(exam 2) ch 21 Microbial diseases of the skin and eyes Flashcards
what are the two primary parts?
1) Epidermis 2) Dermis
what is the epidermis?
Outermost portion contains rows of dead cells; thin outer portion of skin; composed of layers of epithelial cells
keratin?
waterproofing protein coating outer layer of epidermis
what is the dermis?
inner, thick portion of skin; composed mainly of connective tissue
what are three passageways for microbes?
1) hair follicles 2) sweat gland ducts 3) oil gland ducts
what is sebum?
secreted by oil glands contains fatty acids that inhibit pathogens (but, Some microbes can use sebum for growth)
what are mucous membranes (mucosa) ?
Sheets of tightly packed epithelial cells attached to an extracellular matrix (Cells secrete mucus and some cells have cilia) - often folded to maximize surface area
what is exanthem?
skin rash arising from a disease
what is enanthem?
rash on mucous membranes arising from a disease
what are vesicles?
small, fluid-filled lesions; less than 1 cm

what is bullae?
vesicles larger than 1 cm in diameter

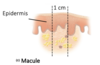
what are macules?
flat, reddened lesions; less than 1 cm
what are papules?
raised lesions
what are pustules?
raised lesions with pus

what two genera typically cause bacterial skin diseases?
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus frequently cause skin infections
what is Staphylococci?
spherical gram-positive bacteria; form irregular clusters

how are Staphylococcal skin infections clinically divided into two groups?
dependent on coagulase production
what is coagulase?
enzyme that clots fibrin in the blood
what is Staphylococcus epidermidis?
~90% of normal skin microbiota (Opportunistic pathogen); Healthcare-associated pathogen; Produces biofilm on catheters; Coagulase-negative
what is Staphylococcus aureus?
Carried in the nasal passages; Golden-yellow colonies (protects them from sunlight); Most pathogenic strains are coagulase-positive and these strains may also produce additional toxins; MRSA strains are antibiotic-resistant.
Staphylococcus aureus is often transported via Autoinoculation which means?
Infection caused by the spread of bacteria from one part of the body to another
what are two main types of Staphylococcus aureus infections?
- Hair follicle infections
- Impetigo
what is Folliculitis?
(Staphylococcus aureus- hair follicle infection) infections of hair follicles (often pimples)
what is a sty?
(Staphylococcus aureus – hair follicle infections) folliculitis of an eyelash
what is Furuncle (boil)?
(Staphylococcus aureus – hair follicle infections) more serious hair follicle infection; contains abscesses = which are localized region of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue (Difficult to treat; antibiotics don’t penetrate well)
what is a carbuncle?
hard, round inflammation of deep skin tissue; Caused from a spreading furuncle; Often causes general illness and fever
what is impetigo and what are the two types?
crusting sores; usually affects children (2-5yr); Highly contagious and spread by autoinoculation and direct contact. Two types, Nonbullous and Bullous
what is Nonbullous impetigo?
(Staphylococcus aureus - Impetigo) Most common; consists of isolated pustules; Typically heal w/o treatment

what is Bullous impetigo?
(Staphylococcus aureus - Impetigo) Caused by a toxin; Causes scalded skin syndrome; It is exfoliation/Separation of skin layers

what is Pemphigus neonatorum?
impetigo of a newborn
what is Scalded skin syndrome?
characteristic in late stages of toxic shock syndrome (TSS); TSS is often caused by S. aureus; Fever, vomiting, shock, and organ failure caused by toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) in the bloodstream
what are Streptococcal Skin Infections?
Gram-positive cocci in chains; Produce hemolysins that lyse red blood cells (Alpha-, beta-, and gamma-hemolytic streptococci)

