Lab 5: Shoulder Treatments OSCE Flashcards
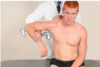
Glenohumeral Joint: Flexion/Extension SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Stabilize shoulder girdle with one hand, contact elbow with the other.
- Engage restrictive barrier in flexion/extension based on diagnosis.
- Apply principles and steps of MET to the motions of the GH joint.
- Reassess.

Glenohumeral Joint: Internal and External Rotation SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Stabilize shoulder girdle with one hand, contact wrist with the other.
- Engage restrictive barrier in internal/external rotation based on diagnosis.
- Apply principles and steps of MET to the motions of the GH joint.
- Reassess.
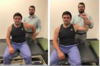
Glenohumeral Joint: Abduction and Adduction SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Stabilize shoulder girdle with one hand, contact elbow with the other.
- Engage restrictive barrier in AB/ADduction based on diagnosis.
- Apply principles and steps of MET to the motions of the GH joint.
- Reassess.

Spencer Stage 1: Extension
How would you preform this treatment?
- Cephalad hand stabilizes shoulder girdle, caudal hand grasps patient’s flexed elbow.
- Move shoulder into extension until restrictive barrier is enganged. With gentle but firm force, move a short distance through the restrictive barrier for 1-2 seconds and release.
- Repeat rhythmically until no further progress in extension can be appreciated.
- Reassess.

MET Modification: Once restrictive barrier is engaged, have patient perform flexion against physician resistance and follow rules of MET
Spencer Stage 2: Flexion
How would you preform this treatment?
- Cephalad hand stabilizes shoulder girdle, caudal hand grasps patient’s flexed elbow.
- Move shoulder into flexion until restrictive barrier is enganged. With gentle but firm force, move a short distance through the restrictive barrier for 1-2 seconds and release.
- Repeat rhythmically until no further progress in flexion can be appreciated.
- Reassess.

MET Modification: Once restrictive barrier is engaged, have patient perform extension against physician resistance and follow rules of MET
Spencer Stage 3: Compression Circumduction
How would you preform this treatment?
- Cephalad hand stabilizes shoulder girdle, caudal hand grasps patient’s flexed elbow.
- Abduct patient’s shoulder to 90° and gently compress elbow toward glenoid fossa.
- Make small clockwise circles, gradually increasing size of concentric circle for 15-30 sec.
- Reverse direction of circle to counterclockwise and continue for 15-30 seconds.
- Reassess.

Spencer Stage 4: Traction Circumduction
How would you preform this treatment?
- Cephalad hand stabilizes shoulder girdle, caudal hand grasps patient’s wrist of elbow.
- Abduct patient’s shoulder to 90° and gentle traction toward ceiling.
- Make small clockwise circles, gradually increasing size of concentric circle for 15-30 sec.
- Reverse direction of circle to counterclockwise and continue for 15-30 seconds.
- Reassess.

Spencer Stage 5A: Adduction and ER
How would you preform this treatment?
- Cephalad hand stabilizes shoulder girdle, and have patient grasp physician’s forearm.
- Slightly flex patient’s shoulder so arm may pass just in front of their body.
- With caudal hand, adduct shoulder to restrictive barrier. With gentle but firm force, move a short distance through restrictive barrier for 1-2 seconds and release.
- Repeat rhythmically until no further progress in adduction can be appreciated.
- Reassess.
MET Modification: Once restrictive barrier is engaged, have patient perform abduction against physician resistance and follow principles of MET

Spencer Stage 5B: Abduction
How would you preform this treatment?
- Return to starting position used in stage 5A.
- With caudal hand, abduct shoulder to restrictive barrier. With gentle but firm force, move a short distance through restrictive barrier for 1-2 seconds and release.
- Repeat rhythmically until no further progress in abduction can be appreciated.
- Reassess.
MET Modification: Once restrictive barrier is engaged, have patient perform adduction against physician resistance and follow principles of MET
Spencer Stage 6: Internal Rotation
How would you preform this treatment?
- Abduct patient’s shoulder 45°and internally rotate shoulder, placing dorsum of patient’s hand in the small of the back.
- Reinforce anterior shoulder with cephalad hand.
- With caudal hand gently pull elbow forward into internal rotation restrictive barrier. With gentle but firm force, move a short distance through restrictive
barrier for 1-2 seconds and release. - Repeat rhythmically until no further progress in adduction can be appreciated.
- Reassess.

MET Modification: Once restrictive barrier is engaged, have patient perform external rotation against physician resistance and follow principles of MET
Spencer Stage 7: Traction with Inferior Glide
How would you preform this treatment?
- Abducts the patient’s arm. The patient’s hand and wrist are placed on the physician’s shoulder that is closest to the patient.
- With fingers interlaced, the physician’s hands are placed just distal to the glenohumeral joint.
- Scoops the patient’s humeral head in a caudad direction, parallel to the table, creating a translatory motion toward the inferior edge of the glenoid fossa.
- Repeat rhythmically until no further progress in shoulder abduction can be appreciated.
- Reassess.
MET Modification: While the physician maintains caudad traction on the patient’s arm, the patient’s hand is pressed down against the physician’s shoulder.
Sternoclavicular Joint: Abduction and Adduction Diagnosis
How would you diagnose these somatic dysfunctions?
- Patient is supine; examiner places index finger on clavicular head next to the sternum.
- Patient then shrugs (ABduction)
- An inferior/caudal movement should be palpated with normal motion at the sternoclavicular joint.
- Patient then lowers shoulders downward (ADduction).
- A superior/cephalad movement should be palpated with normal motion at the sternoclavicular joint.

