Histology - Labs 17 & 18 - Female and Male Reproductive Systems Flashcards

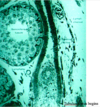
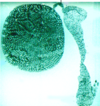
Cortical region of an ovary


Cortical region of an ovary
Note: primary follicles here are UNIlaminar


Unilaminar primary follicle in the process of becoming a multilaminar one

Pre-antral follicle


Multilaminar primary follicle

Granulosa cells undergoing mitosis in a multilaminar primary follicle
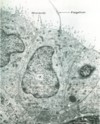
Note theca interna at the bottom of the image with capillaries

Graafian follicle

Wall of secondary follicle


Arrow at theca interna (above the theca externa) of secondary follicle

Wall of developing secondary follicle
- Zona pellucida in upper left corner
- Follicular cells fill most of the field
- Basement membrane (white at bottom) separating the granulosa cells from the theca interna (with RBC in a vessel in it)


Atretic follicle





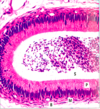
Wall of oviduct
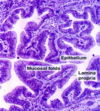

Epithelial lining of oviduct


Oviduct wall with ciliated and secretory cells
Note capillaries in lamina propria to form the transudate of the oviductal fluid

Oviduct wall with ciliated and secretory cells

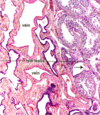
Cross section of uterus with 3 layers
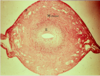

Uterus endometrium in secretory phase post-ovulation

Straight uterine glands in the deep endometrium during the proliferative phase + smooth muscle of the myometrium


Uterine glands in endometrium during the luteal phase


Cervix opening


Vagina
- a: non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- b: lamina propria
- Arrows: muscularis with smooth muscle


Bartholin’s glands