Embryology - Development of Foregut Flashcards
Where does the foregut start/end?
Oesophagus to duodenum (first bit of SI)
When is the primitive gut tube formed?
During embryonic folding - the ventral surface becomes concave in two directions. The sides of the embryo fold in on each other and the head and tail fold toward one another, forming the primitive gut
Where does the primitive gut tube extend to/from?
From the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane
What can the primitive gut tube be divided into during foetal life?
- Foregut 2. Midgut 3. Hindgut
Where does the midgut start/end?
2nd half duodenum to 2/3 along transverse colon
Where does the hindgut start/end?
Distal 1/3 transverse colon to superior 2/3 rectum
When does cranio-caudal folding occur?
Week 3-4
What connects the gut tube to the yolk sac?
Vitelline duct
How is the midgut continuous with the yolk sac?
At the vitelline duct
Where is the epithelial lining of the primitive gut tube derived from?
The endoderm
Where is the smooth muscle and connective tissue of the primitive gut tube derived from?
The surrounding visceral mesoderm
What does the visceral and parietal mesoderm also give rise to?
The visceral and parietal peritoneum
How is the primitive gut tube suspended from the posterior abdominal wall?
By the dorsal mesentery
What is a mesentery?
A double fold of peritoneum that encloses an organ and connects to the body wall
What are the organs enclosed by a mesentery called (e.g. gut)?
Intraperitoneal
What are the organs not surrounded by peritoneum called (e.g. aorta)?
Retroperitoneal
What is function of mesentery?
Acts as route for blood supply, nerve supply and lymphatic drainage for organs
Where is the dorsal mesentery?
From lower oesophagus to cloaca
Where is the ventral mesentery?
- From lower oesophagus to 1st part of duodenum - Forms lesser omentum and falciform ligament (umbilical vein)
What do vitelline arteries give rise to?
Arteries of GIT The vitelline arteries undergo remodelling, losing their connection to the yolk sac to supply the gastrointestinal tract
Directly from the aorta, what unpaired arteries supplying the GIT arise?
- Coeliac trunk –> foregut 2. Sup mesenteric artery –> midgut 3. Inf mesenteric artery –> hindgut
How is the definitive gut formed?
Hollow primitive gut tube –> gut tube occluded by proliferation of endoderm derived epithelial lining –> apoptosis of epithelium occurs over next 2 weeks creating vacuoles –> recanalisation (vacuoles coalesce to fully recanalise the gut tube –> definitive hollow gut tube

When does proliferation of the endoderm derived epithelial lining that occludes the gut tube occur?
Week 6
When do vacuoles coalesce to fully recanalise the gut tube by?
Week 9
What is purpose of hollow tube becoming occluded then hollowed again?
How specialised cells are formed
What can abnormal recanalisation lead to?
Duplications of the GI tract –> cyst

What can incomplete recanalisation lead to?
Stenosis (narrowing) or blockage (atresia) of the gut tube
What is most commonly affected by abnormal recanalisation?
Ileum is most commonly affected followed by duodenum
What can duplication cysts lead to?
Bowel obstruction or intussusception (telescoping of proximal part of bowel into distal part)
What does the foregut give rise to?
Respiratory diverticulum
How is the foregut separated from the respiratory diverticulum?
Tracheoesophageal ridges form tracheoesophageal septum (separating trachea and oesophagus)
What occurs when an oesophageal atresia occurs independently of a TOF?
Displacement of the tracheoesophageal septum separates proximal and distal ends of oesophagus
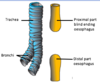
What are dangers of oesophageal atresia?
This prevents the foetus from swallowing amniotic fluid and returning it to the mother through the placental circulation – polyhydramnios
How are oesophageal atresia’s repaired?
Surgical repair results in 85% survival rate
When/where does the oesophagus form?
Week 4 caudal to the lung bud
How does the oesophagus differ from the rest of the gut tube?
- Like the rest of the gut tube, oesophagus has endodermal epithelial lining and smooth muscle layer from visceral mesoderm.
