Embryology 3 exam Flashcards
Pharyngeal apparatus

•Bilateral growth of embryonic tissues in the ventro-lateral region of the head
–5 pairs of pharyngeal arches form in cranial to caudal sequence
- 1, 2, 3, 4, (6)–5 is skipped
- Separated by pharyngeal grooves/clefts on the outside (green arrows)
–Primarily driven by the migration & proliferation of *neural crest, they migrate ventraly.
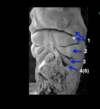
Neural crest cells start to migrate
As the neural crest cells migrate they create bumps.

Anatomy of Pharyngeal Arch
- Outside covering ——>_____1_____*
- Inside lining——-> ______2_______*
- Core of each arch ——–> *mesenchyme (which comes from neural crest cells)
_*Arch 1_ is covered mostly by ectoderm in the inside as well –> oral ectoderm
1- ectoderm
2- endoderm
Anatomy of the pharyngeal arch
Neural crest – major component –> Cartilage & Bone
Mesoderm (paraxial) —> Skeletal muscles (in head and neck area)
Each pharyngeal arch has its own nerve innervation:
1st arch=> cranial nerve V (trigeminal)
2nd arch=> VII (facial)
3rd arch => IX (glossopharyngeal nerve)
4-6 arch=> X(vagus)

Anatomy of the pharyngeal arch
Pharyngeal groove (cleft #1) give rise to external ear.
Pharyngeal cleft/groove: separates pharyngeal arches from the outside (ectoderm lined)
*Pharyngeal pouch: separates pharyngeal arches from the inside (endoderm lined)
*Pharyngeal membrane: where ectoderm and endoderm come together at clefts/grooves
*We only kept one pharyngeal membrane: *tympanic membrane (remnant of first pharyngeal membrane).

Pharyngeal arch neural crest derivatives
They migrate into all arches
Pharyngeal arch 1
*Maxillary prominence –> Maxillary bone, ________ & *squamous portions of temporal bone.
zygomatic

Pharyngeal arch 1
*Mandibular prominence –> *Meckel’s cartilage (temporary mandible that gets replaced), mandible, _______, _______, anterior ligament of the malleus.
malleus;incus

Pharyngeal arch 2
–->*Lesser cornu of hyoid, *stylohyoid ligament, styloid process, & _________
***stapes****

Pharyngeal arch 3
–->*Body and *greater cornu of hyoid

Pharyngeal arch 4 & 6
Majority of the *larynx*
–*Thyroid cartilage & *cricoid cartilage

Summary

Pharyngeal arch *mesoderm derivatives
Pharyngeal arch 1
–->Muscles of mastication (from myotomes) : ____1___, ____2____, ___3______, ant belly of diagastric m, tensor tympani*
Innervated by: trigeminal nerve (V)
1- temporalis
2- masseter
3- mylohyoid

Pharyngeal arch 2
Muscles of *facial expression, *stylohyoid muscle, *post belly of digastric m
They are innervated by__________.
facial nerve (VII)

Pharyngeal arch 3
*Stylopharyngeus*
Innervate by__________
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)

Pharyngeal arch 4 & 6
–*Pharyngeal constrictors, *soft palate m., *laryngeal m.
Innervated by ________
vagus nerve (X)

Summary

Pharyngeal arch innervation
Arch 1 via trigeminal nerve (V)
–Motor–> masticatory muscles, ant belly of digastric, *tensor tympani
–Sensory –> somatosensation of face, teeth, ________\_, & palate.

anterior 2/3 tongue

Arch 2 via _Facial nerve (_VII)
Motor –> muscles of facial expression, post belly of digastric, *stylohyoid.
Sensory –> special sensory (taste) for ____________.
anterior 2/3 of tongue
Arch 3 (IX-glossopharyngeal)
–Motor –> stylopharyngeus*
–Sensory –> ___________; both taste and somatosensory
*posterior 1/3rd of the tongue

