Kaplan Q bank Flashcards
Lead poisoning leads to the inhibition of what enzymes?
- Aminolevulinate (ALA) dehydratase in heme biosynthesis pathway
- Ferrochelatase —> ↑ free erythrocyte protoporphyrin

Which organisms would be on the differential for a neonate born with petechial rash, deafness, jaundice, thrombocytic purpura and periventricular CNS calcifications?
- CMV = most common in U.S.
- T. gondii
- Rubella
What will be seen histologically with adult-onset myotonic dystrophy (DM1)?
Ring fibers w/ central nuclei

Olfactory bulb neurons send axons where?
Piriform cortex aka primary olfactory cortex that overlies uncus of the temporal lobe
Which type of ovarian tumor should be suspected in a girl exhibiting precocious sexual development?
Granulosa cell tumor –> estrogen-secreting
Which type of encephalitis is characterized by hemorrhagic necrosis in the temporal lobes and base of the frontal lobe?
Herpes simplex
A neonate presenting at 24-48 hrs after birth with lethargy, poor feeding, vomiting, hyperventilation, seizures, and cerebral edema should make you suspect what?
- OTC deficiency
- Will have hyperammonnemia w/ ↓ BUN
A child with dyspnea, difficulty feeding, poor weight gain and a strong radial pulse w/ weak femoral pulse most likely has what?
Coarctation of the aorta

Which ovarian tumor exhibits follicle-like structures (Call-Exner bodies) and stain positive for inhibin?
Granulosa cell tumor
What are the clinical manifestations of “dry” vs. “wet” beribri as a result of Thiamine deficiency?
- Dry = progressive polyneuropathy w/ myelin degeneration –> wrist and foot drop
- Wet = high-output cardiac failures –> dilated cardiomyopathy
Dynein is a molecular motor protein important for what 3 functions?
- Ciliary beating: respiratory tract
- Flagellar beating: sperm
- Intracellular vesicle transport
What is the major outlet for the esophageal venous plexus and is the major accessory pathway for venous return in patients with end-stage liver disease and critical portal HTN?
Azygos V.

What occurs to the majority of severe cervical dysplasia (CIN 3) aka high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) after 2 years?
60% of lesions persist at the same level
Which landmark is used for injection of pudendal nerve block?
Ischial spine

The oculomotor n. (CN III) emerges from the interpeduncular fossa of the midbrain and the passes between which 2 arteries?
Superior Cerebellar a. and the PCA

In wound healing what is the dominant cell type found at 2 days, 3-5 days, and one week following the injury?
- 2 days = neutrophils
- 3-5 days = macrophages
- 1 week = fibroblasts
What is the initial type and later type of collagen that is layed down by fibroblasts during wound healing?
Initially deposit type III collagen (granulation tissue), which later is replaced by stronger type I collagen (fibrosis)
Tetralogy of Fallot is more commonly associated with what congenital syndrome?
DiGeorge syndrome
Which congenital heart defect is most commonly seen in Down Syndrome?
Ostium primum ASD, often w/ malformations of AV valves due to endocardial cushion defect

Which virus is associated with focal necrotizing arteritis with fibrinoid necrosis of small- and medium-sized arteries known as Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN)?
Hepatitis B
Which portion of the smooth muscle in the bladder is innervated by the sympathetic NS vs. parasympathetic NS?
- Internal urethral sphincter at bladder neck = sympathetic
- Remaining smooth m. of bladder = parasympathetic
Which structure is resected during a TURP procedure resulting in retrograde ejaculation?
Internal urethral sphincter
Differentiate primary, seconday, and tertiary prevention.
- Primary: reducing # of new cases of disease (incidence) thru eliminating risk factors or immunization
- Secondary: identifying disease in a pre-clinical state, ↑ likelihood of tx or curing disease i.e., cervical cancer screening
- Tertiary: reducing likelihood of disease recurrence or exacerbation in pt who has already been diagnosed w/ disease
Atrophy of which spinal cord structures is associated with tertiary syphilis?
Bilateral degeneration of the dorsal roots and 2’ degeneration of the dorsal columns
Which enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis?
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase

Abdominal pain + cervical motion tenderness or adnexal tenderness is characteristic of which infectious organisms?
Chlamydia
Mitigating the use of antibiotics in children with viral illness is an example of what type of prevention?
Quaternary prevention
Sparse, completely hyalinized seminiferous tubules with complete absence of spermatogonia (germ cells) and rare Sertoli cells is seen with what condition?
Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY)
Cell shrinkage, hyperchromatic pyknotic nuclei, and apoptotic bodies composed of cytoplasm and nuclear fragments describes what?
Apoptosis
Intacytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions containing alpha-synuclein or ubiquitin describes what?
Lewy bodies
What are the 4 exceptions to the informed consent rule?
- Emergency
- Waiver by the patient
- Patient is incompetent
- Therapeutic privilege: pt is unconscious, confused, or the physician deprives pt of autonomy in interest of health
What is the effect of low intrathoracic pressure during inspiration on th pulmonary vasculature and left-side of heart?
↓ pulm. vasculature pressure –> ↑ intravascular volume –> ↓ LA filling –> ↓ LV preload –> ↓ LV EDV –> ↓ LV stroke volume –> ↓ systolic BP
Senile cardiac amyloidosis results from the deposition of what type of amyloid and leads to what?
ATTR-type amyloid —> restrictive cardiomyopathy
Loss of sensation to the medial 1.5 digits, atrophy of intrinsic hand muscles and radial deviation of the hand upon wrist flexion are all sx’s of what?
Cubital tunnel syndrome: Ulnar n. entrapment
What is a prominent histologic feature of Neuroblastomas?
Homer-Wright pseudorosettes

