Lacrimal & Tears - extra Flashcards
What does the lacrimal system consist of?
The lacrimal system consists of the main accessory lacrimal glands and the lacrimal drainage system.
Describe the lacrimal system
This simplified diagram shows the sac and gland.

Where is the lacrimal gland located?
Lacrimal gland is located in the upper lateral portion of the orbit.
Sits in fossa in the frontal bone.
Describe the arrangement of the lacrimal gland and why it is this way.
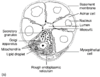
The lacrimal gland exists as two lobes; the Orbital lobe and the Palpebral lobe. It exists this way as it is almost divided by the aponeurosis of the Levator Palpebral Superioris.
You can see the two sections in the diagram marked OL
(orbital lobe) and PL (palpebral lobe).
Describe the structure of the lacrimal gland
Tubuloacinar gland.
Composed of tubules (ducts) and secretory units (acini).
10-12 ducts discharge into upper lateral fornix.
What do fibroblasts produce?
Collagen
What are the predominant cells in the lacrimal gland?
Lymphocytes (B-cells which can turn into plasma cells for IgA production)
Describe the Structure of secretory acini of the lacrimal gland.
- they are composed of secretory cells
- secretory cells contain large amounts of Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
- cells are linked together by tight junctions
- surrounded by myoepithelial cells.
What is a myoepithelial cell?
Epithelial cells containing muscle- thus is able to contract ( usually found near glandular epithelium).
How to ductal cells of the lacrimal gland modify the composition of the tear film?
They do this by secreting electrolytes.
(Background context: Tears freshly secreted from the acini have a different composition to those found in the duct).
Do lacrimal ducts have secretory cells in them?
No, they are attached to acini which have secretory cells.
The duct is yellow in the picture and the acini are the green circles attached to it.
Note that the blue fibres are actually myoepithelial cells (contractile muscles) that can ‘squeeze’ the gland.

How can one instantly cry a large volume of tears?
The lacrimal gland cannot instantly produce that many tears instead it actually acts as a tear reservoir. Such that when myoepithelial cells contract they can release those tears quickly.
What makes tears salty?
High level of electrolytes in them. (sodium , potassium chloride).
What are the three principal components of the tear film layer?
Upper layer-m Lipid layer from meibomian glands
Middle layer- aqueous layer comes from the lacrimal gland
Bottom layer - mucous
What is tear PRODUCTION (not output) controlled by?
Autonomic control. Innervated by the parasympathetic system by fibres that run in the Facial (V) Nerve.
What is the output of the lacrimal gland dependent on?
The output from glands is dependent on the level of corneal stimulation (by sensation experienced on surface of the eye) from the trigeminal nerve.
Which antibody is present in tears?
IgA
Where is IgA produced in the eye?
Secretory IgA is produced by plasma cells in the interstices (means in-between spaces) of the gland.
(IgA is transported across the acini).
How much of the total lacrimal tissue do accessory lacrimal glands make up?
5%
What are accessory lacrimal glands and how is it different from the main lacrimal gland?
Accessory lacrimal glands are small ducts and their respective acini spread across the conjunctiva whereas the main lacrimal gland is the same structured ducts and their respective acini just grouped together in one place.
Why is it when you cry you also tend to get a runny nose?
The tear outflow path consists of the puncta, canaliculi, lacrimal sac, and nasolacrimal duct.
Furthermore, tear outflow is an active process mediated by the contraction of the Orbicularis in blinking.

Describe the Puncta (Size and locations).
0.2-0.3 mm aperture
You have one in the upper eyelid and one in the lower eyelid.
Angled backwards towards the eye.
Where is the lacrimal sac located?
In a fossa formed between the lacrimal and maxillary bone.
Where does the nasolacrimal duct pass through?
Through a canal in the maxillary bone opening in the nasal cavity beneath inferior. nasal turbinate



