Endo/Repro - Physiology - Hormones Flashcards
Describe some of the classifications of hormones based on their starting point and mode of travel.

Endocrine cells typically release peptide hormones in response to increased intracellular concentrations of what substance?
Does this increase or decrease protein phosphorylation and microtubule action?
[cAMP] + [Ca2+]
(and the associated fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane);
increase
Peptide hormone -coding mRNA is translated on the ER to ____________ and then processed via signal peptide cleavage in the ER to ____________.
What happens next?
Preprohormones,
prohormones;
post-translational modifications (e.g. phosphorylation, glycosylation) in the Golgi

Where are preprohormones synthesized from mRNA?
Where are prohormones then produced? How?
What happens next?
ER,
signal peptide cleavage;
post-translational modifications and processing in the Golgi

Thyroid hormones are synthesized from what precursors?
Steroid hormones are synthesized from what precursors?
Tyrosine + iodide;
cholesterol
In which glands are steroid hormones stored?
They are not stored in any appreciable quantity.
Which is more common, genetic causes of peptide hormone disorders or steroid hormone disorders?
Steroid hormone disorders
(usually defects in the enzyme pathyway from cholesterol to the specific hormone)
How do most genetic steroid hormone disorders occur?
How do most genetic peptide hormone disorders occur?
Mutations in the enzymes in the synthetic pathways;
mutations in the hormones themselves
__________ hormones are released from cells via exocytosis.
Peptide

What cytoskeletal structures in particular are necessary for peptide hormone secretion (via exocytosis)?
Microtubules,
microfilaments

An increase in what cellular content(s) will cause exocytosis of peptide hormones from endocrine organs?
cAMP,
Ca2+

Peptide hormones are released from endocrine organs directly into:
The interstitial space

How does an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and cAMP cause increased peptide secretion from endocrine cells?

Increased protein phosphorylation and microtubule activation
(Ca2+ also activates myosin light-chain kinase, promoting granule movement)

Describe how intracellular Ca2+ increases peptide hormone exocytosis in endocrine tissues via its interactions with MLCK.

True/False.
Both negative and positive feedback systems are involved in virtually all levels of endocrine cell functions.
True
(i.e. transcription, translation, secretion)
At steady state, what is a hormone’s metabolic clearance rate?
The mass of hormone removed per unit time
/
plasma concentration of the hormone

What is the equation for metabolic clearance rate?

What organs are the main locations of hormone degradation?
Liver;
kidneys
True/False.
Virtually all peptide hormone degradation is via proteolysis.
False.
Example processes include: proteolysis, oxidation, reduction, hydroxylation, decarboxylation, methylation, etc.
In hormone kinetics, what are meant by H, R, and HR?
H - free hormone
R - free receptor
HR - hormone-bound receptor
At equilibrium (in hormone kinetics), KAssoc =
KAssoc = [HR] / [H][R]
(also = 1 / Kdissoc)
In hormone kinetics, what is represented by R0?
Initial receptor capacity
(R + HR)
What is a Scatchard plot?
What shape does it display?
A graph representing the ratio of bound hormone to free hormone;
theoretically, a straight line —
— in practice, an exponential curve

The slope of the line in a Scatchard plot is:
The intercept of the line in a Scatchard plot is:

- KAssociation
(i. e. Kd)
R0 (receptor number)
True/False.
A small amount of membrane receptors can often yield the maximum response offered by a peptide hormonal system.
True.
(Limits are in place as to how high the maximal effect can be.)
Which is limited in effect by receptor number? (I.e. more receptors = more effect)
Which is fully activated at a low receptor occupancy? (I.e. more hormone won’t make a difference)
Steroid hormones;
peptide hormones
Which has spare receptors that aren’t being used, peptide or steroid hormones?
Which is limited by the number of spare receptors that are available for use, peptide or steroid hormones?
Peptide (fully activated system at low hormone-receptor occupancy);
steroid (more receptors = more effect)
List some of the major intracellular secondary messengers induced by hormonal action.
cAMP
cGMP
Ca2+
IP3
diacylglycerol
What might occur if a tissue is chronically overstimulated by hormone input?
Downregulation of receptors
(desensitization)
What intracellular secondary messenger is increased by ANP binding?
cGMP
(via guanylyl cyclase)
What intracellular secondary messenger is increased by nitric oxide binding?
cGMP
(via guanylyl cyclase)
What GPCR increases intracellular cGMP?
What does cGMP then activate?
Guanylyl cyclase;
cGMP-dependent protein kinase
What are the two main ways in which hormone response curves can change?
How does the curve change in either option?