Arch 4 & 6 (V-vagus)
Motor –> pharynx & larynx
Sensory –> pharynx, larynx, &_________; both taste and somatosensory
esophagus*

summary

Pharyngeal arch endoderm derivatives
Pharyngeal pouch 1 (composed of endoderm)
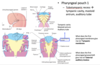
–Tubotympanic recess -> tympanic cavity, mastoid antrum, auditory tube
Pharyngeal pouch 2
Palatine tonsilar bed —> *induces lymphoid tissue invasion and together form the ____________ ( from *endoderm and *splanchnic lateral mesoderm)
palatine tonsil
Pharyngeal pouch 3
–Ventral bud -> *thymus
–Dorsal bud -> inferior parathyroid

Pharyngeal pouch 4
Ventral bud –> ultimopharyngeal body integrated itself into *thyroid, (parafollicular cells in thyroid that produce *calcitonin)
Dorsal bud–> -__________
*superior parathyroid

summary


Pharyngeal groove/cleft transformation

Pharyngeal groove 1
–Gives rise to ___________
*external acoustic meatus
Pharyngeal groove 2-4 (need to go away)
Coalesce into *cervical sinus as arch 2 and 4 expand as folds toward each other and once the folds fuse, the sinus becomes the cervical vesicle*
–The neck line becomes smooth and cervical vesicle *degenerates over time

Clinical Correlations
Cervical (branchial) cyst
–Persistent cervical vesicle
–Presents as asymptomatic swelling on lateral neck, anywhere along the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid
Cervical (branchial) sinus
–Persistent cervical sinus or any cleft/pouch
Cervical (branchial) fistula
–Continuous duct between *pharynx and neck surface
Development of the thyroid gland
*Endoderm between pharyngeal arch 1 & 2 form a *thyroid primordium in the midline and invaginate caudally.
As the thyroid primordium grows caudally, it is still open to the pharynx via the ________\_ which opens into pharyngeal space at *foramen cecum.
thyroglossal duct
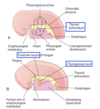
Development of the thyroid gland

•Thyroid primordium continues to grow down below the hyoid bone and takes resident anterior to trachea, caudal to larynx, and matures into _________.
*Thyroglossal duct degenerates
*Portion of it may become the *pyramidal lobe of thyroid
•Foramen cecum becomes a remnant (indentation) between anterior & posterior tongue.
*thyroid gland
Clinical correlation
•Thyroglossal duct cyst (TDC)
Cystic remnant of thryoglossal duct
*Most common mass in the midline of the neck in **children
–Most commonly present at the level of _hyoid bone*_
–May contain ectopic thyroid tissue

Development of the Tongue
1st arch* (gives rise to the majority of the tongue)
–Median lingual swelling (tuberculum impar)-induces *lateral lingual swelling to keep growing.
–Lateral lingual swellings –> give rise to Ant 2/3 of the tongue
2nd arch
–*Copula (signaling sending, to cause the 3rd and 4th pharyngeal arches to develop the hypopharyngeal eminence)
3rd & 4th arches
–Hypopharyngeal eminence –> gives rise to posterior _____ of the tongue
1/3
* Arch 1 is mostly covered by ectoderm, thus the lining of ant 2/3 of the tongue derives from *ectodermal origin whereas post 1/3 of the tongue (and the rest of the pharyngeal) lining derive from *endodermal origin

Landmarks derived from developmental process
Line of fusion between two lingual swellings –> Median sulcus
Line of fusion between arch 1 (anterior 2/3 of tongue) and hypopharyngeal eminence (posterior 1/3 of tongue)–> terminal sulcus
*Foramen cecum is at the center of terminal sulcus is a remnant of the __________.
thyroid primordium

Development of the Tongue
•Skeletal muscles of the tongue derive from *___________ somites ( paraxial mesoderm).
–Migrate into tongue after 5th week, “pulling in” the motor innervation: Hypoglossal nerve
General sensory? trigeminal
Special sensory? _______
occipital
facial