Which mutation is seen in many cases of Neuroblastoma and confers a worse prognosis?
Amplification of MYCN oncogene –> n-myc
Which fungus is found in the body as a small (2-5 um) intracellular yeast (within macrophages) and has no true capsule?
Histoplasma capsulatum
What are the manifestations of carcinoid heart disease?
Fibrotic endocardial thickening of the right heart + tricuspid stenosis and insufficiency
High titers of anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein, RF, and anti-nuclear antibody are suggestive of what?
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease

Anti-centromere antibody is the distinctive marker for what?
- CREST syndrome
- Calcinosis + Raynaud’s + Esophageal dysmotility + Sclerodactyly + Telangiectasia

High-titers of anti-histone antibody without other autoantibodies is a distinctive marker for what?
Drug-induced lupus

Primary oocytes found in the ovary stay arrested in which phase until ovulation; what about secondary oocytes prior to ovulation?
- 1’ oocyte = diploid; arrested in prophase I of the 1st meiotic division
- 2’ oocyte = haploid; arrested in metaphase of the 2nd meiotic division

Familial transthyretin (TTR) amyloidosis is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by what findings?
- Sensorimotor and autonomic neuropathy
- Cardiomyopathy
- AF amyloid protein
Why is Histoplasma capsulatum non-communicable?
Intracellular yeast inside of macrophages
The mechanism by which a temperate phage can accidentally transfer bacterial DNA from cell to cell if there is an error of excision is known as what?
Specialized transduction
Which type of gene transfer occurs from one bacterial cell to another via cell-to-cell contact using a plasmid (fertility factor)?
Conjugation

The aorticopulmonary septum and endocardial cushions are derived from what embryologically?
Neural Crest Cells
Multiple brick-red dots, Schüffner dots, seen in a pt’s erythrocytes are indicative of which organism?
Plasmodium vivax or ovale

Which 2 serological markers are specific, but not sensitive for SLE?
- anti-dsDNA
- anti-Smith
*anti-nuclear Ab is sensitive, but not specific
Renal manifestations such as proteinuria and hematuria should raise suspicion of which disase process in 15-45 y/o woman with chronic, poorly defined sx’s?
SLE
Where is ipoprotein lipase is the enzyme required for metabolism of chylomicrons and VLDL located; what does it require for activation?
Luminal surface of vascular endothelium (capillaries) of adipose tissue; requires Apo C2 for activation

Which hormonal levels will be increased during menopause?
↓ estrogen –> ↑ GnRH, ↑ FSH, and ↑ LH

Dystonia is an extrapyramidal side effect characterized by what; what are some examples?
- Repeated, sustained involuntary muscle contractions, as well as abnormal postures of the trunk, face and/or extremities
- Torticollis, oculogyric crisis, and opisthotonic crisis
Deficiency of what causes a defect in the development of CD4+ cells in the thymus?
MHC class II proteins
Increases in which 2 parameters are seen with obstructive lung diseases such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma?
- Total lung capacity
- Pulmonary compliance = ΔV/ΔP
Beck’s triad: ↓ arterial pressure, ↑ systemic venous pressure, and a small, quiet heart (distant heart sounds) are classic signs of what?
Cardiac Tamponade
Which nerve innervates the posterior compartment muscles of th arm and forearm including the triceps, extensors and the supinator muscle?
Radial n.
Marfarn syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder due to defects in what?
FBN1 gene –> fibrillin-1 an extracellular matrix protein
Which organism causes a high fever for ~3 days that abrupty goes away prior to development of morbilliform rash in 9-12 month olds?
Roseola - HHV-6
Combination of hypotension with normal or ↑ pulse pressure and a HR of 30-45/min should suggest the diagnosis of what?
Complete heart block
Progesterone levels are sustained during the 1st trimester of pregnancy as a response to what?
hCG

Which tumor can cause dysfunction of the vertical gaze center in the dorsal midbrain?
Pinealoma

The most important clnical presentation of pineal germinomas is Parinaud syndrome which is characterized by what 3 major findings?
- Palsy of upward gaze
- Dissociation of light and accomodation (light-near dissociation)
- Failure of convergence
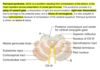
In anemia there is a ↓ O2 carrying capacity of blood leading to low tissue PO2 which causes what adaptive responses?
- Reflex vasodilation of resistance vessels –> ↓ PVR and ↑ flow through capillary beds
- CO and venous return both ↑↑↑
Anastomoses of which vein with the splenic vein would allow for blood to bypass the liver and relieve portal HTN?
Splenic V. –> Left Renal V. (drains directly in IVC)

Which type of blot is used to identify DNA-binding protein interactions?
Southwestern blot
Which tumors would desmin vs. vimentin be found in?
- Desmin: rhabdomyosarcoma; tumors of skeletal m.
- Vimentin: non-skeletal, soft tissue sarcomas and mesenchymal tumors
Case-control studies are analyzed using what ratio and what is the formula?
Odds ratio: (a/c) / (b/d) or (a*d) / (b*c)

Pt’s with Plummer-Vinson Syndrome are at an increased risk for developing which malignancy?
SCC of the upper esophagus


