Day 13, Lecture 4: Human Development 4: Weeks 4-8 Flashcards
(22 cards)
Mesododerm is a germ layer not a cell type may be composed of ____ or ___ throughout the embryonic disk except at
- Mesenchymal or epithelial cells
- throughout the embryonic disk except at the oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes
_____ results in the formation of the three germ layers
- Gastrulation
Mesoderm is organized into 1 midline and 3 paired regions, name them?
- Midline
- Notochord
- Paired regions
- Paraxial mesoderm
- Intermediate mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm
What major events occur in the fourth week of development
- Organization of mesoderm into groups of tissue
- Notochord
- Paraxial Mesoderm
- Intermediate Mesoderm
- Lateral Plate Mesoderm
- Segmentation of paraxial mesoderm into somites
- Body folding
- 3-D establishment of body plan

Organization of Paraxial Mesoderm
- Cranio-Caudal sequence of development initially organize into partially segmented structures termed somitomeres
- More caudal paraxial mesoderm completely separates into segments termed somites
- 7 cephalic somitomeres
- 42-44 somites (occipital + trunk)

What are somites
cuboidal blocks of mesoderm compsed of epithelial cells formed from the paraxial mesoderm

Somites disperse to form
-
sclerotome
- forms from ventromedial side of somite
- forms axial skeleton (vertebrae and ribs)
-
dermamyotome
- forms from dorsolateral side of somite
- Disperses to form two groups of cells
- Dermatome
- Contributes to dermis
- Myotome
- Forms all skeletal muscle
- Dermatome

Intermediate mesoderm forms
- Urogenital system


cervical spinal nerves are numbered by vertebrae below with the exception of
- Spinal nerve C8
- (note the rest of spinal nerves are numbered by vertebrae above)

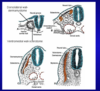
Lateral Plate Mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm splits:
- Forms embryonic coelom
- Somatic and Splanchnic mesoderm, which flank the embryonic coelom
- Somatopleure
- Somatic mesoderm + ectoderm
- body wall
- Somatic mesoderm + ectoderm
- Splanchnopleure
- Splanchnic mesoderm + endoderm
- Visceral wall
- Splanchnic mesoderm + endoderm
- Embryonic coelom
- Forms body cavities
- Pleural
- Pericardial
- Peritoneal
- Forms body cavities

Medial Folding
- occurs in the 4th week of development
- Head folding
- Cardiogenic region and oropharyngeal membrane “swing” ventrally and caudally
- Tail Fold
- Cloacal membrane “swings” ventrally and cranially
- Part of yolk sac incorporated into embryo as primitive gut tube

Embryonic Folding
- Occurs during 4th week of development
- Establishment of body plan
- 3-layered disk transformed into cylindrical embryo by median and horizontal folding
- Median folding (head and tail folding)
- Horizontal folding (lateral folds)
- Purse-string closure mechanism
- put string around periphery of embryonic disk
- tighten string around ventral side of embryo
- closure region is umbilical ring
Horizontal folding (lateral folds)
- Occurs in the 4th week of development
- Lateral plate mesoderm moves ventrally and medially
- participates in forming body wall

Lateral folding in week 4 of developement

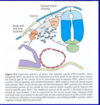
Molecular Regulation of Somite Differentiation
- Sclerotome formation
- SHH produced by neural tube and notochord induce ventromedial portion of somite to become sclerotome
- Sclerotome expresses PAX-1 initiates cartilage and bone formation
- Dermamyotome formation
- WNT from dorsal neural tube and epidermis induces dorsolateral portion to become dermamyotome
- Medial portion expresses MYF5 and becomes epaxial musculature
- lateral portion induced by BMP4 expresses MYOD and becomes hypaxial musculature
Craniocaudal Patterning of embryo
- Hox genes organized in specific spatial pattern on chromosomes
- Hox gene expression occurs in specific spatial pattern based on gene organization
- Spatial expression of Hox genes determines pattern of somite segmentation
- Clusters of genes are on separate chromosomes
- Genes at the 3’ end of the cluster are expressed cranially while genes at the 5’ end are expressed caudally
- Hox6 normally expressed in thoracic region where ribs form

Which hox gene expression regulates Rib formation
- Hox6 normally expressed in thoracic region where ribs form
- Ectopic expression of Hox6 in lumbar region promotes abnormal rib formation
Holoprosencephaly
- Insult in 3rd week of development
- Development occuring during week after 1st missed menses
- Kills cells in anterior midline
- single brain ventricle, cyclopia
- Possible reasons:
- may be caused by alcohol
- Genetic defect in SHH

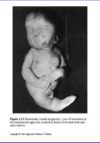
Caudal Dysgenesis (Sirenomelia)
- Insufficient mesoderm forms in caudal-most region
- Effects all caudal mesoderm derived structures
- lower limbs
- kidneys
- genital organs
- rectum/anus
- bladder