Day 15, Lecture 4 (Sept 13): Molecular and Cellular Networks Flashcards
(22 cards)
Most Cellular functions are regulated via

All the places in Red are spots that if a mutation is to occur you could get cancer


Nonsense mediated decay (NMD)

____ nonsense mutation result in effective nonsense mediated decay (NMD) while _____ mutations lead to ineffective NMD
- Primal nonsense mutations result in effective NMD while distal nonsense mutations (e.g. in the last exons) lead to ineffective NMD

Proximal nonsense mutations often result in ____ while distal mutation result in
- Proximal nonsense mutations lead to loss of function due to nonsense mediated decay
- While Distal mutations result in truncated proteins
- Dominant negative effects

What happens if a nonsense mutation is just proximal to an EJC
The signal does not work very well and the protein will most likely still be secreted even though it is truncated
Iron transporter is regulated by
- levels of iron
- RNA-binding protein regulates Fe transport during Fe deficiency
- Iron is stored by ___, which is required at ___ Fe levels .

_______ absorb Fe and is required at ____ Fe levels

Expain how Transferrin receptor and Ferritin are regulated
- Iron Response element (hairpin)- binding protein IRE-BP is activated by decreased levels of Fe
- IRE-BP binds to the Iron Response Hairpin located on the mRNA for both ferritin and transferrin receptors (TfR)
- The difference in action is based on the location of the binding
- In ferritin mRNA IRE-BP binds to the 5’ UTR thus blocking the ribosome and inhibiting translation initiation
- In transferrin mRNA IRE-BP binds to the 3’UTR thus protecting mRNA from degradation

microRNA (miRNA) regulation of gene expression
- Short RNA molecules can degrade transcripts (post-transciptional gene regulation) or induce heterochromatin (transcriptional gene regulation)

miRNA Post-Transcriptional regulation of gene expression
- Pre-miRNA is clipped into shorter sections by dicer to form miRNA
- This and Ago+ other RISC proteins combine to make single stranded miRNA
- this then acts on the its subsequent RNA sequence to lead to degradation

What is the difference between siRNA and miRNA
- miRNA (endogenous)
- siRNA (exogenous)
miRNA Transcriptional regulation (heterochromatin formation)
- Pre-miRNA is clipped into shorter segments by dicer to form miRNA
- miRNA combines with Ago and other RITS proteins (note that this is RITS and not RISK, which is the Post-transcriptional protein)
- goes into the nucleus and clips onto DNA segement
- recruits HMT and DNMT and leads to histone methylation and DNA methylation (thus forms heterochromatin) to inhibit transcription

DNA double-strand breaks can induce _______ arrest and apoptosis
G1/S
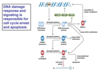

Explain the mechanism/pathway for double stranded breaks cell cycle inhibition
- A double strand break leads to the phosphorylation of ATM dimer (inactive)
- this leads to a phosphorylated ATM monomer (active)
- Once activated ATM does 2 things:
- It recruits proteins to fix the double stranded break (MRE11, RAD50, Nibrin) and BRCA1
- Phosphorylates check 2
- Check2 phosphorylated (active) is now able to phosphorylate p53 thus making it stable and active
- p53 leads to cell cycle arrest at G1/S and apoptosis






