GA 3 gluteal region Flashcards
Superior and inferior boundaries of gluteal region
Iliac crest
gluteal sulcus (groove beneath gluteal fold)
What comes out and goes into the Greater sciatic foramen
(ALL EXIT)
- Gluteal neurovascular bundle
- Piriformis m.
- sciatic nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous
- Pudendal n. and internal pudendal a.
- Nerve to the obturator internus/superior gemellus
What comes out and goes into lesser sciatic foramen?
- Pudendal n. and internal pudendal a. (enter)
- Obturator internus/superior gemellus n. (enter)
- Obturator internus (exit)
Which ligaments create the greater sciatic notch and foramen?
the lesser sciatic notch and foramen?

What are the cutaneous nerves of the gluteal region?
cluneal nerves
Superior cluneal nerves nerve roots?
L1-L3 dorsal rami
Middle cluneal nerve roots?
S1-S3 dorsal Rami
INferior cluneal nerve roots?
S1-S3 ventral rami
What do the different cutaneous nerves of the gluteal region innervate?

What are the nerve roots for Superior gluteal n?
the inferior gluteal n.?
S- L4-S1
I- L5-S2
What are the nerve roots for the sciatic n. and its branches?
- Sciatic- L4-S3
- Tibial branch L4-S3
- Common fibular branch L4-S2
Where does the superior gluteal n. and inferior gluteal n. leave pelvis?
what do they run in between?
What do they supply?

Where does the sciatic leave the pelvis?
What does it run in between?
What does it not innervate?

What supplies more skin than any other cutaneous nerve?
Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve

What innervates the small lateral rotators?

Where does obturator internus/superior gemellus n. travel?

Pudendal nerve travels where?
Under piriformis
over obturator internus

What arteries branch from the internal iliac a?

What does this artery come from?
what does it supply?

Superior Gluteal artery
Largest internal iliac artery branch
- Superficial branch
- gluteus maximus
- Deep branch
- gluteus medius
- gluteus minimus
- tensor fascia lata
What does this artery come from?
What does it supply?

Comes from internal iliac a.
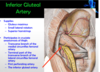
What allows for supply of muscles of leg if femoral artery is occluded?

the artery that is part of the PIN structures
travels where?
supplies what?



If you were to give an injection in the gluteal region where would you inject?


















