DPT 622: Human Imaging in PT Practice I Flashcards
Please match the following cervical spine x-ray views with the most likely visible anatomy.
Oblique: _______
APOM: _______
APLC: _______
Lateral: _______
- Lateral mass of C1
- Atlantodental interval
- Intervertebral foramina
- Tracheal shadow
Oblique: Intervertebral foramina
APOM: Lateral mass of C1
APLC: Tracheal shadow
Lateral: Atlantodental interval
True or False
Spina bifida occulta of the atlas is suggested by an incompletely ossified anteriorarch visible on plain film.
False
The upper limit of the atlantodental interval (AID) is ___ mm in adults.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
C
Label structures 1-8

- Anterior arch of atlas
- Dens
- Body of axis
- Posterior arch of atlas
- Pedicle
- Lamina
- Spinous process
- Articular Facets
True or False

After performing you ABCs scan of the following film, the provided view does not demonstrate any evidence of pathology.
False
True or False
After performing you ABCs scan of the following film, the provided view does not demonstrate any evidence of pathology.

False
Label A-H

A. wing of ilium
B. acetabulum and hip joint
C. greater trochanter
D. femoral neck
E. lesser trochanter
F. Ischium
G. superior ramus-pubis bone
H. inferior ramus of the pubis bone
True or False
A torn ACL of the knee may be associated with a “popping” sensation.
True
What is the correct name of the landmark depicted in the provided image?
a. Shenton’s line
b. Center edge angle
c. Iliopubic line
d. Ischiopubic line

A
Repetitive applications of compressive, rotational, or tensile forces to normal bone may lead to which of the following?
a. Unstable fracture
b. Stress fracture
c. Insufficiency fracture
d. Impacted fracture
B
True or False

The following image appears normally with no evidence of pathology.
False
True or False

The following image appears normal with no evidence of pathology.
False
The signs and symptoms of ulnar entrapment include:
a. Lack of sensitivity to cold temperature
b. Pain relief with repetitive use of hand
c. Numbness in 1st and 2nd digits of hand
d. Loss of strength in intrinsic muscles of hand
e. All of the above
D
Which of the following is not a contraindication to MRI?
a. Cardiac pacemakers
b. Harrington rods (titanium)
c. Brain aneurysm clips
d. Shrapnel
e. All of the above
B

GH Dislocation
Which of the following examinations most likely delivers the highest radiation dos?
a. CT
b. MRI
c. Radionucleide Imaging
d. X-ray
A
Which of the following does not exhibit high signal intensity on T1-weighted MRI images?
a. Bone
b. Proteinaceous material
c. Subactue hemorrhage
d. Muscle
D
The letter “V” in the diagnostic mnemonic “vindicate” delineates
a. Venous
b. Vaccine
c. Vascular
d. Viral
e. None of the above
C
In the radionucleotide imaging of bone, a “hot spot” refers to the following:
a. Osteoclastic activity
b. Bone destruction
c. Necrosis
d. Osteoblastic activity
e. Ischemia
D
Which of the following imaging modalities employs the “Hounsfield” unit?
a. Radionuclide scintigraphy
b. Bone scan
c. CT
d. X-ray
e. None of the above
C
With attention to sensitivity, radiation exposure, and cost, which of the following procedures would be the best choice to initially image the gallbladder for suspected gallstones?
a. X-ray
b. CT
c. Ultrasound
d. Fluoroscopy
e. MRI
C
Label 1, 2, 3, 4, and 8
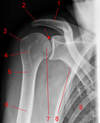
Axially border of scapula: 8
Greater tubercle: 3
Lesser tubercle: 4
Acromion: 2
Clavicle: 1
What is a critical feature of MRI technology?
a. Body density
b. Compton’s effect
c. X-radiation
d. Hydrogen protons
e. Gamma radiation
D
Which examination would be least likely to display a disc lesion?
a. CT
b. MRI
c. Myelography
d. Plain film radiography
D