Changes in:
sensitivity (left- or right-shift)
or
maximal responsiveness (shifts Vmax up or down)

What two tests are very sensitive for amounts of hormone?
What is the drawback to these tests?
Radioimmunoassays, ELISA;
both measure antigenic amount of hormone, not necessarily biologically active hormone
Are radioimmunoassay and ELISA testing more likely to underestimate or overestimate biologically active hormone concentrations?
Overestimate
(because it measures non-active with active)
What is the specific drawback of radioimmunoassays in measuring hormone levels?
What test avoids this drawback with no loss in sensitivity?
Radiation;
ELISA
What are the three portions of the adenohypophysis?
Describe where they are.
Pars distalis
Pars tuberalis
Pars intermedia

What are the three portions of the neurohypophysis?
Median eminence
Infundibulum
Pars nervosa

What three portions of the hypothalamus release corticotropic hormones?
The paraventricular nucleus,
medial preoptic nucleus,
and arcuate nucleus
What two portions of the hypothalamus send hormones to the neurohypophysis?
The paraventricular nucleus,
the supraoptic nucleus
What is found within the median eminence of the pituitary?
The neurovascular region connecting the hypothalamus to the adenohypophysis

What type of circulation connects the adenohypophysis to the median eminence?
A portal system

(capillary bed draining into capillary bed)
Describe the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system.

List the hormonal release triggered by each of the following:
GnRH
TRH
CRH
GHRH
GnRH: LH, FSH;
TRH: TSH, prolactin;
CRH: ACTH;
GHRH: GH
List the corticotropic hormone that causes the release of each of the following:
LH
GH
Prolactin
TSH
ACTH
FSH
LH: GnRH
GH: GHRH
Prolactin: TRH
TSH: TRH
ACTH: CRH
FSH: GnRH
Release of what hormone(s) of the anterior pituitary is inhibited by somatostatin?
GH;
TSH
Release of what hormone(s) of the anterior pituitary is inhibited by dopamine?
Prolactin
(dopamine also known as prolactin-inhibiting factor)
What are the five cell types of the adenohypophysis (in order of decreasing quantity)?
Somatotrophs
Mammotrophs
Corticotrophs
Gonadotrophs
Thyrotrophs
Cellular differentiation in the anterior pituitary is mediated by what transcription factor?
Pit-1
True/False.
Anterior pituitary secretion is near-continuous to meet the body’s continous basal metabolic needs.
False.
Anterior pituitary secretion is pulsatile.
The pituitary gland sits within what bony structure of the _________ bone?
Sella turcica;
sphenoid
True/False.
The anterior pituitary is derived from the fetal neuroectoderm.
False.
The anterior pituitary is derived from the fetal foregut.
What cell type of the adenohypophysis secretes LH and FSH?
Gonadotrophs

What cell type of the adenohypophysis secretes thyrotropin (TSH)?
Thyrotrophs

What cell type of the adenohypophysis secretes growth hormone and somatotropin?
Somatotrophs

What cell type of the adenohypophysis secretes prolactin?
Mammotrophs

What cell type of the adenohypophysis secretes adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)?
Corticotrophs

What type of cell in the adenohypophysis is most abundant? What proportion does it make up?
What three types of cell are next most abundant?
What type of cell in the adenohypophysis is least abundant?
Somatotrophs (50%)
gonadotrophs, corticotrophs, mammotrophs (15% each)
thyrotrophs (5%)

What substances stimulate ACTH secretion from the adenohypophysis?
What are a few positive modulators for this process?
CRH, ADH;
norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and 5-HT
What substances inhibit ACTH secretion from the adenohypophysis?
What are a few negative modulators for ACTH release?
Cortisol, brain natriuretic peptide;
ACTH, endorphins, GABA
Cortisol inhibits which portions of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis?
CRH and ACTH release
What disease is characterized by primary adrenal insufficiency?
Addison’s disease
CRH and ACTH both increase intracellular levels of what enzyme (leading to all other downstream effects)?
PKA
Growth hormone shares homology with what other pituitary hormone?
Prolactin
True/False.
Most of the cells of the adenohypophysis secrete some level of GH.
True.
Pulsatile ______ increases GH release from the adenohypophysis.
Pulsatile ______ decreases GH release from the adenohypophysis.
______ also decreases GH release from the adenohypophysis.
GHRH;
somatostatin;
IGF-1 (increases somatostatin release)
What is the main effect of growth hormone?
Stimulation of postnatal growth
Prolactin release from the adenohypophysis is mostly stimulated by what substance?
Prolactin release from the adenohypophysis is mostly inhibited by what substance?
TRH;
dopamine (PIF)
Which adenohypophyseal hormones are all members of the glycoprotein hormone family?
FSH, LH, TSH, β-HCG
TSH, LH, FSH, and β-HCG are each made of ___ subunits.
Which gives the specificity?
2;
β

Which hormone produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid inhibits TRH and TSH release?
T3
True/False.
FSH and LH decrease after menopause.
False.
They increase.
Name the precusor to ACTH.
What else does this precursor become?
Proopiomelanocortin;
β-endorphins, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone
How many pulses of GnRH per hour are required to maintain baseline levels of both LH and FSH?
1 per hour

Less frequent GnRH pulses (1 per 3 hours) stimulates what?
More frequent GnRH pulses stimulates what?
FSH secretion;
LH secretion