Sternoclavicular Joint: Flexion and Extension Diagnosis
How would you diagnose these somatic dysfunctions?
- Patient is supine; examiner places index finger on the clavicular head next to the sternum; patient flexes shoulder to 90° and reaches for ceiling forcefully (Flexion).
- A posterior movement of the clavicular head should be palpated with normal motion at the sternoclavicular joint.
- Patient then lowers arms back toward the table (Extension).
- An anterior movement of the clavicular head should be palpated with normal motion of the sternoclavicular joint.

Sternoclavicular Joint: Elevated/Adducted SD ART
How would you preform this treatment?
- Patient lying supine with neck fully flexed by physician.
- Physician places thumb over sternal end of the clavicle, exerting a downward/caudal pressure on the clavicle.
- Patient instructed to inhale and exhale fully. During exhalation, the physician springs the clavicle inferiorly/caudally to release restriction.
- Reassess.

Sternoclavicular Joint: Elevated/Adducted SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Patient lying supine, examiner on side of affected shoulder.
- Physician places one hand on the sternal/proximal clavicular head. With the other hand, grasp the patient’s wrist and hold arm extended and internally rotated.
- Patient is instructed to raise arm against physician’s hand toward ceiling (flexion at the shoulder) for 3-5 seconds, then relax.
- Bring joint into new barrier, repeating until no new barriers reached or full ROM restored.
- Reassess.

Sternoclavicular Joint: Horizontal Extension SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Patient lying supine, examiner on side of affected shoulder
- Physician places one hand on the restricted clavicular head and the other hand placed behind axilla to cover the scapula. Patient holds physician’s shoulder with the hand of the affected shoulder.
- Physician then flexes the clavicle toward the manubrium until movement is palpated in the SC joint by pulling scapula anteriorly.
- Posterior force simultaneously applied to proximal clavicle from anterior to posterior to engage restrictive barrier.
- Apply the principles of MET by having patient pulling their shoulder down toward the table.

Sternoclavicular Joint: Clavicle Anterior and Superior Glide ART
How would you preform this treatment?
- Pt lying supine, physician on contralateral side to somatic dysfunction.
- The pt helps to gap the SC joint by aDducting the arm ipsilateral to the SD (using their contralateral hand to aid in the motion). The physician’s ipsilateral hand may be placed on the table under the patient’s axilla to create a fulcrum for the patient to adduct against.
- Articulatory springing is applied laterally, posteriorly, and inferiorly over medial end of clavicle using the physician’s hypothenar eminence of the contralateral arm.
- Reassess.

Acromioclavicular Joint: Cross Arm/Adduction Test Diagnosis
How would you diagnose this?
- Physician monitors the posterior aspect of AC joint.
- Patient is instructed to start with the arm flexed to 90o and add adduction across the body.
- This motion should gap the joint posteriorly.
Positive Finding: Patient perceives pain at the AC joint and/or there is increased tissue texture abnormality

Acromioclavicular Joint: Internal and External Rotation Diagnosis
How would you diagnose this?
- Patient seated, physician stands behind patient.
- One hand contacts and stabilizes the clavicular side of the joint with index finger over the AC joint noting if patient has tenderness.
- Note asymmetry of joint gap compared to opposite side.
- Flex, abduct (approximately 45°) to maximally engage the AC component of GH rotation.
- IR and ER to assess for 90° of motion each direction.
- Note restriction of motion and ease of motion.
- Name dysfunction based on the direction of ease of motion (IR or ER).

Acromioclavicular Joint: Superior Clavicular SD ART
How would you preform this treatment?
- Patient supine with doctor on ipsilateral side.
- Doctor’s index fingerpad monitoring AC joint and other fingers on superior aspect of clavicle; the other hand grasps the patient’s forearm proximal to the wrist.
- Apply a traction force in a caudad direction to gap the AC joint. Use enough force to register a change with the monitoring hand.
- While maintaining the traction force maximally flex the arm.
- Reassess.

Acromioclavicular Joint: Superior Clavicular SD Seated ART
How would you preform this treatment?
- Grasp elbow or forearm of dysfunctional side.
- Grasp dysfunctional clavicle between thumb and fingers of free hand. (Thumb on posterior/superior surface of distal clavicle, and NOT on scapula).
- Apply anterior/inferior pressure with thumb on lateral (or posterior) aspect of clavicle while flexing patients elbow, extending and adducting humerus (to gap AC joint).
- Doctor holds clavicle antero-inferior (with thumb). Shoulder is extended into a circulatory sweep, posterior, superior, then anteromedial while maintaining
adduction and capsular tension - Recheck.

Acromioclavicular Joint: Internal Rotation SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Patient seated, physician stands behind patient.
- Physician places hand on clavicle just medial to AC joint while grasping wrist with the other hand.
- Add compressive force (blocking linkage) to stabilize clavicle/AC joint while flexing, abducting (approximately 45o) & Externally Rotate to restrictive barrier.
- Apply the principles of MET by having the patient Internally Rotate against physician’s resistance for 3-5 seconds.
- Repeat 3-5 times or until motion is fully restored
- Reassess.

Acromioclavicular Joint: External Rotation SD MET
How would you preform this treatment?
- Patient seated, physician stands behind patient.
- Physician places hand on clavicle just medial to AC joint while grasping wrist with the other hand.
- Add compressive force (blocking linkage) to stabilize clavicle/AC joint while flexing, abducting (approximately 45o) & Internally Rotate to restrictive barrier.
- Apply the principles of MET by having the patient Externally Rotate against physician’s resistance for 3-5 seconds.
- Repeat 3-5 times or until motion is fully restored
- Reassess.