Consolidation Flashcards
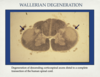
What is wallerian degeneration?





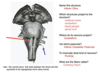
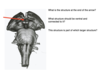


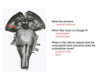
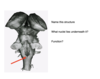
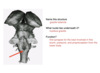
What is the internal capsule?
The internal capsule is a collection of afferent and efferent fibers connecting to the cerebral cortex and the brainstem








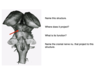





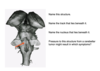


MEDIAL MEDULLARY SYNDROME
- Spastic left hemiparesis - damage to right pyramid (right cortex –> right pyramid –> crosses to left in pyramidal decussation –> results in left hemiparesis)
- Loss of left position and vibration –> dorsal column (info from left body crosses in lower medulla, lesion is above this so loss of right medial lemniscus)
- Right deviation and atrophic tongue –> damage to hypoglossal nerve and tongue deviates toward lesion

Damage to which artery in the brain causes medial medullary syndrome?
Anterior spinal
What are the signs/symptoms of medial medullary syndrome?
Hemiparesis (lose pyramid)
Lose position/vibration/fine touch (medial lemniscus)
Tongue deviation and atrophy (hypoglossal nucleus)


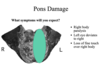




What are the sign’s and symptoms of weber’s syndrome?
CN3 Palsy (damage to oculomotor and edinger-westphal nuclei in midbrain)
Hemiparesis (opposite side as CN 3 palsy) (partial damage to pyramid in midbrain)
Weber syndrome results from a stroke in which artery in the brain?
Posterior cerebral artery











Describe how information travels from the corticospinal and cortiocbulbar pathways to the cerebellum and then back up to the thalamus.
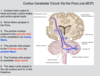
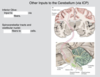

Movement of what areas of the body are impacted by the corresponding areas of the cerebellum?



What is internuclear opthalmoplegia?
Damage to MLF disrupts horizontal gaze and nystagmus. The abducens nucleus is unable to communicate with the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei.