What substance selectively inihibits FSH secretion?
Inhibin
LH secretion is mediated by _______ GnRH pulses.
FSH secretion is mediated by _______ GnRH pulses.
Fast;
slow
Name the respective tropic hormone responsible for increasing release of each of the following:
Prolactin
LH
TSH
GH
FSH
ACTH
TRH
GnRH
TRH
GHRH
GnRH
CRH
Name the respective adenohypophyseal hormones released by stimulation from the following tropic hormones:
TRH
GnRH
GHRH
CRH
TSH, prolactin
FSH, LH
GH
ACTH
What transport protein(s) carry oxytocin and ADH from the hypothalamus to the neurohypophysis?
Neurophysin I (oxytocin)
neurophysin II (ADH)
ADH and oxytocin secretion is mainly mediated via:
Neuronal input
Is transport from the hypothalamus to the neurohypophysis slow or fast transport?
Fast
(mm / hour)
True/False.
The paraventricular nucleus produces only oxytocin and the supraoptic nucleus produces only ADH.
False.
The paraventricular nucleus produces mainly oxytocin and the supraoptic nucleus produces mainly ADH, but both produce a small quantity of the alternate hormone.
True/False.
Both the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei each produce both ADH and oxytocin.
True.
(at least in small amounts)
ADH and oxytocin are released from what portion of the neurohypophysis?
The pars nervosa
What are pituicytes?
Glial cells of the neurohypophysis
Are the axons found in the pars nervosa of the neurohypophysis myelinated or unmyelinated?
Unmyelinated
What are the main functions of ADH?
Increased renal H2O reabsorption;
systemic vasoconstriction (at pharmacological doses)
What are the main functions of oxytocin?
Uterine contraction;
mammary gland myoepithelial contraction;
bonding
ADH and oxytocin are both ___ amino acids in length.
They only differ in ___ amino acid residues.
9;
2
The similarity in structure between ADH and oxytocin means what?
They may have overlapping effects
What are some examples of the types of injury can disrupt the neuronal tracts that transport ADH and oxytocin?
Is regeneration of these axons possible?
Trauma, tumor, surgery;
yes
ADH binds what two receptors?
(What does each do?)
V1 (vasoconstriction)
V2 (vasodilation; renal H2O reabsorption)
What renal effects does ADH cause via the V2 receptor?
1) Reabsorption of NaCl via stimulation of Na/K/2Cl co-transport in the thick ascendening limb
2) Increase the permeability of the collecting duct to urea
3) Increase permeability of the collecting ducts to H2O
What effect does ADH have on cortisol levels?
ADH stimulates release of ACTH
The supraoptic nucleus mainly secretes:
The paraventricular nucleus mainly secretes:
ADH
oxytocin
What is the main stimulus for ADH secretion?
What are two others?
Increased plasma osmolarity
hypovolemia, increased CSF [Na+]
(also, nausea, angiotensin II, temperature increase, nicotene, histamine, bradykinin)
What is the main inhibitory stimulus preventing ADH secretion?
What are two others?
Decreased plasma osmolarity
normo- or hypervolemia, decreased CSF [Na+]
(also, EtOH, ANP, temperature decrease, norepinephrine)
What effect does EtOH ingestion have on ADH secretion?
Inhibition
What are the primary S/Sy of diabetes insipidus?
What are some others?
Polyuria (5-15 L/day), polydipsia;
hypernatremia, increased serum osmolality (290 - 295 mOsm/Kg), muscle weakness, fever, hypoosmotic urine
What are the main electrolyte and osmolality changes seen in diabetes insipidus?
Hypernatremia;
increased serum osmolality (290 - 295 mOsm/Kg)
What are the two types of diabetes insipidus?
Central;
nephrogenic
A patient presents with a 2-week history of polyuria and polydipsia. You suspect diabetes insipidus. This needs to be differentiated from what other potential causes?
Diabetes mellitus,
psychogenic polydipsia/polyuria
What are some potential causes of central diabetes inspidus?
Destruction of hypothalamic nuclei
(tumors, trauma, surgery);
inherited
(neurophysin mutation)
What are some potential causes of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus?
Chronic kidney disease,
ADH receptor or aquaporin2 deficiency,
drugs (lithium)
What test results can be used to diagnose central diabetes insipidus?
Water deprivation test (urine osmolality will not increase);
desmopressin test (urine osmolality will increase)
What is the main therapy for central diabetes insipidus?
Desmopressin
(vasopressin analog)
What are the S/Sy of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)?
Most patients have no signs (no peripheral edema, no signs of dehydration);
hyponatremia below 110 mmol/l –> weakness, lethargy (leading to coma)
What are some potential causes of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)?
Para-neoplastic syndromes (lungs, pancreas, lymphoma);
non-neoplastic lung disease (COPD, pneumonia, TB);
brain disorders (tumors, encephalitis, meningitis, hemorrhage);
certain drugs (antidepressants, diuretics, narcotics)
Describe the expected lab results in a patient with SIADH.
Hypervolemia,
low Serum osmolality (<270 mOsm/kg),
hyponatremia (<130 mmol/l),
hypertonic urine (>300 mOsm/kg),
increased urine [Na+] (>20mmol/l)
What are the main treatment options for SIADH?
Water restriction;
medications to block V2 receptors
On routine labwork in an asymptomatic patient, you notice that they are hyponatremic and their urine is hypertonic. What do you suspect?
SIADH
Oxytocin causes contraction of smooth muscle in what two locations in particular?
Breast myoepithelial cells;
the uterus
What clinical uses does pitocin (oxytocin) have in the peripartum period?
To induce labor;
to stop uterine bleeding after labor
The actions of oxytocin are augmented by what endogenous substance and blocked by what other endogenous substance?
Estrogen;
catecholamines
Which is involved in the let-down reflex in breastfeeding, oxytocin or prolactin?
Oxytocin
Is milk ejection during breastfeeding by positive or negative pressure or both?
(I.e. does the breast use positive pressure to eject the milk or does the infant create negative pressure and draw it out?)
Positive pressure
(myoepithelial cell contraction in response to suckling)
True/False.
Milk ejection from the breast is psychogenic.
True.
After the completion of childhood and puberty, what effect/role does GH still have?
Modulating metabolism
True/False.
Patients with acromegaly or those being treated with GH are at an increased risk of tumor development (and cardiovascular hemorrhage at higher doses).
True.
Is GH a steroid or peptide or other type of hormone?
Peptide
What organ secretes IGF-1?
What effect does this substance have on the adenohypophysis?
The liver;
inhibit GH release (along with somatostatin)
(IGF-1 is also known as somatomedin)
What stimuli increase GHRH secretion?
What stimuli decrease GHRH secretion?
Sleep, stress, fasting;
glucose, free fatty acids, GHRH
GHRH increases what intracellular secondary messengers in somatotrophs?
Ca2+, cAMP, IP3
True/False.
Thyroid hormones, cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone all synergistically decrease GH synthesis and release.
False.
Thyroid hormones, cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone all synergistically increase GH synthesis and release.
What two factors increase somatostatin release from the adenohypophysis?
GH;
somatomedin (IGF-1)
What generic growth types are increased by GH action?
Linear growth,
organ size,
lean body mass
What effect does GH have on IGF-1 secretion by the liver?
An increase
True/False.
An amino acid-rich meal increases GH release.
True.
True/False.
GH levels are higher in children and adolescents than adults.
True.
(Peak during puberty)