Innervation of the Tongue
•Anterior 2/3
–Somatosensory – V3 (mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve)
–Special sensory (Taste) - VII (facial nerve)
•Posterior 1/3
–Somatosensory – IX (glossopharyngeal nerve) & X (vagus nerve)
–Special sensory - IX (glossopharyngeal nerve)
•Muscles (motor)
–XII (hypoglossal nerve)
Review questions:
1- What embryonic germ layer gives rise to the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Paraxial mesoderm ->occipital somites
2-Intrinsic muscles of the tongue are innervated by?
Hypoglossal nerve (motor)
3- What is the second’s pharyngeal arch contribution to the tongue?
Taste buds in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
4- What is the third’s pharyngeal arch contribution to the tongue?
Posterior 1/3 of the tongue (from hypopharyngeal eminence)
5-Myoblasts from which pharyngeal arch give rise to anterior digastric muscle?
1st pharyngeal arch
6-Neural crest from which pharyngeal arch give rise to body of hoyd bone?
-Third pharyngeal arch
Malleus and incus? Come from pharyngeal arch 1
Papillae and taste buds of tongue
4 types of papillae (~week8)
–Filiform (NO TASTE BUDS)
–Fungiform* (round)
–Folliate* (on dorsal surface)
Circumvallate* (round and larger than fungiform papillae- they have serous glands underneath that produce watery saliva)
The * all contain ________.
taste buds
Tastebuds
–Multicellular receptor organs in fungiform, folliate & circumvallate papillae
–Transmit taste information to CNS via VII (facial)** & **IX (glossopharyngeal).
–*Functional in utero
*Fetal swallowing of amniotic fluid changes in response to sweet or bitter substances
*Exposure to carrot juice in utero (3rd trimester) or via postnatal lactation resulted in reduced negative response of infants to carrot juice
Face Formation
Requires tightly coordinated growth & fusion events
Starts at around week ______.
Face begins as five facial primordia (bumps) around stomodeum*
4 (FOUR)

Face formation
______1______ (ectodermal thickening) form on FNP.
Underlying *mesenchyme** around **nasal placodes proliferates, creating elevations around the placodes.
Nasal placodes “sink in” & become **nasal pits, then dilate to become ____2____
Elevated regions around the nasal pit are called *nasal prominences –> divided into medial and lateral portions
1- nasal placodes
2-nasal sacs

Face formation cont’d
MxPs grow & enlarge, “pushing” nasal prominences toward midline of the face
*Medial nasal prominences* fuse (Week 6-10), giving rise to
1) *Bridge of the nose
2) *Intermaxillary segment yellow structure, very important, gives tise to (:
–>Portion of the upper lip (philtrum)
–>Upper jaw with 4 incisors
–>*Primary palate

MxPs (maxillary prominences) fuse with the *intermaxillary segment
–Ventral region –> smooth upper lip
–Dorsal region –> fusion of primary and secondary palate

Face formation:
-Lateral nasal prominences give rise to the alae of the nose
- Lateral nasal prominences fuse with MxP (on both sides)
- At the site of fusion, **ectoderm thickens into a cord then “sinks” into underlying mesenchyme which canalizes to become the
*nasolacrimal duct*

Development of nasal cavity
- Two nasal pits –> nasal sacs
- Nasal sacs fuse in the midline, forming a single nasal cavity separated from oral cavity by a thin *oronasal membrane
- Oronasal membrane ruptures dorsal to *primary palate –> oral and nasal cavities become continuous
- Formation of _________ separates nasal cavity from oral cavity.
- Nasal septum separates right and left nasal cavities
*secondary palate

Nasal conchae develop from the *lateral walls of the nasal cavities.
Cranial ectoderm in the nasal cavity differentiate and specialize–> __________
olfactory epithelium

Development of the palate
Palate: separates nasal cavity from oral cavity, preventing aspiration of food
•Anatomical division
–Hard palate: Anterior, bony portion, comprises the majority of the palate
–Soft palate: Small, fleshy, posterior portion, terminating in the uvula*

