Forearm and hand Flashcards
Superficial and deep muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm?


Place your hand on the medial epicondyle.
Thumb represents the pronator teres, second finger=flexor carpal radialus, middle finger=palmarus longus, 4th=flexor digitorum superficialus (although considered to be in the superficial group it is actually under the palmarus longus), 5th=flexor carpiunlarus.
Common origin of the flexor muscles is the medial epicondyle therefore it is termed the common flexor origin.



Superficial and deep muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm?
(Where do they originate from?)



What are the bones and what is a pneumonic to remember it?
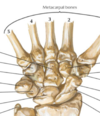
Some lovers try positions they cant handle.
She looks too pretty, try to catch her (proximal lateral to distal medial).

What type of joint is the wrist?
What movements does it allow?
What ligaments are associated with the wrist joint?

What are the two midcarpal joint types?

What are the muscles which act on the palmar and dorsal side of the wrist joint?
When the muscles with the dots acts together they can cause flexion, extension, adduction (medial/ulnar deviation) or abduction (lateral/radial deviation).

What are the joint types at the carpometacarpal joints?
(there are two of them so explain)

What are the movement types here?

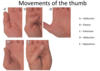
Adduction: when the thumb is toward the palm it is the adducted position.
Abduction: movement away from the palm.
Flexion: Thumb moving toward the palm is flexion.
Extension: Away from the palm is extension.
Opposition: fingertip to the thumb.
What type of joint is the metacarpophalangeal joint? Movements? Ligaments associated with the joint?
Palmar ligament and connected by a deep transverse metacarpal ligament (which prevents the metacarpal bones from separating).

What type of joint is the Interphalangeal joints? Movements? Ligaments associated with the joint?

What are the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles which cause movement of the thumb?

Boundaries of the anatomical snuff box?
What is contained in the anatomical snuff box?

Radial artery



All of the thenar muscles come off the ________ __________. All of the muscles will insert into the __________ _________ apart from the ________ which inserts into the ________ bone.
flexor retinaculum, proximal phalangeal joint, opponens which inserts into the metacarpal bone.



Extrinsic flexors of the fingers.

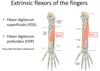
Flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus origin, insertion and function?