Name some of the effects of GH on adipose tissue, muscle, and the liver.

Name some of the diverse effects of GH and IGFs on tissues besides the liver, muscle, and adipose tissues.

Is somatostatin a steroid or peptide hormone?
Peptide
What effect does somatostatin have on GHRH-secreting cells of the hypothalamus?
Decreased intracellular cAMP and Ca2+;
decreased frequency/amplitude of GHRH pulses
What is the main stimulating substance for GH release?
What is the main inhibiting substance for GH release?
GHRH;
somatostatin
What effect does obesity have on GH levels?
A reduction in GH responses to all stimuli, including GHRH
Name a few stressors that can increase GH release.
Exercise, trauma, surgery, anesthesia, fever
True/False.
A morning surge in GH occurs at 1-2 hours after waking.
False.
A nocturnal surge in GH occurs at 1-2 hours after the onset of deep sleep.
What are two signs of a childhood GH deficiency?
Short stature, moderate obesity
True/False.
All of the following are effects of administration of GH to GH-deficient children:
Enhance positive nitrogen balance
Decrease urea production
Redistribute fats
Reduce carbohydrate utilization
(does not increase the incidence of diabetes mellitus)
True.
What effect does GH replacement for GH-deficient children have on adiposity?
Decreased
GH activates what receptor type?
JAK-STAT tyrosine kinases
Insulin-like growth factors (a class of peptide hormone) are also known as what?
Somatomedins
GH promotes the synthesis of what two substances in many tissues?
Where do most protein-bound, circulating IGFs originate?
IGF-1, IGF-2;
the liver
True/False.
IGFs inhibit tissue growth.
False.
IGFs mediate the process of growth.
GH stimulates the transformation of ____________ into chondrocytes, which then start secreting _____.
Prechondrocytes,
IGF-1
How does GH influence longitudinal bone growth?
It increases chondrocyte maturation;
the chondrocytes secrete IGF-1;
stimulates clonal expansion in endochondral growth plates

