterior Hip Precautions: limit adduction, IR, and flexion >90degrees
-less common now, less advanced, more precautions, easier to do for surgeon
Anterior: limit ER and extension past neutral
- more common now, more advanced and complex, highly trained surgeon, harder to complete
- doesnt cut through any muscle
Lateral: no abduction for short period of time
Hip Ligamentous Support
•Ligamentous Structures - thickened portions of capsule
Iliofemoral Ligament (Y Ligament of Bigelow) - from AIIS to intertrochanteric line; strongest ligament; located anteriorly
-Become taut with hyperextension of hip
Pubofemoral Ligament – runs anterior and inferior
-Becomes taut with hyperextension and abduction of hip joint
Ligamentum teres- acetabular cup to center of fovealar head-ligament for support of the artery (but doesn’t do much)
Ischiofemoral Ligament - arises posteriorly but spirals superolaterally to the anterior femoral neck
-Becomes taut with hyperextension of hip

Paraplegia and Iliofemoral Ligament
- person with paraplegia standing with aid of braces at the knees and ankles. Leaning the pelvis and trunk posteriorly orients the body weight vector (red arrow) posterior to the hip joints (small green circle), thereby stretching the iliofemoral ligaments. This stretch provides a passive flexion torque at the hip, which helps to balance the extension torque generated by gravity. Once counterbalanced, these opposing torques can stabilize the pelvis and trunk, relative to the femur, during standing



