Cranial nn. VII - XII details Flashcards
What are the cranial nuclei of the seventh cranial nerve?
Quality of fibers?
n. facialis
4 nuclei:
- ncl. n. facialis = SVM
- ncl. salivatorius sup. = GVM
- ncll. tractus solitarius = SVS
- ncl. spinalis n. trigemini = GSS
Differentiate btw the 2 parts of n. VII and its type of fibers.
- facialis part = SVM, GSS
- n. intermedius = GVM, SVS
Describe the pathway of n. VII.
n. facialis
- exits brain seperately at angulus pontocerebellaris
-
canalis n. facialis
- enters through porus acusticus int.
- forms geniculum, receives fibers from ggl. geniculi, giving off 3 branches
- exits in foramen stylomastoideum, give off 3 mm. branches
- forms motor plexus intraparotideus at gl. parotis
1 = geniculum + ggl. gen., 2 = for. stylom., 3 = at gl. par.

List all branches of n. VII.
Where do they originate?
in order, 7 branches:
- n. petrosus maj.: in geniculum n. VII
- n. stapedius: in desc. part of canalis n. VII
- chorda tympani: before leaving canalis n. VII
-
mm. branches
- n. auricularis post.: at for. stylomastoideum
- r. digastricus, stylohyoideus: at for. stylom.
- plexus intraparotideus: at gl. parotis
1 = gen., 2 = for. stylom., 3 = plexus intrap., 9 = n. auric. post., 10 = n. petr. maj., 12 = chorda tymp.

Describe the various functions of the facial part of n. VII.
Refer to the responsible branches and quality of fibers.
SVM
- n. auricularis post. → mm. of ext. ear
- plexus intraparotideus → mm. of facial expression
- r. digastricus → venter post. m. digastrici
- r. stylohyoideus → m. stylohyoideus
- n. stapedius → m. stapedius
GSS
- n. auricularis post. → skin of post. ear
Which branches of n. VII are considered part of n. intermedius?
Describe their function, also refer to the quality of fibers.
SVS = taste
- chorda tympani → ant. 2/3 of tongue
parasymp. GVM
- chorda tympani → gl. subm., subl., gl. lingualis ant.
- n. petrosus maj. → gl. lacrimalis
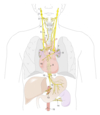
Describe the pathway of n. petrosus maj.
N. facialis or n. intermedius?
Function?
branch of n. intermedius
- preganglionic parasymp. fibers from NTS branch off at geniculum n. VII into hiatus canalis n. petrosi maj.
- run through for. lacerum and
- canalis pterygoideus to form together w/ n. petrosus prof. n. canalis pterygoidei
- terminate in ggl. pterygopalatinum
→ eventually fibers carried via branches of n. V to gl. lacrimalis (cf. own card)
3 = NTS, 4 = n. VII, 6 = n. petr. maj., 7 = ggl. pterygop., 9 = gl. lacr., 10 = r. comm. of n. zyg., 11 = n. lacr. (V1)

Describe the pathway of n. stapedius.
N. facialis or n. intermedius?
Function?
branch of n. facialis
branches off in des. part of canalis n. facialis to
→ m. stapedius (sound adaptation)
Describe the pathway of chorda tympani.
N. facialis or n. intermedius?
Function?
branch of n. intermedius
- SVS fibers (from NTS), GVM fibers (from ncl. sal. sup.) branch off from n. facialis before leaving canalis n. facialis
- in plica malleolaris through tymp. cavity
- exits skull through fissura petrotympanica
- fibers run together w/ n. lingualis
→ GVM fibers to ggl. submandibulare, SVS fibers continue to ant. 2/3 of tongue
2 = ncl. sal. sup., 3 = NTS, 4 = n. fac., 5 = ggl. gen., 12 = chorda ty., 13 = n. ling., 14 = ggl. subm., 17 = taste fibers

Where can ggl. geniculi be found?
Function?
at geniculum in canalis n. facialis
- pseudounipolar SVS perikarya for taste innervation of ant. 2/3 of tongue (NTS → chorda tympani)
- pseudounipolar GSS perikarya for sensory innervation of post. ear (ncl. spinalis n. V → n. auricularis post.)
3 = NTS, 4 = n. facialis, 5 = ggl. gen., 12 = chorda ty., 17 = taste fibers

Where does n. auricularis post. branch off from n. VII?
Function?
first branch of n. VII at foramen stylomastoideum
- SVM: venter occ. m occipitofrontalis + mm. of ear
- GSS: post. ear
Where can plexus intraparotideus be found?
Branches?
Function?
mm. branches of n. facialis exiting gl. parotis
⇒ mm. of facial expression
2 main branches:
-
n. temporofacialis
→rr. temporales, zygomatici
→ rr. buccales → m. buccinator -
n. cervicofacialis
→ r. marginalis mandibulae
→ r. colli (part of ansa cerv. superf.) → plathysma
3 = enters gl. par., 4 = rr. temp., 5 = rr. zyg., 6 = rr. bucc., 7 = r. marg. mand., 8 = r. colli