Administration of IGFs to GH-deficient children or adults decreases plasma amino acid levels due to enhanced ______________.
Protein synthesis
What effect do GH and IGF have on body composition?
Lean body mass increases,
fat mass decreases,
bone formation is enhanced
What effect do GH and IGF have on body metabolism and function?
Increased:
BMR, exercise capacity, sense of well-being
GH and IGF increase the secretion of what two ECM substances in particular?
Collagen, chondroitin sulfate
GH stimulates synthesis of what substances in almost all cell types?
DNA, RNA, protein
True/False.
GH and insulin work synergistically.
False.
GH increases insulin expression but opposes insulin action.
GH decreases glucose uptake by what tissue types?
GH increases catabolism of what macronutrient type?
Muscle, adipose;
lipids
What effect does GH have on adipose tissue and free fatty acids?
Free fatty acids (and ketones) increase;
adipose tissue decreases
GH can be considered a ________genic hormone.
Diabeto-
While GH and insulin have many opposing effects, what effect do they share?
Increased IGF production, leading to increased lean body mass
What vital role does GH play in opposing insulin?
Preventing hypoglycemia
If [GH] is high and [insulin] is low, what will IGF be?
Low
(requires both)
True/False.
Acromegaly diagnosis can be delayed 15 - 20 years until onset of clinically noticable S/Sy.
True.
True/False.
Prolactin is glycosylated in the Golgi and then deglycosylated in the ER.
False.
Prolactin is glycosylated in the ER and then deglycosylated in the Golgi.
Besides dopamine, what other two factors inhibits prolactin secretion?
Somatostatin,
GnRH
True/False.
Prolactin secretion is only possible when the hypothalamus is closely connected to the adenohypophysis.
False.
Disruption of pituitary connections to the hypothalamus leads to a great increase in prolactin secretion
What effect does prolactin have on hypothalamic function?
It inhibits GnRH secretion
A 46 year old African-American male presents himself to a primary care physician for evaluation of sudden weight loss. He complains of palpitations and racing heart beats. He always feels warm and nervous with shaky hands. He is irritable, fatigued, apprehensive, and unable to concentrate.
Make the diagnosis.
Hyperthyroidism
Describe the general histology of thyroid follicles.
Cuboidal, single-layered circular follicles;
the follicular lumen contains colloid material (hormone storage)
What is the main hormone secreted from the thyroid?
What is secreted in smaller quantities?
Tetraiodothyronine (T4);
triiodothyronine (T3)
Which thyroid hormone is biologically active?
T3
What are the two main substrates for thyroid hormone synthesis?
Tyrosine + iodide
What are the main steps of thyroid hormone synthesis?
- Uptake / concentration of iodide
- Oxidation of tyrosine residues with iodide
- Coupling of two iodinated tyrosine residues
Where does thyroid hormone synthesis occur?
The thyroid follicles
The tyrosine residues to be iodinated in thyroid hormone synthesis are held as links of what peptide?
Thyroglobulin
What enzyme iodinates thyroglobulin during thyroid hormone synthesis?
Thyroid peroxidase
After thyroglobulin is iodinated in thyroid follicles, what occurs next?
Proteolytic cleavage of thyroid hormones from thyroglobulin
Where is the majority of T3 produced?
Target tissues
(converted from T4)
Via what mechanism is iodide transported into follicular cells of the thyroid?
Na+-cotransport
(secondary active)
What is the chemical formula for iodide?
I-
Na+-I- cotransport (secondary active transport) into thyroid follicular cells is known as:
Iodide trap
True/False.
The iodide trap (sodium-iodide cotransport into thyroid follicular cells) leaves a larger concentration of iodide in the plasma than the follicular cells.
False.
The iodide trap (sodium-iodide cotransport into thyroid follicular cells) leaves a much larger concentration of iodide in the follicular cells than in the plasma.
What two tyrosine residues are produced from thyroid peroxidase activity acting on thyroglobulin?
Monoiodotyrosine;
diiodotyrosine
What enzyme found in the thyroid contains heme?
Thyroid peroxidase
One molecule of T3 is made from a molecule of ____________ being coupled to a molecule of ____________.
One molecule of T4 is made from a molecule of ____________ being coupled to a molecule of ____________.
Diiodotyrosine + monoiodotyrosine;
diiodotyrosine + diiodotyrosine
What is the ratio of T4 to T3 in the thyroid?
10:1
Where are iodinated thyroglobulin stored?
The thyroid colloid
How do iodinated thyroglobulin leave the thyroid follicular lumen?
Via what receptor?
Endocytosis;
megalin
Once iodinated thyroglobulin is reabsorbed into thyroid follicular cells from the thyroid colloid, what happens next?
Lysosomal enzymes release T4 and T3 from thyroglobulin
(T4 and T3 are then released from the cells into the capillary blood)
What happens to unused monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine in the thyroid?
Deiodinase removes the iodide for reuse
What type of drug blocks thyroid peroxidase?
Thiouracils
What type of drug is used to treat hyperthyroidism?
Via what mechanism?
Thiouracils;
inhibition of thyroid peroxidase
True/False.
Iodine can be used to treat hyperthyroidism.
True.
(Both as radioactive iodine and to inhibit T3 and T4 release.)
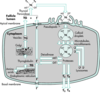
Describe how iodide is absorbed / thyroid hormones formed / thyroid hormones secreted in thyroid follicular cells.