- However, also has some skeletal muscle
Where is the skeletal muscle of the oesophagus derived from?
The paraxial mesoderm
What happens if the stomach doesn’t descend correctly? What is this called?
Some of stomach in thorax (supradiaphragmatically)
Congenital hiatal hernia
How is a congenital hiatal hernia different from an adult acquired hernia?
Adult –> top part of stomach slides through opening into thorax due to pressure
Congenital –> failure of oesophagus to elongate
When/how does the stomach appear?
In 4th week as a dilation of the foregut
How is the stomach suspended in the abdomen?
By the dorsal and ventral mesenteries
What is the lesser omentum?
Ventral mesentery that goes from lesser curvature of stomach to liver
What is the falciform ligament?
From liver to anterior wall, derivative of mesentery
How does the greater curvature form?
Differential growth in week 5 forms the greater curvature (i.e. the dorsal wall)
How/when does the stomach rotate?
•In weeks 7-8, the stomach underdoes rotation around 2 axes
How does the lesser curvature move during stomach rotation?
•90° clockwise rotation around the craniocaudal axis causes the lesser curvature to move from ventral position to the right.
How does the greater curvature move during stomach rotation?
The greater curvature moves from dorsal position to the left
How are the vagus nerves moved during stomach rotation?
The vagus nerves are initially located on left and right sides of the gut tube but are also rotated such that the left vagus trunk becomes anterior and the right becomes dorsal (posterior)
There is also some rotation around the ventrodorsal axis. How does this affect the lesser/greater curvatures?
- the greater curvature faces slightly caudally
- the lesser curvature slightly cranially
As the stomach rotates around the craniocaudal axis, it creates a space behind it. What is this called? What is the remaining peritoneal cavity now known as?
•the lesser peritoneal sac (omental bursa)
- The greater sac
What connects the greater and lesser sacs?
The epiploic foramen (of Winslow) –> a narrow opening
What are greater and lesser peritoneal sacs created by?
Rotation of stomach
How does the stomach attach to the posterior wall?
Via the dorsal mesentery (dorsal mesentery attached to the greater curvature of the stomach) and the posterior abdominal wall (dorsal mesentery) continues to grow rapidly.
The dorsal mesentery folds back on itself to form what?
Reflects back on itself to form an extension of the lesser sac (omental bursa) –> 4 layers
What does greater omentum attach to?
Posterior wall
The ventral and dorsal folds fuse before birth. What does the posterior layer of the greater omentum also fuse with?
The mesentery of the transverse colon
What is congenital pyloric stenosis?
Narrowing of pyloric sphincter caused by hypertrophy of smooth muscle
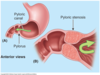
Is pyloric stenosis more common in men or women?
More common in males 5:1
What is effect of pyloris stenosis?
- Restricts gastric emptying which can lead to dilation of the stomach
- Signs include:
ØPalpable pyloric mass
ØProjectile vomiting
ØVisible peristalsis
What can inappropriate epithelial differentiation of the gut tube lead to?
Ectopic gastric tissue
What can ectopic gastric tissue lead to?
- Due to acid production, this can cause inflammation and ulceration in the surrounding area
- Damage can result in strictures due to scarring or rupture of the gut wall
What is the duodenum continuous with?
Duodenum
When does the duodenum elongate? What does it result in? What then happens?
Week 4 - resulting in a ventrally projecting C-shape
This is then dragged to the right by the rotating stomach
What happens to the dorsal mesentery attached to the duodenum?
Degenerates so that the (majority) duodenum lies against the posterior abdominal wall – secondarily retroperitoneal
What is oesophageal stenosis?
- Occurs when the oesophagus fails to recanalise
- Typically associated with polyhydramnios prenatally.
- Postnatally, the child will regurgitate IMMEDIATELY upon feeding.
- However, there is usually NOT a tracheoesophageal fistula, so the lungs will usually NOT be congested.


