Ch 5. Review Flashcards
(20 cards)
Which of the following is not true for the critical path?
A. It has zero float.
B. It’s the shortest activity sequence in the network.
C. You can determine which tasks can start late without impacting the project end date.
D. It controls the project finish date.
B. It’s the shortest activity sequence in the network.
The critical path is the longest path on the project. The tasks have zero float because the critical path controls the project end date. Using critical path, you can determine which tasks can start late or go longer than planned without impacting the project end date.
You are a project manager for a major movie studio. You need to schedule a shoot in Denver during ski season. This is an example of which of the following?
A. External dependency
B. Finish-to-start relationship
C. Mandatory dependency
D. Discretionary dependency
A. External dependency
A requirement such as weather conditions or a specific season that drives the scheduling of a task is an example of an external dependency.
What is analogous estimating also referred to as?
A. Bottom-up estimating
B. Expert judgment
C. Parametric estimating
D. Top-down estimating
D. Top-down estimating
Analogous estimating is also called top-down estimating. It is used early in the project, when there is not enough detail to do a detailed estimate.
You are working on your network diagram. Activity A is a predecessor to Activity B. Activity B cannot begin until Activity A is completed. What is this telling you?
A. There is a mandatory dependency between Activity A and Activity B.
B. There is a finish-to-start dependency relationship between Activity A and Activity B.
C. Activity A and Activity B are both on the critical path.
D. Activity B is a successor to multiple tasks.
B. There is a finish-to-start dependency relationship between Activity A and Activity B.
There is a finish-to-start dependency relationship between Activity A and Activity B. You do not have enough information to determine whether the dependency between the two activities is mandatory, discretionary, or external or if they are critical path activities.
What are the most commonly used forms to display project schedules? Choose two.
A. PERT charts
B. Gantt charts
C. CPM diagrams
D. A spreadsheet
A. PERT charts
B. Gantt charts
PERT charts and Gantt charts, a type of bar chart, are the most common ways to display a project schedule.
What are the crashing and fast tracking techniques used for?
A. Duration compression
B. Activity sequencing
C. Precedence diagramming
D. Task definition
A. Duration compression
Duration compression involves either crashing the schedule by adding more resources or creating a fast track by working activities in parallel that would normally be done in sequence.
Which of the following is true for float?
A. It’s calculated by adding the durations of all tasks and dividing by the number of tasks.
B. It’s time that you add to the project schedule to provide a buffer or contingency.
C. It’s the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
D. It is calculated only on the longest path of the project schedule.
C. It’s the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
Float time is the length of time a task may be started late or the additional duration a task may take without impacting the project completion date. The early start and late start dates are the same, and the early finish and late start finish dates are the same.
You have added a checkpoint in the project schedule to determine whether the work is accurate. What is this called?
A. Governance gate
B. Quality gate
C. Approval gate
D. Checkpoint gate
B. Quality gate
A quality gate is used to determine whether the work is accurate and meets quality standards.
Activity B on your project schedule starts on Monday, October 3, and ends on Wednesday, October 12. You calculate duration in workdays, and the team does not work on Saturdays or Sundays. How many days is the total duration of this task in workdays?
A. 9 days
B. 10 days
C. 8 days
D. 7 days
C. 8 days
The total work day duration is eight days. The first day counts as one full day.
Which of the following is not true for critical path tasks?
A. The early start date is less than the late start date.
B. These activities are on the longest full path on the project schedule.
C. The float time for tasks is zero.
D. The late finish date is the same as the early finish date.
A. The early start date is less than the late start date.
Float is always zero for the critical path activities, so early start and late start are the same date.
Starting two activities at the same time that were previously scheduled to start sequentially is known as which of the following?
A. Fast tracking
B. Mandatory dependency
C. Crashing
D. Baselining
A. Fast tracking
Fast tracking is a technique where you perform multiple tasks in parallel that were previously scheduled to start sequentially.
Your task requires 4 miles of paving, and it will take 30 hours to complete a mile. On a past project similar to this one, it took 150 hours to complete. Which of the following is true regarding this estimate?
A. The total estimate for this task is 120 hours, which was derived using expert judgment.
B. The total estimate for this task is 120 hours, which was derived using parametric estimating.
C. The total estimate for this task is 150 hours, which was derived using analogous estimating.
D. The total estimate for this task is 150 hours, which was derived using expert judgment.
B. The total estimate for this task is 120 hours, which was derived using parametric estimating.
If you didn’t know the quantity and rate, option C or D would be acceptable. In this case, you’d use the parametric estimating technique because you do know the quantity and rate; 30 hours times 4 miles is a total duration of 120 hours.
Governance gates include all of the following except for which one?
A. Assigning a go/no-go decision point
B. Obtaining client sign-off
C. Securing management approvals
D. Obtaining legislative approvals
E. Assuring the work is performed correctly
E. Assuring the work is performed correctly
Governance gates might include go/no-go decisions, client sign-off, management approval, and legislative approval.
You’re working on a project that you and your team have estimated takes 15 business days to complete. Your team does not work on Saturday, Sunday, or holidays. Given the work calendar shown here and a start date of Tuesday, November 1, what is the scheduled completion date for this task?
A. 21
B. 15
C. 22
D. 23

C. 22
The task will take 15 business days to complete (not counting weekends or holidays) so that makes the task completion date the 22nd. Day 1 counts as the first full day of work.
All of the following are true regarding milestone charts except for which one?
A. Milestone charts list the major deliverables or phases of a project.
B. Milestone charts show the scheduled completion dates.
C. Milestone charts show the actual completion dates.
D. Milestone charts are commonly displayed in bar chart format.
D. Milestone charts are commonly displayed in bar chart format.
Milestone charts list the major deliverables, key events, or project phases and show the scheduled and actual completion dates of each milestone. They may include other information, but that information would not be displayed as bar charts.
You’re in the process of developing a project schedule for a new project. You’ve just completed the WBS. What would be the project manager’s next step in figuring out what tasks go into the project schedule?
A. Develop a task list.
B. Determine the critical path tasks.
C. Develop a project schedule.
D. Estimate activity duration.
A. Develop a task list.
After the WBS is developed, the next step involves creating an activity list that describes the activities required to complete each work package on the WBS.
After the schedule is approved by the sponsor, customer, and key stakeholders, what happens next?
A. The resources are assigned.
B. The schedule baseline is established.
C. The task start and end dates are finalized.
D. The critical path is finalized.
B. The schedule baseline is established.
Once the schedule is approved by the sponsor, customer, and stakeholders, the schedule baseline is set. The baseline is the approved project schedule and shows task start and end dates and resource assignments.
Which is the most commonly used logical relationship?
A. Finish-to-start
B. Start-to-finish
C. Start-to-start
D. Finish-to-finish
A. Finish-to-start
Finish-to-start is the most commonly used logical relationship in network and schedule diagrams.
How long is the critical path in days in the graphic shown here if you eliminate Task B?
A. 13 days
B. 20 days
C. 27 days
D. 30 days
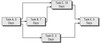
B. 20 days
Eliminating Task B leaves you with the longest path through the network diagram, which is path A-C-E for a duration of 20 days.
The following exhibit shows a series of tasks in a project schedule. Which path represents the critical path?
A. A-E-F-G
B. A-C-D-G
C. A-B-D-G
D. A-B-D-F-G

C. A-B-D-G
Tasks A, B, D, and G represent the longest dependent path through the network diagram at 41 days.