Describe if each of the following occur within the thyroid follicular cell or at the interface of the apical membrane and colloid:
Iodide Trap
Thyroglobulin Synthesis
Iodination
Coupling
Proteolytic Cleavage
Iodide Trap - Intracellular
Thyroglobulin Synthesis - Intracellular
Iodination - Colloid
Coupling - Colloid
Proteolytic Cleavage - Intracellular
(See image for clarification.)
True/False.
Iodide is coupled to free tyrosine residues in the colloid to form monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine.
True/False.
Iodide is coupled to thyroglobulin tyrosine residues in the colloid to form monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine.

Thyroglobulin tyrosine + one iodide atom =
Thyroglobulin tyrosine + two iodide atoms =
Thyroglobulin tyrosine + one iodide atom = Monoiodotyrosine
Thyroglobulin tyrosine + two iodide atoms = Diiodotyrosine
What two products can result from one monoiodotyrosine molecule being coupled with one diiodotyrosine molecule in the thyroid colloid?
T3;
reverse T3

The TRH gene codes for the amino acid sequence glutamine-histidine-proline-glycine. How is this peptide turned into TRH?
Removal of the glycine
(TRH = glutamine-histidine-proline)
True/False.
Plasma TRH desensitizes / down-regulates its receptor to diminish its effectiveness on thyrotrophs.
True.
Which actions of the thyroid follicular cells are controlled by TSH?
Virtually all of them

i. Iodide trapping
ii. T4 and T3 synthesis
iii. Colloidal endocytosis
iv. Proteolytic release of T4 and T3 from the gland.
iv. Metabolism and growth of thyroid cells
An iodine deficiency or defect in thyroid hormone production lead to what effect as a result of chronically elevated TSH levels?
Goiter
(TSH stimulates follicular cell growth and replication as well as hormone production)
Why does hypothyroidisim result in increased thyroid size (goiter) if thyroid function is decreased?
Elevated TSH –>
stimulates follicular cell growth and replication as well as hormone production
True/False.
Primary hypothyroidism can lead to a diminished size adenohypophysis even as it leads to an enlarged thyroid (goiter).
False.
Primary hypothyroidism can lead to an enlarged adenohypophysis (increased number of thyrotrophs) as it leads to an enlarged thyroid (goiter).
Besides thyroid hormones, what are some other substances that decrease TSH release from the adenohypophysis thyrotrophs?
Dopamine, somatostatin, cortisol, growth hormone
True/False.
T3 and T4 circulate freely in the bloodstream.
False.
They circulate bound to thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) (20%), albumin, and transthyretin.
T3 and T4 circulate in the bloodstream bound to what substances?
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) (20%),
albumin,
transthyretin
How does the body buffer against acute changes in thyroid function?
Excess T4 circulates as a reservoir bound to thyroxine-binding globulin and transthyretin
Free T4 / Bound T4 =
Free T4 / Bound T4 = 1 / KEq [TBG]
True/False.
About 3% of total T4 and T3 are in the free state and available for use.
False.
About 0.03% of T4 and 0.3% of T3 are in the free state and available for use.
What are some examples of disorders that can affect thyroid function by changing [thyroxine-binding globulin]?
Acute hepatic disease;
pregnancies, estrogen therapy;
kidney disease
T4 has only ___% of the hormonally activity of T3.
What enzyme converts T4 to T3?
25%
5-monodeiodinase
What are the three major target tissues of thyroid hormone?
Liver,
kidney,
skeletal muscle
Does cellular uptake of T3 and T4 require energy expenditure?
Where in the cell do these hormones exert their effects?
Yes;
the nucleus (affecting gene expression)
Describe the effects of thyroid hormone on metabolism.

