Congenital Murmurs in Puppies & Kittens Flashcards
(71 cards)
what are pathological cardiac murmurs
- incompetent or stenotic valves
- flow through shunts
what are physiological (functional) murmurs
changes in blood viscosity or velocity (anemia), hypoproteinemia, fever
also athletes (big stroke volume)
what are innocent murmurs
soft (max G1-2/6)
systolic, short, variable, localized
young animals
what are not innocent murmurs
NEVER diastolic or continuous
what are causes of murmurs in kittens and puppies (3)
- could be innocent flow murmur
- systemic disease (anemia)
- could be acquired disease but very unusal (early onset cardiomyopathy in cats, myocarditis in puppies)
what are almost all louder systolic mumurs and all continuous murmurs due to
congenital anatomical defects
what are the characteristics of innocent murmurs (3)
- low grade systolic murmur
- left heart base
- usually gone by 16-20 weeks
if G3+ most likely congenital disease (not innocent)
what are the causes of congenital murmurs in dogs in order of prevelance (8)
- aortic stenosis
- patent ductus arteriosus
- pulmonary stenosis
- ventricular septal defect
- mitral valve dysplasia
- tricuspid valve dysplasia
- tetralogy of fallot
- persistent right aortic arch
what are the causes of congenital murmurs in cats in order of prevelance (6)
- ventricular septal defect
- mitral valve dysplasia
- tricuspid valve dysplasia
- aortic stenosis
- persistent right aortic arch
- tetralogy of fallot
what are the causes of congenital murmurs
majority is unknown
some may be genetic (known prevalence in pure bred dogs; some screening in some breeds ex boxer)
which breed has a genetic predisposition to aortic stenosis
newfoundland
autosomal dominant with modifiers
what breeds have a genetic predisposition to patent ductus arteriosus
poodle
polygenic
female:male 2-4:1
what breeds have a predisposition to tetralogy of fallot
keeshond
polygenic
what breeds have a predisposition to pulmonary stenosis
beagle
polygenic
what breeds have a predisposition to persistent right aortic arch
german shepherd
polygenic
how are congenital murmurs diagnosed (7)
- history
- breed/sex/age
- physical exam
- thoracic radiography
- echocardiography
- electrocardiography
- angiography
what are left base murmurs and when would they be heard (4)
- patent ductus arteriosus (continuous)
- aortic stenosis (systolic)
- pulmonary stenosis (systolic)
- innocent/functional murmurs (systolic)
what murmurs can be heard at the left apex and when can they be heard
- mitral valve dysplasia (systolic)
hat are right side murmurs and when can they be heard (3)
- tricuspid valve dysplasia (systolic)
- ventricular septal defect (systolic)
- tetralogy of fallot (systolic, also at left base)
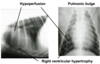
what will thoracic radiography show (3)
- chamber enlargement: left or right sided
- pulmonary circulation: vascular congestion or decreased vascularity
- great vessel dilation
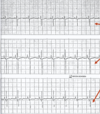
what will electrocardiography show
- left sided enalrgement: aortic stenosis, PDA
- right sied enlargement: right axis deviation –> pulmonary stenosis, tetralogy of fallot
what will echocardiography show (6)
- chamber dilation
- wall hypertrophy
- abnormal valve appearance
- valvular incompetence
- high velocity flow across valves
- shunts
what is the pathology of aortic stenosis
- sub-aortic stenosis (muscular ridge)
- valvular aortic stenosis (valve cusps or annulus)
turbulent flow across aortic region
muscular or fibromuscular ridge or ring beneath the aortic valve
sometimes there is valvular stenosis where the valve cusps are abnormal
can get secondary changes to the valve due to the subaortic stenosis
what is the pathophysiology of aortic stenosis