what are Beta-hemolytic streptococci ?
Often cause disease and are differentiated into groups A through T based on antigenic cell wall carbohydrates
what are antigens?
foreign substance that causes an immune response
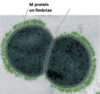
what are Group A streptococci (GAS)?
(most important group of Beta-hemolytic streptococci ) Almost exclusively Streptococcus pyogenes and among most common human pathogens; Divided into more than 80 immunological types (based on antigenic properties of M proteins and the M protein for GAS is external to cell wall on fimbriae)
what are the four virulence factors of Group A streptococci (GAS)?
1) Streptolysins: lyse RBCs
2) M proteins: allow adherence and immune system avoidance
3) Hyaluronidase: dissolves connective tissue
4) Streptokinases: dissolve blood clots
what is Erysipelas?
(Streptococcal skin infections) caused by S. pyogenes that infects the dermal layer of the skin; presentation includes reddish skin patches with raised margins; usually on face (infection may progress to local tissue destruction and sepsis)

what is Necrotizing fasciitis?
(Streptococcal skin infection) known as “Flesh-eating” disease; Causes rapid tissue destruction; S. pyogenes toxins act as superantigens (which cause extreme immune response)
what is Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome?
(Streptococcal skin infection) Similar to staphylococcal TSS; But here, M proteins shed from bacteria act as toxin
what is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
(Bacterial - Pseudomonads infection) it is a Gram-negative, aerobic rod that produces exo- and endotoxins for pathogenicity; Widespread growth in moist environments; Forms dense biofilms and are resistant to many antibiotics and disinfectants

what is Pseudomonas dermatitis?
(type of Pseudomonas aeruginosa) it is a self-limiting rash acquired in swimming pools
what is Otitis externa?
(a type of Pseudomonas aeruginosa) known as “Swimmer’s ear”
what is Pseudomonas aeruginosa in assosiation with HAIs? Which two types of patients are most at risk for this infection?
opportunistic pathogen; Because there are biofilms on indwelling medical devices; and it is especially dangerous for Cystic fibrosis patients and Burn patients
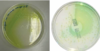
what is a “tell tell” sign or characteristic of P. aeruginosa infection on a plate?
Pyocyanin – which is a bacterial pigment; blue-green pus characteristic of P. aeruginosa infection
what is the most common bacterial skin disease in humans?
Acne; Typically skin cells shed from hair follicles; Acne occurs when cells combine with sebum causing blockages
what are Whiteheads (comedos)?
sebum/cell accumulation
what are Blackheads (comedones) ?
blockage protrudes through skin
what affects sebum formation?
Sebum formation is affected by hormones, not diet
what are three forms of acne?
- Comedonal (mild)
- Inflammatory (moderate)
- Nodular cystic (severe)
1) Comedonal (mild)
2) Inflammatory (moderate)
3) Nodular cystic (severe)
what is Comedonal (mild) acne?
This type of acne is not usually associated with bacterial infection and is easily treated with topical formations
what is Inflammatory (moderate) acne?
Caused by Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes); Metabolizes sebum (fatty acids produce an inflammatory response); Treated with antibiotics and benzoyl peroxide
what Nodular cystic (severe) acne?
Characterized by nodules or cysts; it is inflamed lesions with pus deep in the skin; Can result in scarring of face and upper body and is usually treated with drug treatment – isotretinoin

what are warts / papillomas?
(viral disease) small skin growths caused by papillomavirus; transmitted via contact; incubation period of several weeks; treated with cryotherapy, electrodesiccation, or salicylic acid

what is smallpox / variola virus?
(viral disease) Caused by Variola virus; Two forms of the disease (two virus variants), Variola major has 20–60% mortality and Variola minor has <1% mortality. Respiratory transmission, moves into the bloodstream, and infects the skin. Lesions become pustular after ~10 days