Describe the effects that increased thyroid hormone has on each of the following:
Thermogenesis
Sweating
Blood flow
BMR
Ventilation
O2 consumption
Increased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Thyroid hormone is especially important in the fetal development of what two organ systems?
Brain,
bone
What effect does thyroid hormone have on cardiac activity?
Increased cardiac stroke volume, heart rate, systolic blood pressure;
decreased diastolic blood pressure
What is the main mechanism by which thyroid hormone increases mitochondrial O2 consumption?
Increased Na+/K+ ATPases
What is the effect of thyroid hormone on the kidneys?
Increased kidney size, renal plasma flow (RPF), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and transport in kidney tubules
True/False.
Thyroid hormone increases catabolism of vitamins, steroid hormones, and many drugs.
True.
What are the general S/Sy of hyperthyroidism?
Elevated heart rate,
sweating,
heat intolerance,
thirst,
increased thirst,
muscle weakness,
osteoporosis
List a few causes of hyperthyroidism.
1. Grave’s disease (autoantibodies stimulate TSH receptors)
2. Benign thyroid neoplasm
3. Thyroid inflammation
4. Ingestion of thyroid hormone or excess iodide
5. Elevated TSH
List a few treatments for hyperthyroidism.
Surgery,
β-blockers,
short-term iodine excess,
thiouracils,
radioactive iodine
Describe some general S/Sy of hypothyroidism seen in either adults or children.
Cold intolerance,
decreased sweating,
dry skin,
low cardiac output,
weight gain
Describe the clinical S/Sy of cretinism.
Mental retardation, delayed body development;
lethargy, growth retardation, and poor performance
What is the most common cause of goiterous hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
What antibody is the main cause of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Anti- (thyroid peroxidase) antibodies
True/False.
Mutations in thyroid hormone signal transduction can result in clinical hypothyroidism.
True.
From external to internal, what are the three layers of the adrenal cortex?
*Which is largest?
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata*
Zona reticularis
What is the main product of the zona glomerulosa?
What is the main product of the zona fasciculata?
What is the main product of the zona reticularis?
Aldosterone (mineralocorticoids)
Cortisol (glucocorticoids)
DHEA (androgens)
True/False.
Fetal adrenal glands are very functional, and the glands grows rapidly after birth.
False.
Fetal adrenal glands are very large, and the glands reduce in size rapidly after birth.
The functional cells of the adrenal medulla are known as what?
Pheochromocytes (chromaffin cells)
How much of the adrenal gland is made up by the cortex?
What is the epinephrine-to-norepinephrine ratio secreted by the medulla?
80%
80:20
Where are steroid hormones stored in the adrenal glands?
They are not
What substance(s) increase(s) zona glomerulosa secretions?
What substance(s) increase(s) zona fasciculata secretions?
What substance(s) increase(s) zona reticularis secretions?
Angiotensin II (to a small degree, ACTH);
ACTH;
ACTH
What three substances are necessary to cytochrome P450 function in steroid hormone synthesis from cholesterol?
O2;
NADPH;
adrenoxin (iron-containing protein)
What is the most common cause of excessive secretion of cortisol and adrenal androgens?
ACTH hypersecretion by the adenohypophysis
The direct precursor to aldosterone is:
The direct precursor to cortisol is:
18-OH corticosterone;
11-deoxycortisol

Which cholesterol carbons must be hydroxylated in creating cortisol?
C-17, C-21, and C-11
Synthesis of aldosterone requires addition of an _______ group in case of the C-__ methyl group/
Aldehyde;
18
Upon being released from the adrenal zona reticularis, what happens to the androgen precursors (e.g. DHEA)?
Peripheral conversion to testosterone or estradiol
What are three precursor androgens released by the adrenal zona reticularis?
Androstenedione
DHEA
DHEA-S
Adrenal androgen precursors supply a larger proportion of the androgenic demand in which sex?
Females
(most male androgens come from the testes)
True/False.
ADH has a strong stimulatory effect on ACTH secretion.
False.
ADH has a weak stimulatory effect on ACTH secretion.
What effect does cortisol have on either the hypothalamus or adenohypophysis?
Inhibition of both CRH and ACTH secretion
____________-induced analgesia inhibits cortisol release.
Endorphins
True/False.
Cortisol directly stimulates many processes such as glycogenolysis.
False.
Cortisol is a permissive hormone and enhances these processes when stimulated.
What is the main purpose of cortisol in the stress response?
Gluconeogensis
(increased plasma glucose)
What are three tissue types upon which excessive cortisol has deleterious effects?
Bones, skin and muscle
What hormone of the adrenal cortex decreases bodily insulin sensitivity?
Cortisol
(a diabetogenic hormone)
True/False.
Cortisol stimulates protein conversion to glucose AND glucose conversion to hepatic glycogen.
True.

Cortisol permits maximum growth hormone and epinephrine stimulation of __________.
Lipolysis
What effect does cortisol have on adipose distribution?
Central adiposity increases
Name the effect of cortisol on each of the following tissues’ growth/function:
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac function
Arteriolar tone
Bone
Connective tissue
Fetal maturation
GFR
Decrease
Maintain
Increase
Decrease
Decrease
Increase
Increase
What are a few examples of conditions that might indicate an individual should not be administered glucocorticoids?
Infections, diabetes, osteoporosis
What are the clinical S/Sy of Cushing’s syndrome?
Thin skin, easy brusing (capillary weakness);
muscle weakness, osteoporosis, fatigue;
central obesity
What are the two main effects of aldosterone?
Maintaining ECF volume;
maintaining normal plasma [K+]
ANP and BNP inhibit ___________’s effects on the nephron tubules.
Aldosterone
What effect does dopamine have on aldosterone?
Decreased synthesis / secretion
What are the main categories of the S/Sy seen in Addison’s disease?
Hypoaldosteronism: natriuresis, hypotension
Hypocortisolism: weakness, stress intolerance, weight loss
Androgen loss: anemia, loss of body hair
What percentage of pancreatic islet cells are β cells?
And α cells?
And δ cells?
70%
20%
10%
What do pancreatic β cells secrete?
And α cells?
And δ cells?
And PP cells?
Insulin;
glucagon;
somatostatin, gastrin;
pancreatic polypeptide
True/False.
Insulin promotes a catabolic state, and glucagon promotes an anabolic state.
False.
Insulin promotes an anabolic state, and glucagon promotes a catabolic state.
Describe insulin’s structure.
An A peptide chain (21 amino acids) and a B peptide chain (30 amino acids) connected by 2 disulfide bonds
Describe the synthesis and modification of insulin from its gene.
Gene –> mRNA –>
preproinsulin –> proinsulin + N-terminus –>
insulin + C-peptide

Describe the structure of proinsulin.
The A and B chains connected by C-peptide in addition to their disulfide bonds.

