Bony landmarks- Sphenoid bone Flashcards
(20 cards)
The __________ muscle attaches to the body of the sphenoid bone.
superior oblique muscle (eye)

The sulcus chiasmatis houses the___________
optic chiasm
The sella turcica has the hypophyseal fossa, which houses the ________.
pituitary gland
Posterior clinoid process

Carotid groove

houses internal carotid artery and carotid nerve
Foramen rotundum (part of greater wings of sphenoid) transmits the _________ nerve.

maxillary
Foramen ovale (part of greater wing of sphenoid) transmits the _______ nerve and _________ artery.
mandibular nerve; accessory meningeal

The spine serves as an attachment for:
tensor palatini muscle and sphenomandibular ligament
Foramen spinosum transmits the middle meningeal artery, and the meningeal (recurrent) branch of the __________nerve
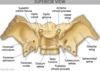
mandibular nerve
The lateral surface of the greater wing serves as an attachment for the ________ and ______ muscles.
temporalis and lateral pterygoid muscles
The orbital surface of the sphenoid bone forms the superior orbital fissue that transmits:
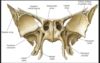
- ophthalmic nerve
- oculomotor nerve
- trochlear nerve
- abducens nerve
-ophthalmic vein
Foramen lacerum

The lesser wing of the sphenoid process serves as an attachment for the ___________ muscle.
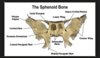
levator palpebrae superioris
On the lesser wing, the anterior clinoid process serves as an attachment to _________.
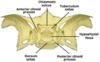
tentorium cerebelli
pterygoid process

The pterygoid fossa serves as an attachment to _________ muscle.

medial pterygoid
The scaphoid fossa serves an the attachment for the _________ muscle.

tensor palatini
The pterygoid canals transmit the nerve of the _______ canal.
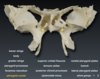
pterygoid
Lateral pterygoid plate serves an attachment for _______ and ________ pterygoid muscles.
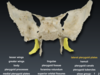
lateral and medial
Medial pterygoid plate has the pterygoid hamulus, which deflects the tendon of the tensor palatini muscle.
It also serves as an attachment for the _________ & ___________ muscles and pterygomandibular nerve.

buccinators; superior constrictor muscles


