Acquired Murmurs in Adult Dogs Flashcards
(59 cards)
what are endocardial diseases of acquired heart murmurs in dogs
- degenerative (mitral) valve disease (DMVD), myxomatous (mitral) valve disease (MMVD), endocardiosis
- endocarditis (usually bacterial)
what are the myocardial causes of acquired heart murmurs in dogs (4)
- dilated cardiomyopathy (primary, secondary)
- arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (secondary) - rare
- myocarditis
what breed is degenerative mitral valve disease/myxomatous mitral valve disease/endocardiosis commonly seen in
CKCS
what is degenerative mitral valve disease/myxomatous mitral valve disease/endocardiosis
myxomatous degenerative of the heart valves and chordae
collagen loss and thickening of the valve margins and chordae leads to progressive distortion of the valve leaflets and the possibility of chord rupture

what is the most common cardiac disease in dogs
mitral valve disease
causes of 75% of all congestive heart failure in dogs
what is the pathophysiology of mitral valve disease

what are the clinical features of mitral valve disease (6)
- common in middle aged (5 years+) or older
- small to medium sized
- pure and mixed breed dogs
- some large breeds
- CKCS, poodles, terriers, dachshunds, chuhuahuas, sight hounds, collies, setters, GSDs
- males > females
what is seen on history with mitral valve disease (4)
- asymptomatic
- signs of left sided cardiomegaly (cough)
- signs of left sided CHF & reduced output: tachy/dsypnea (pulmonary edema), cough, exerciseintolerance
- +/- signs of right sided CHF: ascites, dyspnea due to pleural effusion
what are the clinical findings of mitral valve disease (6)
- systolic murmur over mitral +/- tricuspid valve
- murmur grade +/- related to severity of disease
- early stages good myocardial function and good pulse quality
- +/- dyspnea
- +/- ascites
- +/- arrhythmias
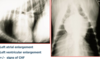
what is seen on chest radiographs with mitral valve disease (2)
- cardiomegaly
- airway compression

what is the cause of the cough in mitral valve disease
main left stem bronchial compression by the enlarged heart (LA) is a relatively common cause of a cough
how does CHF by mitral valve disease show on radiography
- cardiomegaly
- venous congestion
- alveolar pattern

what is shown on the ECG with mitral valve disease (4)
- chamber enlargement: large R wave
- supraventricular premature beats: from atria
- atrial fibrillation
- ventricular arrhythmias

what is seen on echo mitral valve proplapse
enlarged LV and LA
mitral valve cusp prolapsing into LA

what biomarker can be used to diagnose acquired murmurs
NT-proBNP
how is mitral valve disease treated
depends on severity
severity is based on congestive heart failure classification scheme to guide treatment
what is the prognosis of mitral valve disease
gaurded when/if CHF develops 6-24 months survival
more rapid progression in CKCS and large breeds
what is bacterial endocarditis
affects valves on the left side of the heart
which valve is most commonly affected in what is bacterial endocarditis in dogs
aortic valve
which valve is the second most commonly affected in what is bacterial endocarditis in dogs
mitral valve
what predisposes dogs and cats to bacterial endocarditis
congential aortic stenosis
what are the clinical findings of bacterial endocarditis (3)
- pyrexia
- joint pain/stiffness & (shifting) lameness
- new left sided murmur
how is bacterial endocarditis diagnosed (7)
- blood culture
- urine analysis & culture
- +/- joint taps
- echocardiography
- thoracic radiography
- abdominal ultrasonography
- hematology and blood biochemistry
what is the treatment of bacterial endocarditis
- treat with antibiotics (pref based on C&S) often IV to start, supportive therapy as needed
may eventually develop left CHF
prognosis is guarded