Development of the palate
Embryonic division
Primary palate
- Derives from intermaxillary segment (fused medial nasal prominences)
- Gives rise to anterior, triangular portion of the hard palate
Secondary palate
- Derives from the fusion of palatine shelves that grow from the MxPs
- Gives rise to the *majority of hard palate and all of soft palate

Development of the secondary palate
**Palatal processes (palatine shelves) form from MxP internally
–Grow caudally on either side of the developing tongue
–~Week9, growth of mandible “drops” tongue, allowing palatine shelves to swing up and fuse with:
–>each other in the midline
–>primary palate anteriorly (to create a seamless palate)

Secondary palate formation is complete at 12 weeks*

Clinical correlation
Cleft lip (unilateral or bilateral)
–May or may not involve palate
What structures failed to fuse?
A-intermaxillary segment and maxillary prominence failed to fuse superficially.
Cleft palate
The palatine shelves failed to fuse in the midline
Oblique Cleft
Lateral nasal promience and maxillary prominence did not fusion
Treacher Collins Syndrome
–Autosomal dominant gene mutation in a nucleolar phosphoprotein (TREACLE) involved in preribosomal processing
–1:50,000 live births
–Hypoplastic zygoma
–Low-set, malformed pinna
–Micronathia
–Malformed or absent ossicles –> conductive deafness
–Cleft palate in 35% of cases
Defects in what embryonic germ layer and structures?
Neural crest insufficient (give rise to bony and cartilagnous structures) into first pharyngeal arch.
Pierre Robin Syndrome
–Heterogeneous birth defects with wide range of severity
–1:8,500 live births
–Micronathia (tongue can block airway due to small cavity)
–Cleft palate
–Susceptible to respiratory distress syndrome at birth
Defects in what embryonic germ layer and structures?
Germ layer: neural crest
Mandibular prominence of the 1st pharyngeal arch
DiGeorge Syndrome
–90% of patients have a 3Mb microdeletion of 22q11.2 (~30 genes).
–1:3,000 – 1: 4,000 live births
–Wide range of severity
- Thymic insufficiency –> defective cell-mediated immunity
- Parathyroid insufficiency –> hypocalcemia
- Craniofacial defects –> Micronathia, cleft palate, low-set ears
- Cardiovascular defects –> persistent truncus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect
–High mortality rate within the 1st year
Defects in what embryonic germ layer and structures?
3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouch lined by the endoderm
Tooth development
The dental lamina forms in the epithelium of the mandible and maxilla.
The ectodermal epithelium then invaginates to form dental buds - 10 per jaw (8 wks).
The bud epithelium then invaginates, forming a cap around condensing dental papilla mesenchyme, which is derived from __________ (10 wks).
During the *****bell stage, neural crest mesenchyme cells become odontoblasts (crest cells derived), destined to produce ____1___, and inner epithelial/ectodermal cells differentiate as ameloblasts (ectoderm derived), which will produce ______(3 months +).
neural crest cells
1- dentin
2- enamel

__________ are sloughed off when the teeth erupt postnatally.
Baby/deciduous teeth erupt in a typical sequence.

Ameloblasts
Tooth development
Both baby/deciduous teeth, and adult/permanent/successional teeth are generated during fetal development, although their development is staggered.
Much of the growth of the maxilla and mandible during later gestation and postnatally is to accommodate growth of the second set of tooth buds.
Tooth development is *key to normal jaw growth.

Review Questions
1- Dentin is produced by which cell population?
-Odontoblasts, which come from neural crest cells.
2- Enamel is produced by which cell population?
Ameloblasts, which come from oral ectoderm
3- Fusion of which embryonic structures gives rise to intermaxillary segment?
medial nasal prominences (right and left)
4- Which developmental event transforms primitive choana into definitive choana?
Palatine shelves fusing in midline and with primary palate to form palatine proper.