what is monkeypox virus?
Related to smallpox, Endemic to small animals in Africa it can jump from animals to humans. Prevention by the smallpox vaccination
Is smallpox still around?
No, it is eradicated from the human population by vaccination; There is no animal reservoir and the last case estimated was in 1977
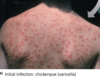
what is chickenpox / varicella?
Herpesvirus varicella-zoster (human alphaherpesvirus 3); Respiratory transmission with localized skin infection after ~2 weeks; Typically mild disease overall and causes pus-filled vesicles
What is Reye’s syndrome?
Severe complications of chickenpox; vomiting and brain dysfunction; can affect children and teenagers; and aspirin use increases risk
what is unique about chickenpox / varicella that leads to infection later in life?
After primary infection, virus becomes latent in dorsal root ganglion (near spine) so later (up to decades) the virus can reactivate, move along nerves, and cause a new skin infection. Often due to stress or lowered immunity.
what is shingles / herpes zoster?
(virus that infects year after inital infection with chickenpox) Follows the distribution of affected cutaneous sensory nerves; Typically limited to one side of the body and usually near waist; Disease state differs due to partial immunity; Unvaccinated children exposed to shingles get chickenpox. Typically occurs once and in older adults
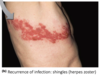
what is postherpetic neuralgia?
persistent burning and/or stinging nerve pain after shingles
is chickenpox (varicella) and Shingles (Herpes Zoster) still around today?
yes, there was a vaccine developed in 1995; it is a live, attenuated virus and is 97% effective but wanes over time. A breakthrough varicella – infection occurs after vaccination which consits typically of mild disease with rash. There is a boster vaccine for adults over 60
what is Herpes Simplex?
Human alphaherpesvirus 1 (HSV-1) and 2 (HSV-2); •Ninety percent of the U.S. population is infected with HSV-1; •Usually develop as cold sores or fever blisters.
what is HSV-1?
(Herpes Simplex) 90% of population and asymptomatic; HSV-1 remains latent in trigeminal nerve ganglia and outbreaks are triggered by the sun, stress, or hormonal changes
what is HSV-2?
(types of Herpes Simplex) Remains latent in sacral nerve ganglia near the spine
what is Herpes gladiatorum?
(HSV-2) vesicles on the skin (common in wrestlers)
what is Herpetic whitlow?
(type of HSV-2) vesicles on the fingers (seen amoung healthcare workers)
what is Herpes encephalitis?
(type of HSV-2) virus spreads to the brain
how are herpes simplex (specifcally HSV-1 and HSV-2)?
Treated with acyclovir
what is Measles (Rubeola)
caused by Measles morbillivirus; Respiratory transmission and is extremely contagious; Causes cold-like symptoms, macular rash; Koplik’s spots (diagnostic indicator); Particularly dangerous in infants and elderly

what are Koplik’s spots and what disease do these spots indicate?
Red spots on the oral mucosa opposite the molars; it is a diagnostic indicator for Measles (Rubeola)
what is Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis?
Rare; occurs 1 to 10 years after measles recovery; causes severe neurological symptoms and death
Are Measles (Rubeola) still around today?
Yes, but it is prevented by the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine which is 95% effective; Children under 1 year old cannot receive the vaccine and it is not reccomended for pregnant people.
what is Rubella (German Measles)?
caused by Rubella virus; Milder than measles; Macular rash and light fever. Respiratory transmission with a 2- to 3-week incubation

