Eyelid Disorders Flashcards
What is a disorder of the eyelashes called?
Trichiasis
What are examples of anomalies in lid positions?
Ptosis
Entropion/ectropian
What is Ptosis?
Ptosis (pronounced toe-sis) , also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid.
What is Entropion?
Entropion is a medical condition in which the eyelid (usually the lower lid) folds inward.
Why is entropion an uncomfortable condition?
It is very uncomfortable, as the eyelashes continuously rub against the cornea causing irritation.
What is Ectropion?
It is a condition in which your eyelid turns outward. This leaves the inner eyelid surface exposed and prone to irritation.
What are some examples of benign lid lesions?
Hordeolum (internal and external)
Chalazion
Cysts of Moll and Zeis
Molluscum contagiosum
What is hordeolum?
(Basically a stye) A hordeolum (stye) is an acute, localized swelling of the eyelid that may be external or internal and usually is a pyogenic (typically staphylococcal) infection or abscess.

Define pyogenic
involving or relating to the production of pus.
What is a Chalazion and what can it occur as a result of?
A chalazion is a small, slow-growing lump or cyst that develops within the eyelid. (Not usually painful and usually go away).
A chalazion can develop when a meibomian gland at the edge of an eyelid becomes blocked or inflamed.

What are cysts of Moll and Zeis?
A benign swelling of either the gland of Moll or Zeis.

What is Molluscum contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum is an infection that causes small dimpled spots to appear on the skin.
Molluscum is a type of wart - around the eyelid it affects the conjunctiva

Name examples of malignant eye lesions.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
How common is basal cell carcinoma and what does it look like?
If left untreated what can occur?
The vast majority of skin cancers around the eyes are basal cell carcinomas.
It can spread to the eye.

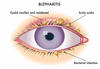
What is blepharitis and why does it occur?
Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. Blepharitis usually affects both eyes along the edges of the eyelids. Blepharitis commonly occurs when tiny oil glands (meibomian glands) near the base of the eyelashes become clogged, causing irritation and redness.
What is an internal hordeolum?
Infection of the meibomian glands
What is an external hordeolum?
Infection of glands associated with eyelashes - so the glands of Zeis and Moll
What is the difference between hordeola and hordeolum?
Hordeola is singular
Hordeolum is plural
When internal Hordeolum fail to resolve what happens?
They turn into a chalazion. (pronounced Ka-lay-zee-on)
What is Trichiasis?
A common condition in which eyelashes grow towards the globe rather than outwards.
Who is Trichiasis most common in?
Most common in the elderly.
What are the symptoms of Trichiasis?
A foreign body sensation ( as eyelashes are extremely sensitive) as a result you have epiphora associated with red-eye.

What do treatments for Trichiasis include?
lubricants/bandage contact lens, epilation (basically hair removal these regrow in 4-6 weeks) or electrolysis/cryotherapy (destroying eyelash follicle to destroy regrowth).
What are the causes of ptosis?
Can be congenital, however, this is rare.
Mostly acquired ( age, trauma, neurological (ocular motor nerve pathology -remember this innervates the levator palpebrae superioris), myogenic (originating from muscle tissue))








