Day 7, Lecture 4 (Aug 30): Cancer II: Carcinogenesis Flashcards
Carcinogenesis
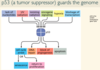
The process by which cells acquire attributes that confer a malignant phenotype. This is a synonym for the [obsolete] term cancerogenesis”




Explain how Malignancy is typically a stepwise process


Do cancer’s invent new biological properties through which they achieve the malignant phenotype
They simply borrow exisiting cellular pathways
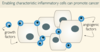
Hallmarks of cancer?

Describe Hallmark 1 (How cancers avoid apoptosis)
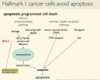
Effect of increasing BCL2 in cancer cells

Explain hallmark 2 of Cancer cells: cancer cells use growth signaling pathways
- example:
- Breast carcinoma
- oncogene: HER2, a receptor tyrosine kinase
- Amplification (too many copies) of HER2 (aka ERBB2) → overexpression of HER2 → increased signaling → proliferation
- oncogene: HER2, a receptor tyrosine kinase
- Breast carcinoma

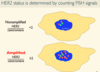
How can HER2 amplication (in breast carcinoma) be detected
- by FISH (fluoroescence in-situ hybridization)
- Marks centromeres and HER2 gene
- then you do counts
Breast carcinoma with HER2 amplification respond to what drug
- Trastuzumab

Explain Hallmark 3 of cancer cells: cancer cells escape control of growth
- example RB is the “master brake” protein at G1 to S (tumor suppressor)
- in some cancers Rb is mutated and not able to bind to E2F and stop it from pushing the cell cyle forward



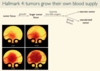

What is bevacizumab used to treat
It is a VEGF (Vascular endothelial growth factor) inhibitor and thus turns of angiogenesis
Explain Hallmark 5: cancer cells divide without end
- Telomeres normally shorten with age.
- normal cells observe the Hayflick limit
- this means they stop dividing (senescence) due to shortening of telomeres
- normal cells observe the Hayflick limit
- Normal cells have little to no telomerase activity while cancer cells have high telomerase, which rebuilds the telomeres after division. Thus they are immortalized
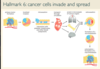

_____ loss and matrix _____ allow cancer invasion
E-cadherin and matrix metalloproteinases (which eat through basement membrane) allow invasion
Do tumor cells communicate with normal cells
Yes
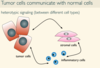
local conditions that enable cancer growth, brought about by interactions of tumor cells with stroma, inflammatory cells, blood vessels, etc.
Tumor microenvironment
what is the warburg effect
- (“aerobic glycolysis”)
- It is an emerging hallmark that cancer cells have altered metabolism

Explain the emerging hallmark: cancer cells escape detection
- cancer cells can turn off antigen expression and secrete antipoliferative factors