Joints of the Pelvic Limb Flashcards
Flexor Surfaces

Sacroiliac Joint

- Connection of the sacrum and the wing of the illium
- Stability joint, NOT MOVEMENT
- Articular surfaces are united by fibrocartilage (hyaline cartilage)
- Dorsal sacroiliac ligament
- Ventral sacroiliac ligament
- Ligaments reinforce the joint
Sacrotuberous Ligament
(Dogs)

- Collagenous cord
- Inserts on ischiatic tuberosity
- Origin of several muscles
Large animals = Sacrosciatic ligament
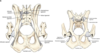
Coxofemoral Joint (Hip Joint)

- Ball and socket joint
- Flexion and extension movements
- Opposed action from medial and lateral rotator muscles limits movement
- Joint capsule
- Neck of the femur to acetabular lip
- Ligament of the femoral head
- Short, thick band of collagenous tissue
- Covered by a synovial membrane
- Acetabular attachment blends slightly with the transverse acetabular ligament

Transverse acetabular ligament

- Connects the femur to the acetabulum
- Ventrocaudal aspect of the acetabulum
- Thick band of collagenous tissue
Attachments:
(O): Acetabular fossa
(I): Fovea capitis

Sacrosciatic Ligament
(Large Animals Only)
Collagenous cord
Inserts on ischiatic tuberosity
Origin of several muscles
Equivalent of the Sacrotuberous ligament in dogs
Accessory Ligament of the Femur
(Horses)

Detached from the prepubic ligament
Inserts close to the ligament of the femoral head
Restricts the way that a horse kicks
Coxofemoral Joint

- Transverse acetabular ligament
- Small, thick, collagenous band
- Extends across the acetabular notch
- Continues as the Acetabular lip
- Forms a fibrocartilaginous border around the acetabulum

Stifle Joint Sacs

“The Knee”
Composed of 3 joint sacs that communicate with eachother:
- 2 Femorotibial joint sacs
- Medial and Lateral Femorotibial Joint Sac
- Between femoral and tibial condyles
- Extend caudally to incorporate the articulation of the gastrocnemius sesamoids (fabellae)
- Lateral continues dorsally through extensor groove as the tendon sheath for the long digital extensor
- Around the tendon of origin of popliteus m.
- Medial and Lateral Femorotibial Joint Sac
- 1 Femoropatellar joint sac
- Beneath the patella
Hip Luxation
Most commonly luxated joint in dogs
Dislocation of the hip joint
- Displacement of the head of the femur from the acetabular socket
Result of trauma or severe hip dysplasia

Patellar Ligament
(Stifle Joint)
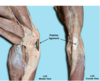
- Attaches the patella to the tibial tuberosity (sits there)
- Tendon of insertion for quadriceps femoris m.
Infrapatellar fat pad:
- Protective cushion between patella and tibia

Infrapatellar fat pad
(Stifle Joint)
Protective cushion between patella and tibia

Radiograph of the Stifle Joint

Patellar Luxation

Patella is dislocated
- Moves out of its normal location when the knee is flexed
- Dog will have a problem bearing weight
- Does not seem very painful
Caused by:
- Shallow trochlear groove (most common)
- Patellar ligament attachment (not at center)
Common in small and toy breed dogs
Surgery depends on severity
- Happens once in awhile- pop back in
- Happens all the time - deepen trochlear groove
Patellar Ligaments of the Large Animal
(3)
(Stifle Joint)
3 Patellar Ligaments (Dog has 1)
- Lateral patellar ligament
- Medial patellar ligament
- Right behind the medial trochlear ridge
- Middle patellar ligament
Important part of the stay apparatus in the horse

Femoropatellar ligaments (2)
(Stifle Joint)

- Medial femoropatellar ligament
- Lateral femoropatellar ligament
- Extend from the patella to the sesamoids of the gastrocnemius m.
- aka fabellae
Meniscus
(Stifle Joint)
- Semilunar fibrocartilage
- “C” shape
- Between each femoral condyle and corresponding tibial condyle
- Medial meniscus
- Attached to the medial collateral ligament
- Only moves slightly when the stifle is flexed
- Lateral meniscus
- Medial meniscus
- Compensate for the difference between the femur and the tibia
- Cushioning between bones
- Prevent grinding
- Each attaches to intercondylar areas of the tibia via:
- Cranial & caudal meniscotibial ligaments
- Transverse ligament

Cranial Meniscotibial Ligament
Caudal Meniscotibial Ligament
(Stifle Joint)

Each attaches to the corresponding intercondylar areas of the tibia
- Cranial goes cranial
- Caudal goes caudal
Image shows a top-down view
Transverse ligament
(Stifle Joint)

Connects the cranial ends of the menisci to eachother
- Medial and lateral menisci
Meniscofemoral ligament
(Stifle Joint)

Attaches the caudal part of the lateral meniscus to the intercondylar fossa of the femur
Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Caudal Cruciate Ligament
(Stifle Joint)

Pass between intercondylar areas of the tibia and femur
Cross eachother near their attachments in the intercondylar fossa of the femur
Cranial cruciate ligament:
- (O): intercondylar fossa of the femur
- (I): Caudomedial part of the lateral condyle
- Keeps the tibia from sliding cranially when bearing weight
- Prevents tibia from shooting forward
- Limits medial rotation when flexed
Caudal cruciate ligament:
- (O): Proximal intercondylar fossa of the femur
- (I): Medial edge of the popliteal notch of the tibia, behind the caudal attachment of the medial meniscus
- Prevents caudal movement of the tibia while bearing weight
Ruptured Cranial Cruciate Ligament
(Stifle Joint)
Most common knee injury in dogs
- Sudden rear leg lameness
Tibia won’t budge unless you have a ruptured cruciate ligament
- Cranial drawer sign
- Stabilize the femur
- Manipulate the tibia with the other hand
- Tibia movement towards cranial cruciate ligament = ruptured
- Usually need to sedate to do properly
- Can’t have the dog tense - won’t see tear
- Tibial thrust
* Less reliable
Multiple surgical repair techniques
- Lateral suture stabilization
- TPLO
- Change the angle of the femur

Femorotibial ligaments
Medial collateral ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
(Stifle Joint)

Medial collateral ligament
- (O): Medial epicondyle of the femur
- (I): Medial side of tibia (distal condyle)
- Fuses with the lateral aspect of the medial meniscus
Lateral collateral ligament
- (O): Lateral epicondyle of the femur
- (I): Head of the fibula
- Extends over the tendon of origin popliteus m.
- Keeps the stifle from moving side-to-side

Tarsal Joint
(aka “the Hock”)
(4 Major Joints)

Tarsocrural joint
Proximal intertarsal joint
Distal intertarsal joint
Tarsometatarsal joints
- Numerous articulations for each
- Numerous joint sacs
Medial and lateral collateral ligaments occur at the tarsal joint