What happens to proinsulin after C-peptide is cleaved off and it becomes insulin?
It is packaged in storage granules until release
What transporter allows uptake of glucose into pancreatic β cells?
What happens next?
GLUT2;
they enter glycolysis –> [ATP] increases –> KATP channels close –> cell depolarization –> insulin release
Influx of ___ allows for exocytosis of ___ from pancreatic β cells.
Ca2+;
insulin
When graphed, the relationship between plasma glucose and plasma insulin is _________ (shape of the curve).
Sigmoidal
Virtually no insulin is secreted below a plasma glucose threshold of ≈ ___ mg/dl.
A half-maximal insulin secretory response occurs at a plasma glucose level of ≈ ___ mg/dl.
Maximal insulin response occurs at a level of ≈ ___ mg/dl.
50
150
300
Describe the insulin response to continous glucose stimulus.
Biphasic:
pulse peaking at 1 min.
long-term pulse starting at 10 min. and peaking over several hours
Fasting and prolonged exercise _________ plasma insulin levels.
Obesity markedly _________ insulin secretion.
Sustained physical conditioning _________ insulin secretion.
Decrease;
increases
decreases
True/False.
Insulin secretion is stimulated by all of the following: certain amino acids (arginine and lysine), free fatty acids, triglycerides, potassium, calcium, and vitamin D.
True.
Early type II diabetes mellitus is characterized by a complete loss of recognition of ________ as a stimulus for ________ secretion.
Glucose;
insulin
Insulin circulates bound to what protein?
How long is insulin’s half-life?
None;
5 - 8 minutes
An increase in intracellular ____ and ____ are the usual secondary messengers for hormone release from peripheral endocrine tissues.
Ca2+; cAMP
What feedback process regulates oxytocin secretion during childbirth?
Positive feedback
(uterine contraction / cervical stretching –> increased oxytocin secretion until the baby is ejected and the cervical stretching stops)
Are the overall effects of GH anabolic or catabolic?
Anabolic
When are GH levels highest?
Adolescence
(decreases with age)
GH acts through which specific receptor-associated tyrosine kinase system?
JAK-STAT
Describe the effects of GH on each of the following (increased/decreased):
Lean body mass
Fat mass
Blood sugar
Protein synthesis
Lipolysis
Resting BMR
Increased
Decreased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Name a few diabetogenic hormones that have antagonistic effects towards insulin (typically via phosphorylation of intracellular insulin receptor substrates).
Glucagon,
epinephrine,
growth hormone,
cortisol
What hormone is mainly anabolic but also acts to increase lipolysis and blood glucose?
Growth hormone
Via what action does aldosterone synthase convert corticosterone to aldosterone?
Oxidation of the C18 methyl group
Describe the insulin-mediated mechanism of GLUT4 expression on skeletal muscle and adipose cells.
Insulin –> extracellular alpha receptor –> intracellular beta subunit –> tyrosine kinase activity on insulin receptor substrate 1 –> PI3 kinase activity –> GLUT4 brought to membrane
True/False.
Insulin up-regulates insulin receptors.
False.
Insulin downregulates insulin receptors.
How do many diabetogenic hormones (cortisol, epinephrine, GH, glucagon) act to down-regulate insulin’s effects?
Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1)
(inhibited GLUT4 membrane fusion –> increased insulin –> insulin receptor down-regulation)
True/False.
Glucagon inhibits insulin release.
False.
Glucagon stimulates insulin release.
What is the ratio of insulin:glucagon when fasting?
What is the ratio of insulin:glucagon for a few hours after eating?
1: 2
2: 1
True/False.
Insulin stimulates glucagon secretion.
False.
Insulin inhibits glucagon secretion.
If blood sugar is above __ mM, a person is said to be hyperglycemic.
If blood sugar is below __ mM, a person is said to be hypoglycemic.
6.7;
2
Pancreatic polypeptide inhibits what?
Exocrine secretion
Elevated pancreatic polypeptide is indicative of what?
An islet cell tumor
What pancreatic cell type secretes gastrin?
Islet G cells
What hormones are produced by pancreatic islet cells?
Insulin (+C-peptide),
glucagon,
somatostatin,
gastrin,
pancreatic polypeptide,
VIP (non-beta islet cells)
What are the two important substrates activated by insulin receptors?
IRS1,
PI3 kinase