Where can ggl. pterygopalatinum be found?
Which nerves only cross it w/o synapsing?
Target organs?
in fossa pterygopalatina
- symp. root:
- *n. petrosus prof.** (plexus car. int.) → lacrimal gland
- sensory root:
- *rr. ganglionares** (V/3) → mucosa of nasopharynx, palate, nose
7

Where does ggl. pterygopalatinum receive its preganglionic fibers from (nucleus + nerve)?
Where to (nerve + target organ)?
GVM fibers from ncl. salivatorius sup.
preganglionic parasymp. fibers:
- n. petrosus maj. (VII)
postganglionic parasymp. fibers:
- rr. ganglionares, n. zygomaticus (V/2), n. lacrimalis (V/1) → lacrimal gland
- nn. nasales post. (V/2) → nasal glands
- nn. palatini (V/2) → palatine glands
Where can ggl. submandibulare be found?
Which nerves only cross it w/o synapsing?
Target organs?
between gl. lingualis and submandibularis
- symp. root:
- *plexus car. ext.** along a. facialis
-
sensory root:
rr. ganglionares of n. lingualis
⇒ gl. subm., subl., lingualis ant.
14 = ggl. subm., 15 = gl. subm., 16 = gl. subli.

Where does ggl. submandibulare receive its preganglionic fibers from (nucleus + nerve)?
Where to (nerve + target organ)?
GVM fibers from ncl. salivatorius sup.
preganglionic parasymp. fibers:
- chorda tympani (VII), n. lingualis (V/3)
postganglionic parasymp. fibers:
- rr. glandulares → gl. subm., gl. subl
- n. lingualis (V/3) → gll. lingualis ant. (NUHN-BLANDIN)
12 = chorda tymp., 14 = ggl. subm., 15 = gl. subm., 16 = gl. subli.

Where does the eighth cranial nerve originate?
Quality of fibers?
Function?
n. vestibulocochlearis (SSS)
2 branches:
- n. cochlearis
- n. vestibularis
→ auditory perception + position, locomotion
Describe the pathway of n. VIII.
-
n. cochlearis originates from ggl. cochleare
* *n. vestibularis** originates from ggl. vestibulare - both nerves fuse to n. VIII in meatus acusticus int., exit at porus ac. int.
- enter brain in angulus pontocerebellaris
- terminate seperately in ncl. cochleares, vestibulares
5 = n. vest., 6 = ggl. vest., 8 = n. cochl., 9 = ggl. cochl., 10 = porus ac. int., 11 = ang. pontoc.

What is special about ggl. cochleare, vestibulare?
both contain perikarya of bipolar neurons
-
ggl. cochleare:
organ of Corti → n. cochlearis -
ggl. vestibulare:
semicircular ducts, sacculus, utriculus → n. vestibularis
2 = semic. ducts, 3 = sacc., 4 = utr., 5 = n. vest., 6 = ggl. vest., 7 = cochlea, 8 = n. coch., 9 = ggl. cochl.

List the nuclei of n. IX.
Quality of fibers?
n. glossopharyngeus
5 nuclei:
- ncl. ambiguus = SVM
- ncl. salivatorius inf. = parasymp. GVM
- ncll. tractus solitarius = SVS
- ncl. spinalis n. trigemini = GSS
- ala cinerea lat. = GVS
Describe the pathway of n. IX.
General function?
n. glossopharyngeus
- exits brainstem in sulcus paraolivaris lat.
- runs caudally through foramen jugulare, forming:
- ganglion sup. n. IX
- ganglion inf. n. IX
- then btw m. stylopharyngeus, m. styloglossus to root of tongue → terminal branches
→ sensory innervation of tongue, motor innervation of pharynx
1 = for. jug., 2 = ggl. sup., 3 = ggl. inf., 7 = m. stylogl., 8 = m. styloph.

Where can ggl. superius of n. IX be found?
What is its function?
Another name?
- *= Ehrenritter’s ganglion**
sup. to foramen jugulare
contains: pseudounipolar GSS perikarya for sensory innervation of post. 1/3 of tongue, parts of pharynx, meningei, auditory tube, tonsills, etc. (ncl. spinalis n. V → various)
Where can ggl. inferius of n. IX be found?
Another name?
Function?
= ganglion petrosum
in fossula petrosa
contains:
- pseudounipolar GVS perikary for glomus caroticum (ala cinerea lat → Hering’s nerve)
- preganglionic SVS perikary for taste innervation of post. 1/3 of tongue (NTS → rr. linguales)
List all branches of n. IX.
in order
- n. tympanicus
-
1 muscular branch
- r. m. stylopharyngei
-
3 (types of) sensory branches
- rr. pharyngei
- rr. linguales
- r. sinus carotici
4 = n. tymp., 9 = rr. pharyngei, 10 = r. sinus car.