Intestinal Flashcards
(13 cards)

Cholangiohepatitis:
=inflammation of live( cat)
- inflammation of hepatocytes and bileducts
- paler lesions= where inflam takes place and may spread to other lobules
- whole liver is paler than normal, and enlarged

Cholangiohepatitis:
- lobular structures w/ portal area, artery, vein, bile duct
- lymphocytic portal hepatitis( inflam cells around the bile duct-> lymphoctes, neutrophils, histocytes)
- dilated blood vessels
- white RBC in lumen of bileducts, bile duct proliferation and destroyed w/ epithelial layer
- large necrotic haemorrhages of the lobules
- inside the necrotic are: identify the karyolysis and the haemorrhages(blood filled microspaces)
- plasma cells and fibrocytes can also be seen

Infectious canine hepatitis/ Rubarth´s disease:
- parenchymal (centrolobular) necrosis
- Councilman´s bodies= apoptotic hepatocyte
- Cowdry A -type intranuclear inclusion bodies
- atypical hepatocytes
- portal and sinusoidal inflammation and “DISSE” spaces w/ RBC and neutrophil accumulation

Infectious canine hepatitis/ Rubarth´s disease:
- parenchymal (centrolobular) necrosis
- Councilman´s bodies= apoptotic hepatocyte
- Cowdry A -type intranuclear inclusion bodies
- atypical hepatocytes
- portal and sinusoidal inflammation and “DISSE” spaces w/ RBC and neutrophil accumulatio

Liver cirrhosis:
*cirrosis process:
1) necrosis of hepatocytes
2) connective tissue proliferation/necrosis
3) Regeneration(nodules= proliferating hepatocytes)

Liver cirrosis:
- extensive interlobular connective tissue proliferation
- intralobular connective tissue proliferation (broken up lobules)
- Pseudo lobules= no central vein in the pseudo-lobules, cells with pale cytoplas and fatty infiltration
- bile vessels( proliferation)
- no central vein with thick connective tissue septa

Paratuberculsus enteritis (Johne´s disease)
=proliferative enteritis
- necrosis and wrinkling of mucosa
- proliferation of epithelial cells and LAnghans type giant cells= in the necrotized mucous membrane
- bacteria (inside the giant cells cytoplasm)
- Inflammatory cells in the mucosal membrane= neutrophils , eosinophils and histocytes
+ lots of GOBLET CELLS

Parvovirus enteritis:
- small intestines villi
- atrophied villi( loss of inner structure)
- inflammatory cells
- remnants of Lieberkuhn crypts( regeneration starts after 3-4days)
- mitotic features
- atrophied peyers patches

Acute leptomeningitis (Glassers disease):
- brain tissue( lots of Glial cells)
- Dilated blood vessels
- Inflammatory cells ( neutrophis, lymphocytes, histocytes/monocytes, plasma cells an Eosinophi granulocytes
*leukocytodiapedesis (neutrophil moving through vessel wall)
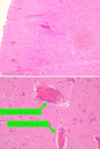
Acute leptomeningitis (Glasser disease)

West-Nile encephalitis:
-neurons are degenerated or destructed due to viral infection= microglia and astrocyes appear around them and will remove them via phagocytosis which results in FOCAL GLIAL CELL PROLIFERATION
*lymphocytes, plasma cell, macrophages, glial cells and neuronphagia

West-Nile encephalitis:
Encephalitis caused by Listeria monocytogenes:
- dilated blood vessels filled with RBC
- Ring shaped/round accumulation of inflammatory cells around the blood vessels( lymphocytes, histocytes, neutrophils)
- Destroyed motor neurons
- Granular glial cells and neutrophils around the destroyed neuron
- Abscesses of glial cells and neutrophils


