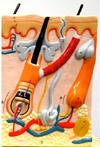
Integumentary System Flashcards
(69 cards)
Integumentary System Function
Protection, insulation, cushion the underlying body tissues and protects the entire body from abrasion, exposure to harmful chemicals, temperature extremes, and bacterial invasion.
2 regions of the skin
Epidermis and dermis
Deep to the dermis is?
Hypodermis or superficial fascia, which is not considered part of the skin. Consisting primarily of adipose tissue.
Epidermis Layers (superficial to deep)
Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
Stratum Corneum
Most superficial layer; 20-30 layers of dead cells, essentially flat membranous sacs filled with keratin; glycolipids in extracellular space
Stratum Lucidum
A very thin translucent band of flattened dead keratinocytes with indistinct boundaries. Not present in thin skin
Stratum Granulosum
One to five layers of flattened cells, organelles deteriorating; cytoplasm full of lamellar granules (release lipids) and keratohyaline granules
Stratum Spinosum
Several layers of keratinocytes joined by desmosomes. Cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin
Stratum Basale
Deepest epidermal layer; one row of actively mitotic stem cells; some newly formed cells become part of the more superficial layers.
Keratin
A fibrous protein that gives the epidermis its durability and protective capabilities
Keratinocytes
The most abundant epidermal cells, their main function is to produce keratin fibrils; connected to each other by desmosomes
Melanocytes
Spidery black cells that produce the brown to black pigment called melanin.
Melanin
Provides a protective pigment umbrella over the nuclei of the cells in the deeper epidermal layers, thus shielding their genetic material (DNA) from the damaging effects of UV radiation
Dendritic cells (langerhans cells)
Play a role in immunity
Tactile (Merkel) cells
Occasionally spiky hemispheres that, in combination with sensory nerve endings, form sensitive touch receptors called tactile or merkel discs located at the epidermal-dermal junction
Dermis Layers (superficial to deep)
Papillary layer and Reticular layer
Dermis
Dense irregular connective tissue that varies in thickness.
Papillary layer
More superficial dermal region composed of areolar connective tissue. Contains dermal papillae, capillary networks, pain (free nerve endings) and touch receptors (tactile corpuscles in hairless skin)
Dermal papillae function
Attach the dermis to the epidermis, form the fingerprints
Reticular layer
Deepest skin layer composed of dense irregular connective tissue and contains many arteries and veins, sweat and sebaceous glands, and pressure receptors (lamellar corpuscles)
Hypodermis
Deep to the dermis, AKA superficial fascia, not considered part of the skin. Consists primarily of adipose tissue.
Eccrine Gland
AKA merocrine sweat glands, distributed all over the body. Produce a clear perspiration consisting primarily of water, salts (mostly NaCl), and urea. Under the control of the Nervous system, important for heat regulation.
Apocrine Gland
Found predominantly in the axillary and genital areas, secrete basic components of eccrine sweat plus proteins and fat-rich substances. Function unknown but thought to be the human equivalent of the sexual scent glands of other animals
Sebaceous Gland
Found nearly all over the skin except for palms and soles. Ducts usually empty into a hair follicle but some open on the skin surface. Produce Sebum which is a mixture of oily substances and fragmented cells that acts as a lubricant to keep the skin soft and moist and hair from becoming brittle.