what is Congenital rubella syndrome?
Fetal damage due to Congenital rubella syndrome which can cause deafness, heart defects, mental retardation in 35% of cases and 15% mortality within first year of life
what prevents both Rubella (German measles) and Congenital rubella syndrome?
Prevented by the MMR vaccine which is not recommended for pregnant women
what is Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum)?
(viral disease) caused by parvovirus B19; mild flulike symptoms; “slapped-cheek” facial rash
what is Roseola?
(viral diease) Human herpesviruses 6 and 7; causes high fever; body rash; recovery usually is within 1 to 2 days
what is Hand-foot-and-mouth disease?
(viral disease) caused by enteroviruses; It is spread via mucous or saliva; Causes fever and sore throat; rash on the hands, feet, mouth, and tongue
what is Mycosis?
fungal infection of the body
what is cutaneous mycoses?
Colonize the hair, nails, and outer epidermis and metabolize keratin
what are dermatomycoses?
Informally known as tineas or ringworm; there are four different kinds and treatment is usually topical drugs (miconazole and clotrimazole)
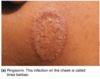
what is Tinea capitis?
(type of dermatomycoses) scalp ringworm
what is Tinea cruris?
(type of dermatomycoses) jock itch
what is Tinea pedis?
(type of Dermatomycoses) athlete’s foot
what is Tinea unguium?
(type of Dermatomycoses) ringworm of nails
what is Subcutaneous Mycoses?
(fungal disease) More serious than cutaneous mycoses; can penetrate the stratum corneum and is usually caused by fungi that inhabit the soil.
what is Sporotrichosis?
related to Subcutaneous Mycoses; it is when it enters a wound; forms a small ulcer; Treated with potassium iodide
what is Candidiasis?
(fungal disease) Overgrowth of Candida albicans (yeast) - Forms pseudohyphae, making it resistant to phagocytosis; Occurs in the skin and mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract and mouth. Results when antibiotics suppress competing bacteria or a change occurs in the mucosal pH
What is thrush?
C. albicans infection of the oral cavity
what do we know about fulminating disease in the immunosuppressed?
Appears suddenly and severely
what is Scabies?
(Parasitic Infestation of the Skin) Caused by Sarcoptes scabiei mites; Burrow into skin to lay eggs causes intense local itching; Causes inflammatory skin lesions; can cause secondary infections from scratching; Transmitted via intimate contact; Treatment with permethrin (topical)
What is Pediculosis (Lice)? Feed on blood from the host; Itching due to sensitization from saliva; They lay eggs (nits) on the hair and attach to the shafts; Treatment with topical insecticides (permethrin or pyrethrin)
what is Pediculus humanus capitis?
(parasitic disease) head louse?
what is P. h. corporis?
(parasitic diseases) body louse
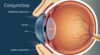
what is the Conjunctiva?
Epithelial cells covering the eye that are considered a continuation of the skin or mucosa; covers outer surface of the eye and lines the eyelid; it is a mucous membrane
what is Conjunctivitis?
(microbial disease of the eye) aka. red eye or pinkeye; it is inflammation of the conjunctiva; commonly caused by (Haemophilus influenza, Pseudomonads, or Adenoviruses); Associated with unsanitary contact lenses

what is Ophthalmia Neonatorum?
(bacterial disease of the eye) Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Transmitted to a newborn’s eyes during passage through the birth canal; Large amount of pus forms and ulceration of corneas results- Untreated cases may lead to blindness! Prevented by treating a newborn’s eyes with antibiotics
what is Inclusion Conjunctivitis (chlamydial conjunctivitis)?
(bacterial diseases) Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis (Serotypes D-K); less servere; Transmitted to newborn’s during birth; spread through unchlorinated pool water; Treated with tetracycline
What is Trachoma?
(Bacterial diseases) Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis (Serotypes A-C); Transmitted via hand contact; Disease progression = Repeated infection causes conjunctivitis leading to trichiasis (in-turning of eyelashes)- Eyelashes abrade and scar cornea leading to blindness. This is the leading cause of blindness worldwide; Oral azithromycin are used in treatment.

what is Keratitis? and what is the cause in US compared to the cause in Africa and Asia?
Inflammation of the cornea - Bacterial (United States) and Fungal (Africa and Asia)
what is Herpetic keratitis?
(infectious disease) Caused by herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1); Infects cornea and may cause blindness; Treated with trifluridine
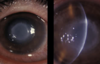
what is Acanthamoeba keratitis?
(infectious disease of the eye) Mild inflammation followed by severe pain; Ameba transmitted via water and soil; Associated with unsanitary contact lenses; Treatment with 2% chlorhexidine and propamidine isethionate eye drops or topical neomycin. May require a corneal transplant.